What is Data Processing?Types, and Compliance Requirements
In today’s digital world, businesses collect and process vast amounts of personal data. Understanding data processing is crucial for legal compliance under GDPR and CCPA.
In the current digital age, organizations generate excessive amounts of raw data, but if they do not process the data, it is worth nothing.
Data processing is an organized and systematic process of collecting, structuring, and transforming raw input data into a more intelligible form that is easy to utilize.
From decoding customer behavior to forecasting market trends, data processing is the solution for deciphering information and guiding choices.
From small to gigantic levels of companies, its optimal processing of data increases accuracy, speed, and, ultimately, strategic control.
This guide explains what data processing is, its types, and how businesses can stay compliant
What Is Data Processing?
Data processing refers to the collection, organization, and change of raw data into meaningful and useful information. Data could be defined as raw facts, digits, or information which are collected from sites. It could be figures, texts, images, sounds, or video recordings.
These data points, in their original form, are devoid of context and sense; hence, they cannot be used solely by themselves. They are required to be processed to find patterns, trends, or useful information.
The difference between data and information is an essential aspect of data processing. Data is raw usually valueless; on the contrary, information is the output of processing and analyzing the data to get meaning.
A collection of temperature readings for different cities, for example, is nothing but data, but when interpreted, it can be turned into information expressing trends in temperatures or identifying weather patterns.
Data is raw material processing, which gives utility, but the information is that which gives utility by itself. The organization uses data processing systems to manage data in a manner that is effective.
Data processing systems are hardware and software tool combinations to process, store, collect, and analyze data.
Data processing systems are very simple– such as filling out forms and calculating statistics, as well as very complex, autonomous technologies– such as machine learning algorithms, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing environments.
These systems enable organizations to process a huge amount of data in a few seconds without necessarily compromising the accuracy of the output.
Effective data processing is of prime importance for businesses and organizations, as it leads to decision-making, opportunities, and the optimization of their operations.
Thus, data processing can help organizations turn raw data into structured and meaningful information from which they can intelligently predict, learn about customers’ behaviors, and benchmark themselves in the market.
Stages of Data Processing Under GDPR
The flow chart for processing data is a step-by-step process that transforms raw data into valuable and informative information. Every step of the process is highly crucial for advanced cleaning, precision, and formatting to mold the data into decision-making.
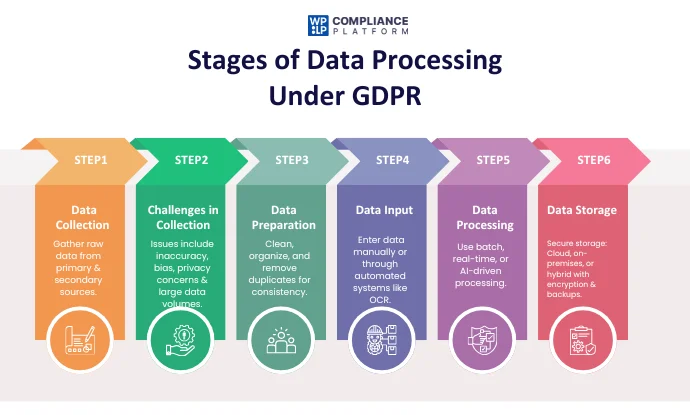
Now let us proceed to talk about each step in detail:
1. Data Collection
The beginning of a processing pipeline. Data collection is collecting raw data from various sources, which can afterward be processed to determine beneficial insights. There are primarily two sources of data.
- Primary Data: Fresh data is gathered directly from the source by surveying, experimenting, interviewing, or simply observing. Primary data is tailored according to the current needs of the research or business needs, therefore, more relevant and accurate to the study.
- Secondary Data: This is the data that already exists and has been obtained by some other individuals for some other purpose different from your own. Examples include government reports, research reports, or data sets in the public domain.
Secondary data might not always be applicable to your specific project, and the accuracy could be unknown. But it is simpler to use.
2. Problems Within Data Collection
- Inaccuracy of data: Raw data are inaccurate and incomplete, resulting in incorrect conclusions during final analysis.
- Bias: Questionnaires and experiments used in data collection can bring about bias that will destroy the validity of the finding.
- Volume of data: Data collected from more than one source can take a long time and be very complex.
- Privacy and Ethical Issues: It typically involves compliance with all laws, such that the data collection process is in accordance with privacy law, particularly when dealing with sensitive data like GDPR or CCPA.
