9-Step GDPR Compliance Checklist You Need To Follow

Are you looking to follow the key GDPR compliance checklist to align with the GDPR law?
As businesses gather and handle large amounts of personal information. It is crucial to do so in a manner that respects individuals’ privacy rights.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is an EU regulation designed to protect the personal data of EU residents.
Whether your organization is located in the EU or processes EU citizens’ data, compliance with GDPR is essential.
This guide will walk you through the necessary steps to ensure your organization meets GDPR requirements.
By using this methodical approach, you can handle the intricacies of GDPR compliance.
This involves evaluating your existing data processing practices, overseeing consent, and maintaining data security.
What is GDPR?

The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is the strongest privacy law in the world, created by the EU to regulate how organizations collect, use, and protect the personal data of EU residents. It took effect on May 25, 2018, and is a binding law in all EU Member States. It strengthens privacy rights by giving people control over how their personal data is collected, used, and shared.
The GDPR brought together different data security laws in the European Union (EU), making a single set of rules for protecting data.
Additionally, it broadened the application of these rules to include non-EU organizations that handle personal information collected from EU citizens.
The goal was to prevent the improper use of the data belonging to EU citizens. The security of citizens’ personal information must be guaranteed by the organizations that handle it.
All organizations that handle users’ personal data must follow this law, and failure to comply can result in fines and penalties.
The protection covers theft, distortion, and any form of modification. Creating GDPR-compliant websites is a method to ensure that data remains safe from external threats.
In technical terms, any website that collects data from citizens in any capacity acts as a data controller. The data controller must safeguard this data and ensure the website complies with GDPR.
Failing to meet these requirements can result in penalties of up to 4% of a company’s annual revenue or €20 million. With around 172 million websites powered by WordPress, GDPR compliance applies globally—any business that interacts with EU citizens must follow this law.
What is Defined as Personal Data in GDPR?
Under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), personal data refers to any information related to an identified or identifiable natural person (Article 4).
This includes any data that can directly or indirectly identify an individual. Examples include:
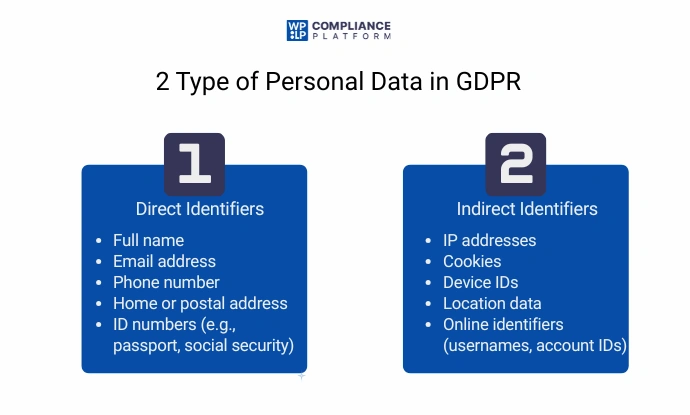
Special Categories of Personal Data
The GDPR also defines a category called “special categories of personal data,” which includes highly sensitive information that requires stronger protection. This category covers:
- Racial or ethnic origin
- Political opinions
- Religious or philosophical beliefs
- Trade union membership
- Genetic and biometric data (used for identification)
- Health data
These types of data require stricter protection and often need explicit consent for processing.
What Are Consumer Rights Under GDPR?
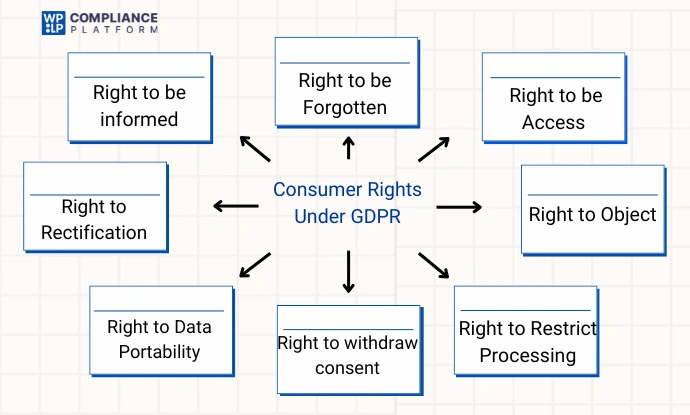
The GDPR outlines eight core data subject rights, along with the right to withdraw consent. Here’s a closer look:
- Right to be informed: Individuals have the right to be informed about how their personal data is collected and used.
- Right of access: Individuals have the right to view and request a copy of their personal data.
- Right to rectification: Individuals have the right to request that inaccurate or outdated personal data be corrected.
- Right to be forgotten / Erasure: Individuals have the right to request the deletion of their personal data. This right may be limited by certain legal exceptions.
- Right to data portability: Individuals can request their data in a machine-readable format or ask for it to be transferred to another controller.
- Right to restrict processing: Individuals have the right to request the restriction or suppression of their personal data.
- Right to withdraw consent: Individuals can withdraw their previously given consent to process their personal data.
- Right to object: Individuals have the right to object to the processing of their personal data.
- Right to object to automated processing: Individuals have the right to object to decisions made solely through automated processing, including profiling.
Key Principles of GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is based on seven key principles that guide how organizations handle personal data responsibly. These principles promote transparency, trust, and accountability.
- Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency: Organizations must collect and use personal data legally, fairly, and in a transparent manner. People should know how their data is being used.
- Purpose Limitation: Data should only be collected for specific, clear, and legitimate purposes and not used in ways that go beyond those purposes.
- Data Minimization: Only the data that is truly necessary for the intended purpose should be collected. Avoid gathering excess or irrelevant information.
- Accuracy: Personal data that is collected should be kept up-to-date. Organizations should correct or delete inaccurate information promptly.
- Storage Limitation: Data should only be kept for as long as necessary to fulfill its intended purpose. After that, it should be securely deleted.
- Integrity and Confidentiality: Organizations must protect personal data against unauthorized access, loss, or damage through proper security measures.
- Accountability: Organizations are responsible for complying with GDPR and must be able to demonstrate how they meet these principles.
These guidelines stress how crucial it is to only gather relevant and essential data while retaining as little of it as possible.
Who Needs to Comply with GDPR Standards?
Any entity that handles the personal data of residents in the European Union (EU) must comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). This requirement applies regardless of the organization’s location. The GDPR covers the following:
Organizations Based in the EU
The GDPR applies directly to all entities operating within the EU or the European Economic Area (EEA). Any organization in the EU that collects, processes, or stores personal data from individuals, whether customers, employees, or others.
Non-EU Organizations Targeting EU Customers
Organizations outside the EU, such as those in the U.S., Canada, or India, must comply if they offer goods or services to people in the EU or monitor the behavior of EU residents.