3. Data Preparation
Following the completion of data collection, data processing is for cleaning and preparing data into a format appropriate for subsequent processing. It is one of the most important processes because if data are disorganized or inconsistent, then conclusions drawn could be unnecessary.
1. Cleaning and Organizing Data
- Data cleaning refers to the process of error or inconsistency identification and correction. All such processes may involve the removal of typos, unit normalization, or rectification of incorrect values.
- Data organization refers to the consolidation of data and organizing them in a way that proper analysis can be done.
2. Duplicates and Errors Handling
Duplicate record issues are a usual occurrence in a big dataset. Duplicate removal is performed to prevent any biases in the analysis and create reliability in the dataset that should not be impacted.
This makes sure the end product becomes accurate and representative.
4. Data Input
The data is thus required to be entered into a system for processing after it is prepared. The input of data means transferring that cleaned and organized data into storage in a system, be it a database or data processing application.
Data entry methods are usually adopted by organizations in the following forms:
Manual Data Entry involves humans reading data into spreadsheets or forms. It is time-consuming and often subject to human error, but it can sometimes become the only option.
Automated Data Entry does capture information entered into forms, sensors, or over the internet. By automating this process, the errors caused by people can be reduced dramatically, increasing the speed of turn-around, especially if there is a high volume.
Data Entry automation is on the rise among modern companies, especially with the invention of Automated data extraction tools and Optical Character Recognition (OCR).
These systems could scan the data inked on paper documents like old records and fill the data into the system automatically, thereby saving time and correcting human errors.
5. Data Processing
In this stage, it enters the data processing, where the core data manipulation and managing happen after it is inserted into the system. Here it is possible to employ different types of processing according to data.
1. Types of Data Processing:
- Batch Processing: Batch processing refers to the type of processing in which data collects and stores until a certain period for mass processing. This system works well on payroll and billing systems because they don’t require the immediate processing of data.
- Real-Time Processing: Real-time processing occurs continuously and immediately as data is generated. Applications needing rapid analysis and response can use this type of processing, like stock market trading, fraud detection, and monitoring traffic.
- Distributed Processing: Computers often process data and distribute it to various computers and servers for further processing.
2. Processing Techniques:
- Statistical Analysis: In this, the data are further processed so that the analysis may reveal tendencies, means, correlations, or some other dependable relationships, which may be classified under the term ‘statistical’.
- Machine Learning: Advanced data processing may involve machine learning algorithms that improve prediction or classification accuracy with increasing amounts of data.
- Data Mining refers to the search of large datasets for hidden patterns and insights, often using algorithms to detect trends that may not be overt.
6. Data storage
Processed data needs to be retained for future analysis. It is an integral part of a data processing system because it maintains valuable information and makes it readily available when needed.
1. Storage Options
- Cloud Storage: The data is kept on remote servers and is available online. Since cloud storage has become flexible, elastic, and accessible, increasingly more companies are utilizing it
- On-Premises: The information is permanently kept on high-performance servers, which are owned and managed by the organization. Such organization can have much better control over its information; however, developing infrastructure for it demands quite huge investments in hardware and security.
- Hybrid storage: The reason is that this method is both cloud and in-house storage, thus allowing organizations to decide depending on sensitivity, cost, and scalability of data.
2. Security Measures for Data Storage
Data storage must be very safe and secure. Strict security practices incur expenses on shielding any data from unauthorized access, breaches, or corruption, and these include:
- Encryption: Even if it is intercepted, compromise cannot be made on data because it is encrypted.
- Backup Systems: Regular backup protects the information from loss due to hardware failure or cyber-attacks.
Access Restrictions: Restriction of access to sensitive data should be so limited that the fewest appropriate authorized members can view or change at any given time.
Different Types of Data Processing Explained
Data processing involves a number of techniques that convert raw data into information. These techniques are categorized into different types, each suited to different contexts and needs.
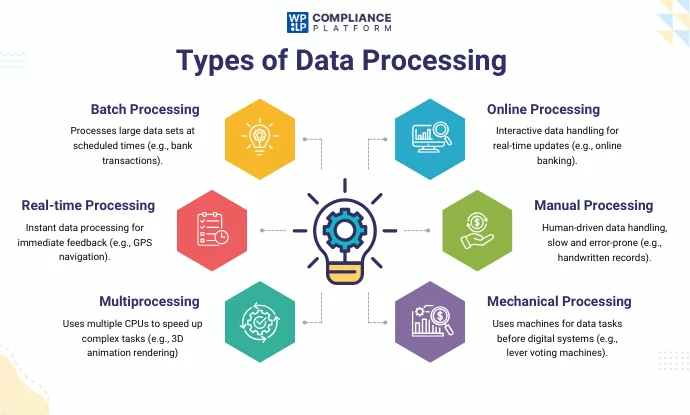
Here, let us take a look at different types of data processing:
1. Batch Processing
Batch processing includes vast amounts of data that are kept and processed at specific times, which is well suited to the non-time-critical process.