Organizations That Process Personal Data
GDPR applies to any organization that processes personal data such as names, email addresses, phone numbers, financial information, location data, and online identifiers like IP addresses and cookies. Whether it’s a startup, corporation, nonprofit, or public entity, GDPR applies if personal data is involved.
Controllers and Processors
A controller decides how and why personal data is processed. A processor handles data on the controller’s behalf, such as a third party managing payroll or IT services. Both roles carry legal responsibilities under GDPR and must ensure data is processed lawfully, transparently, and securely.
Public Bodies and Authorities
Public authorities and institutions in the EU, including government departments and local councils, must also follow GDPR. These bodies regularly handle personal data for administrative tasks, and GDPR ensures such data is processed with respect for individuals’ rights and freedoms.
Exceptions and Exemptions
Some organizations or data processing activities may be exempt from certain GDPR rules. For instance, GDPR doesn’t apply to personal or household data. Specific rules also apply to sectors like law enforcement or healthcare, which may follow separate data protection frameworks.
Steps to Comply with GDPR Regulations
Organizations must implement a structured approach to comply with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Below are the essential steps for meeting GDPR criteria.
Step 1: Review and Remediate Processor Risks
Under the GDPR, the controller is accountable for any actions or law-breaking by the processor. It’s important to review processor data transfers and contracts as carefully as your own data handling. This ensures a defensible position in case of a law break and helps organizations quickly identify what data was affected.
Step 2: Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
Under the GDPR, organizations must appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) if they operate as a public authority or body, regularly and systematically monitor individuals on a large scale (such as tracking online behavior), or process special categories of data or criminal records on a large scale.
The DPO is responsible for ensuring GDPR compliance. They monitor internal compliance, advise on data protection obligations, guide Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs), and act as a contact point for data subjects and data protection authorities.
Step 3: Generate a Processing Register for Article 30
The GDPR requires organizations to keep updated records of their data processing activities. Data mapping helps build and maintain a clear overview of how data flows within the organization.
Although the GDPR doesn’t explicitly mention data mapping, it requires both controllers and processors, whether B2B or B2C, to maintain records of processing activities. Article 30 sets specific requirements, so organizations must update or redo any previous data mapping to meet GDPR standards.
Step 4: Build a Framework for Consent Management
The GDPR sets a higher standard for processing data based on consent. Consent must be specific, clear, and written in plain language, not be coated in heavy legal text or grouped with other notices. It must also be easy to withdraw. Additionally, organizations must be able to prove that consent was obtained faithfully and transparently.
Step 5: Build a Data Subject Rights (DSAR) Request Portal
The GDPR grants data subjects specific rights, such as data portability, access, erasure (or the “right to be forgotten”), rectification, and more. There are also specific record-keeping requirements, including response time, the option to request an extension, identity verification, and secure transmission of responses. An automated portal is essential for receiving, sorting, and managing DSAR requests, as well as tracking and reporting them effectively.
Step 6: Meet EU Cookie Compliance Requirements
Under the ePrivacy Directive, organizations must inform users about cookie use, explain their purpose, and get clear, active consent. This applies to both anonymous and personal data. Essential cookies are exempt. When cookies involve personal data, GDPR rules like DPIAs and processing records also apply. The upcoming ePrivacy Regulation will bring stricter enforcement.
Step 7: Perform Privacy Impact Assessments (PIA)
The GDPR requires organizations to conduct Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs), also known as Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs), when processing is likely to result in a high risk to individuals’ rights and freedoms. These assessments help identify and minimize data protection risks in projects that involve personal data.
Step 8: Verify Third-Party Compliance
Ensure that any third-party vendors or partners you collaborate with comply with GDPR standards. This includes ensuring they have appropriate contracts regarding data processing activities.
Step 9: Implement GDPR Compliance Training
The GDPR requires the data protection officer to monitor an organization’s compliance, which includes raising awareness and training staff. Organizations should provide both initial and refresher training to employees. A system must also be in place to record training sessions as evidence of compliance.
How can Businesses Comply with GDPR Rules?
It is essential to make your website or business comply with GDPR requirements so that you do not have to pay any penalties or fines, and people trust your organization. You can take several key steps to do so. Some of them are:
- Create a clear and comprehensive privacy policy that informs people about the GDPR and how their data is collected, used, and stored, as well as how they can exercise their rights.
- Honor universal opt-out mechanisms (UOOMs)—such as the Global Privacy Control (GPC) as a valid way for users to signal their preference to opt out of data processing or sales.
- Adopt data minimization practices, ensuring you only collect information that is necessary for your operations, and avoid gathering any excess or irrelevant data.
- Appoint a data privacy officer (DPO) to oversee UCPA compliance efforts and manage your organization’s internal privacy protocols, if feasible.
By implementing these steps, you can better align with GDPR requirements and build stronger trust with your audience.
To adhere to GDPR privacy regulations, website operators can utilize a specific platform to meet legal obligations. WPLP Compliance Platform provides essential tools to make compliance easy.
Privacy policy generator and consent management platform are the two tools provided by WPLP that make GDPR compliance easier.
These tools offer features that assist businesses in conforming to data protection laws and maintaining data transparency with their website users.
Privacy Policy Generator