Because actual handling costs place data processing in an effective way for companies by bringing it together and executing the work during off hours to minimize the impact on normal operations.
Example: Banks batch process transactions and checks into the night to sweep account balances into one master transfer for speed and accuracy.
2. Real-time Processing
Real-time processing is done for the applications that need data to be processed instantaneously whenever it is received to provide instant or immediate process feedback.
The important factor is that these applications demand prompt reactions to time-accepted delays.
Example: GPS navigation systems apply real-time processing to give turn-by-turn directions, modifying their routes in accordance with live conditions in traffic and on roads to route the shortest path.
3. Multiprocessing (Parallel Processing)
Multiprocessing or parallel processing refers to using two or more processing units, CPUs, to perform different tasks simultaneously. This enhances speed in processing and is usually adopted for difficult calculations that can be divided into minor tasks, thus making overall processing time faster.
Example: This feature is widely acknowledged in movie making, where complex 3D animated scenes are rendered. The rendering is divided among several computers, hence reducing the entire project completion time and, thus, better production cycles together with improved visual quality.
4. Online Processing
Online processing allows for interactive data processing through the channels with continuous input and output for immediate feedback. It enables systems to respond directly to user requests, thus making it almost the entirety of e-commerce and online services.
Example: Online banking systems use online processing for real-time monetary transactions, allowing customers to transfer funds, pay bills, and check account balances with real-time updates.
5. Manual Data Processing
This is found in human input, processing, and output of data, typically without any electronic gadget. Such a condition is laborious and fraught with errors, but it was the most common way before computerized systems existed.
Example: Before the onset of computers, librarians used to carefully store information on individual books by writing it down by hand for inventory and retrieval.
6. Mechanical Data Processing
Mechanical data processing refers to the use of machines or equipment to perform data task management and processing, which is the most common in the pre-digital ages. This method involves using a gross, purely mechanical instrument to input, process, and then output data.
Example: In the early 20th-century elections, people voted through mechanical lever machines. Each vote was tallied by pulling a lever for each choice. This made vote counting quite simple and reduced fraud in votings.
Technologies & Tools for Data Processing Under GDPR
A number of emerging technologies and tools are behind pulling out meaningful information from raw data. This section discusses Databases and Data Warehouses, Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning, and Cloud Technology & Data Analytics Platforms.
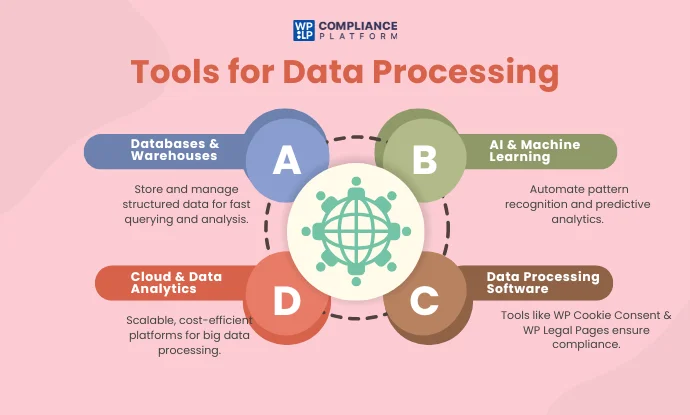
1. Databases and data warehouses
Databases play a critical role in storing structured data, and they are the basis for data processing operations. They support querying, updating, and retrieving data at high rates.
Examples of the most popular databases are SQL-based systems such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server.
On the other hand, data warehouses are high-capacity storage systems that bring together data from many sources. They are query-optimized and data-intensive to analyze large amounts of data to provide business intelligence and decision-making.
Warehouses generally use big data technologies like Hadoop, Apache Spark, and data lakes, single stores that hold large amounts of data.
2. Artificial intelligence & machine learning
Being the backbone of the majority of contemporary data processing techniques, machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) enable companies to predict results and establish patterns from available information.
Typical ML programming languages are Python, R, and SAS, which are adaptive and have numerous libraries for the data processing streams.
A few of the most effective ML techniques to employ in data processing are:
- Supervised learning: Training models on labeled data to make predictions
- Unsupervised learning: Learning patterns in unlabeled data, e.g., clustering or dimensionality reduction
- Reinforcement learning: Learning actions from the environment at run-time
3. Cloud technology & data analytics platforms
Cloud technology has revolutionized how business companies handle data processing and cost-efficient and scalable solutions. Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform are the top-ranked cloud service providers.
These allow organizations to implement data analytics platforms and infrastructure without it requiring ownership in terms of hardware at their location.
Cloud-based data analytics platforms provide data ingestion, processing, and visualization tools and frameworks. Common elements of such platforms are:
- Data storage: Storing data in data lakes or other distributed file systems
- Data processing: Executing big-data tasks such as ETL jobs and analytics jobs
- Data orchestration: Scheduling this tasks between different systems and tools
Data visualization: Displaying processed data in a usable form for decision-makers
4. Data Processing Software and Frameworks
Data processing software and frameworks are critical in efficiently managing, organizing, and analyzing vast data.
In the context of compliance and website data management, plugins like WP Cookie Consent and WP Legal Pages help businesses adhere to global data protection regulations while streamlining legal documentation.
These tools ensure websites handle user data responsibly, aligning with laws such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), and other privacy frameworks.
WP Cookie Consent: Ensuring Compliance with Privacy Laws

WP Cookie Consent is a powerful WordPress plugin that helps websites manage user consent for cookies and trackers. Since data privacy laws mandate websites to inform users about data collection practices, this plugin plays a crucial role in ethical data processing.
Key Features of WP Cookie Consent
- Automated Cookie Scanning: Scans the website for cookies and generates a list to help site owners maintain transparency.
- Customizable Cookie Banners: Displays transparent and customizable cookie consent pop-ups that align with legal requirements.
- Granular Consent Management: Allows users to accept or reject specific types of cookies (e.g., necessary, analytics, marketing).
- Geo-Targeting for Compliance: Ensures compliance with region-specific regulations like GDPR (EU), CCPA (California), and LGPD (Brazil) by displaying consent banners based on user location.
- Cookie Blocking Before Consent: It prevents websites from placing cookies until the user consents, ensuring strict compliance with privacy laws.
How WP Cookie Consent Aids in Data Processing
WP Cookie Consent automates cookie consent management, ensuring websites collect and process user data only with explicit permission. This reduces legal risks, enhances transparency, and builds trust with visitors.
Example: An e-commerce business in Europe and the U.S. uses WP Cookie Consent to display region-specific consent banners. This ensures that GDPR-compliant users can opt out of tracking, while CCPA-compliant users can request “Do Not Sell My Personal Data” preferences.
WP Legal Pages: Automating Legal Documentation for Data Protection

WP Legal Pages is another essential WordPress plugin that simplifies the creation of legally required website pages. It ensures that businesses comply with data privacy laws by providing pre-written legal templates tailored to various industries.
Key Features of WP Legal Pages
- Over 25+ Prebuilt Legal Templates: Covers a wide range of legal documents, including:
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- GDPR & CCPA Compliance Statements
- Cookie Policy
- Refund and Return Policies
- Easy Customization: Users can personalize templates to fit their business model, branding, and legal needs.
- One-Click Policy Generation: Generating legally compliant documents in minutes saves businesses time and legal expenses.
- Regular Updates for Compliance: Ensures that legal documents remain aligned with changing privacy regulations.
- Integration with WP Cookie Consent: Works seamlessly with WP Cookie Consent to ensure cookie policies align with legal requirements.
By integrating these plugins, businesses can ensure that their data processing workflows remain ethical, compliant, and user-friendly.
How WP Legal Pages Aids in Data Processing
This plugin ensures that businesses transparently disclose how they collect, process, and store user data. WP Legal Pages protects website owners from legal disputes and regulatory fines by providing clear privacy policies and terms.
Example: A SaaS company handling customer data uses WP Legal Pages to generate a GDPR-compliant Privacy Policy that outlines how they collect, store, and protect user data. This allows them to operate legally across multiple jurisdictions.
Challenges and Solutions in Data Processing
As data processing becomes more sophisticated, businesses face several challenges in ensuring efficiency, security, and compliance. Below are some of the key challenges and their corresponding solutions.