Privacy Policy Generator aids website proprietors in generating and overseeing critical legal documents, such as Privacy Policies, Disclaimers, and Terms and Conditions. This tool provides 35+ customizable templates and pre-written content that you can easily tailor to fit a website’s specific needs.
Companies can utilize this tool to guarantee that their websites comply with GDPR standards related to data protection disclosures.
It assists in delivering legal documentation to visitors about data handling practices. This promotes adherence to regulations and safeguards both organizations and their users.
Cookie Consent Manager

Cookie Consent Manager is a tool intended to manage cookie consent in accordance with GDPR. Website managers can notify visitors regarding cookie usage on their website.
This can be accomplished by showing a cookie consent banner. Another option is to utilize a pop-up to alert users about cookie usage.
It enables users to either accept or decline cookies, ensuring that no unnecessary cookies are placed on their devices without their consent. Furthermore, Cookie Consent Manager offers customization options that align with the website’s identity and design.
Both tools contribute to a more open and compliant digital space. They build trust with site visitors while meeting the legal obligations set by GDPR regulations.
Penalties and Fines for Non-Compliance

Organizations that make no effort to comply with the GDPR face the highest fines—up to €20 million (approx. $24 million) or 4% of global annual revenue, whichever is greater.
In January 2019, regulators imposed the first significant GDPR penalty, which was approximately €50 million, but that was just the beginning. The regulation has led to total fines amounting to €4 billion ($4.5 billion).
To avoid such penalties, organizations should clearly communicate:
- How are they prepared to respond and demonstrate accountability if something goes wrong
- What steps are they taking to comply with GDPR
- How they are actively avoiding non-compliance
FAQ
Companies that break the GDPR may face fines of up to €20 million or 4% of their global annual revenue, whichever is greater. Minor infringements can lead to fines of up to €10 million or 2% of the company’s annual global revenue, whichever is higher.
Individuals have the right to access their personal information, make changes, delete it, and transfer it via data portability.
Companies are required to assist individuals in exercising their right to alter or eliminate their personal information.
Furthermore, individuals are entitled to challenge the processing of their data in certain circumstances.
WPLP Compliance Platform offers customizable legal page templates that are pre-designed to ensure your website adheres to GDPR rules and other data protection laws. Privacy policy generator provides user-friendly tools to help you create essential legal pages for your website. It assists in crafting privacy policies, cookie notifications, and terms and conditions. These pages are designed to protect your site and build trust with your users.
Conclusion
Complying with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) not only fulfills a legal obligation but also builds trust and transparency with your users.
By following the steps in this guide, your organization actively protects personal data, maintains compliance, and avoids costly fines.
When you evaluate your current data practices and implement secure data management, you take crucial steps toward full GDPR compliance.
By respecting data subject rights and applying strong security measures, you safeguard both your customers’ information and your organization’s reputation.
Taking these actions demonstrates your commitment to responsible data handling and helps you build lasting trust with customers and stakeholders.
If you like this article, you can consider reading.
- An Overview of Iowa Consumer Data Protection Act (ICDPA)
- WPLP Compliance Platform Now Supports Google Consent Mode v2
- How to Make Your WordPress Website CCPA Compliant
Grab WPLP Compliance Platform now!