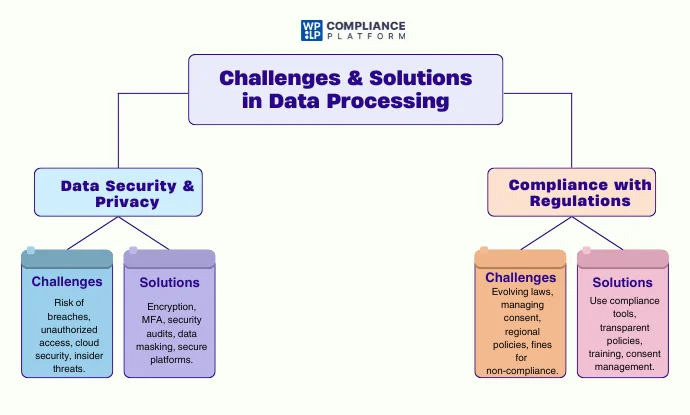
1. Data Security and Privacy Concerns
The increasing amount of data processed raises significant security and privacy concerns. Businesses must protect sensitive data from cyber threats such as hacking, breaches, and unauthorized access.
Challenges:
- Risk of data breaches and leaks.
- Unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Difficulty in securing cloud-based and distributed data systems.
- Insider threats and human errors leading to data exposure.
Solutions & Best Practices:
- Implement Strong Encryption: Encrypt data during transmission and storage to prevent unauthorized access.
- Adopt Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Strengthen access controls to prevent security breaches.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct periodic audits to identify vulnerabilities and improve data protection measures.
- Data Masking & Tokenization: Replace sensitive data with anonymized values to protect personally identifiable information (PII).
- Use Secure Data Processing Platforms: Employ platforms that comply with industry security standards.
Example: A financial institution processing customer transactions uses end-to-end encryption and role-based access control to protect sensitive payment data.
2. Compliance with Regulations (GDPR, CCPA, etc.)
Global data privacy laws such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) require businesses to handle user data responsibly and transparently.
Challenges:
- Keeping up with evolving compliance requirements.
- Managing user consent and data subject requests.
- Implementing region-specific data processing policies.
- Risk of hefty fines for non-compliance.
Solutions & Best Practices:
- Use Compliance Tools: Implement plugins like WP Cookie Consent and WP Legal Pages to automate compliance.
- Maintain Transparent Data Policies: Communicate how data is collected, processed, and stored.
- Regular Compliance Training: Educate employees about legal requirements and best practices.
- Implement Consent Management: Ensure users can control their data and opt in or out of tracking.
- Data Retention & Deletion Policies: Set policies for how long user data is stored and when it should be deleted.
Example: An e-commerce website using WP Cookie Consent ensures GDPR compliance by displaying region-specific consent banners and allowing users to manage their cookie preferences.
FAQ
Data processing is the entire stage of gathering, converting, and transforming raw data in such a way that we can have significant information required to make decisions.
The primary types of data processing comprise manual processing, automated processing, batch processing, real-time processing, distributed processing, and cloud processing.
Data security protects personal information from hacker attacks, breaches, or misuse, thereby reducing legal and monetary risk.
Businesses ensure compliance with the laws by inputting transparency privacy policies, giving user consent management systems, encryption, and ongoing compliance audits.
AI enhances data processing by automating, improving predictive analysis anomaly detection, and enabling real-time decision-making.
Cloud computing assures great scalability, flexibility, and cost-effective storage options to enable organizations to process big volumes of data efficiently.
WP Cookie Consent and WP Legal Pages are tools that automate compliance by managing user consent and creating privacy policies.
Conclusion
In today’s business practices, the data processing has become the foundation that enables organizations to work with huge amounts of data efficiently.
The demands towards data security threats, changes in legislation, and management of big data are the areas where organizations need to comply with best practices and orchestration of new tools and technologies.
AI, Big Data, cloud computing, and compliance software such as WP Cookie Consent and WP Legal Pages will help an organization in the secure, efficient way of processing and managing data without compromising compliance.
Proactive measures toward security controls, notifications for compliance, and advanced processing will enable organizations to benefit maximally from data value without compromising user trust.
If you like this article, you might also like:
- How to Create a WordPress Privacy Policy for Your Website
- How to Create a Privacy Policy For Landing Pages
- What is Privacy Statement and How to Create One?
Need a GDPR-compliant data processing policy? Use the WPLP Compliance Platform to automate compliance.
