ePrivacy Directive vs GDPR: Key Differences for 2026

Summary
As of 2026, the ePrivacy Regulation proposal has been withdrawn, so businesses must continue to comply with both laws for full data protection and privacy compliance.
Has your company ensured full compliance with data privacy regulations? Protecting data nowadays is a key priority, especially when guiding principles are in place for both companies and individuals.
Two of the most important laws that govern privacy and security on the internet are the ePrivacy Directive and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Both try to safeguard user data. However, they differ in coverage, purpose, and enforcement. What is ePrivacy Directive vs GDPR? How do they relate and what about the relationship between GDPR and ePrivacy Directive?
This article outlines the differences between ePrivacy Directive vs GDPR so that you can systematically prepare for 2026.
- What is the ePrivacy Directive?
- What is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)?
- ePrivacy Directive vs GDPR – Key Differences
- The Impact of the ePrivacy Directive and GDPR on Businesses
- Data Protection Requirements for Websites and Apps
- ePrivacy Regulation: The ePrivacy Directive Will Be Changed in the Forthcoming Future
- How It Will Work Alongside GDPR
- FAQs
- Conclusion
- WPLP Compliance Platform
What is the ePrivacy Directive?

Definition and Purpose
The ePrivacy Directive has a history of governing data protection and online privacy across the European Union (EU).
Formally, the Privacy and Electronic Communications Directive 2002/58/EC, the Directive outlines rules that cover the use of cookies and email marketing, as well as data minimization and digital privacy.
While GDPR is a regulation with direct enforcement, the ePrivacy Directive is dependent and must be transposed into national legislation by member states of the European Union.
Revisions were made in 2009 to the Directive that was originally introduced in 2002, and it will eventually be replaced by an ePrivacy Regulation.
Navigating the transformation of ePrivacy legislation poses a challenge for businesses aiming for compliance alongside evolving regulatory frameworks, and understanding the interplay of GDPR with ePrivacy is critical.
Attention is also given to present-day debates on the ePrivacy Directive versus GDPR. This key area is important in saying both/and proposition when it comes to holistic data management.
Key Focus Areas
- Cookies & Tracking: Cookies and other forms of spying on websites must get permission from the users before being allowed to store consented cookies in the user’s system, save for the cookies that aid a site in performing basic functions. Basic advertising and analytics spying also fall within this category.
- Electronic Communications: Emails as well as SMSs, the sending or receiving VoIP calls and any messaging applications are part of the private communications that the ePrivacy Directive is concerned with, and their users are supposed to have private communication.
- Marketing Regulations: Unsolicited marketing messages require consent from the recipient, and business practitioners are obliged to follow the strict consequences attached to it, as a rule of thumb on promotional text messages or emails, there is a need to opt-in.
As both regulations shape the global data protection landscape, the ePrivacy Directive vs GDPR is still being debated.
While the ePrivacy Directive focuses solely on privacy protection in digital communication, compliance with GDPR entails more comprehensive data protection measures.
Lawmakers and executives need to grasp both epitomes of legislation when determining policies and strategies in 2026.
What is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)?

Definition
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a groundbreaking law from the European Union (EU) that applies to both EU and non-EU organizations with regard to handling the personal data of EU citizens.
GDPR implementation began on May 25, 2018, after the European Parliament and Council of the EU adopted the law in 2016.
The regulation:
- Establishes the legal frameworks for data transfer and processing.
- Sets out precise instructions on protecting personal data both stowed and in transit.
- Mandates shielding EU citizens from the collection, exploitation, and control of their private data without authorization.
In the scope of compliance with GDPR criteria, personal data describes any piece of information that can identify an individual directly or through other means.
Credit cards and names fall under direct identifiers, whilst indirect identifiers entail features such as physical description and birthdates, which, when taken together, could point to an individual.
The data subject in GDPR speaks of the person to who the data is attributed to. For example, when a business posts email addresses, they are the owners of those emails and, hence, referred to as data subjects.
Even though GDPR is an EU regulation, its scope is worldwide. Every organization, irrespective of their geographical location, which processes or collects personal data of residents of the EU has to comply.
Analyzing the connection between GDPR and the ePrivacy Directive is important, especially when looking at the differences in laws pertaining to ePrivacy Directive vs GDPR.
Both regulations are significant in the framework of data privacy laws on a global scale.
Purpose
The General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR, was created to protect people and their information while mandating that businesses manage this data responsibly.
Compliance with GDPR mandates that businesses take reasonable steps to secure personal data from access, unlawful processing, accidental loss, destruction, or damage.
Also, GDPR sets strict rules on how data can be collected. Organizations must have a valid and defined reason for collecting an individual’s personal data and cannot use it in ways that go beyond the stated purpose.
The regulation also enforces data minimization, stating that only the necessary information for processing is to be collected. In addition, businesses must ensure that the data they collect is accurate and current.
For a business grappling with various privacy laws, grasping how GDPR correlates with the ePrivacy Directive is important.
In distinguishing the ePrivacy Directive vs GDPR, the former is narrower and addresses privacy in electronic communications, whereas the latter develops the backbone of data protection legislation.
Together, they make modern compliance with data privacy laws possible.
Core Principles of GDPR
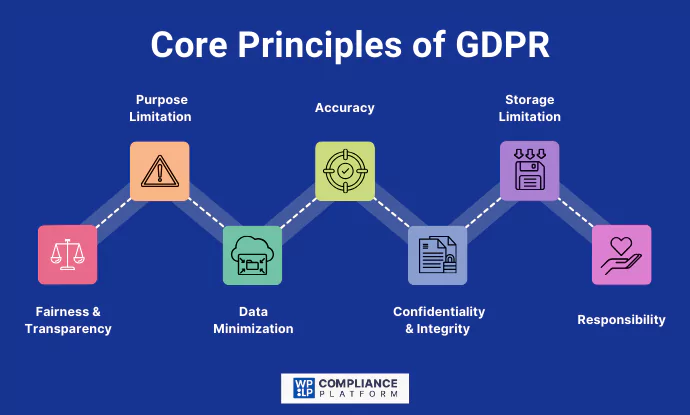
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is built on numerous guiding principles underlying the regulation’s basic and rudimentary framework concerning the ethical and legalistic aspects of dealing with personal information.
As such, these principles aid businesses with protecting the privacy of their customers, users or clients and concurrently enables them to maintain compliance with the regulatory framework.
Having these principles highlighted is relevant, especially in the context of the intersection of the GDPR and ePrivacy Directive, since both frameworks are crucial in the data protection and privacy ecosystem.
1. Lawfulness, Fairness And Transparency
Personal information must be processed in a legally permissible and open manner. Individuals must be fully told how their data is collected and used and where it is stored.
2. Purpose Limitation
Data collection should be only made for legally acceptable stated reasons without using data for other unapproved purposes.
3. Data Minimization
The captured information must be relevant or related to the intended goal, thus excessive information capture will be deemed inappropriate.
4. Accuracy
Personal data captured by organizations must be kept up to date and verifiable. Obsolete or false information must be removed, replaced or deleted in a relevant timeframe.
5. Storage Limitation
No personal data should be kept longer than needed. Secure deletion of the data must be done once it is declared as unnecessary.
6. Confidentiality and Integrity
According to GDPR, organizations must take specific security precautions to protect personal data from breaches, unauthorized access, and unlawful processing.
7. Responsibility
Compliance with GDPR must be demonstrated through adequate documentation of all data processing activities and the appropriate policies adopted.
In comparing the ePrivacy Directive vs GDPR, one can note that while GDPR concerns itself with the holistic protection of personal data, the ePrivacy Directive deals specifically with electronic communications and privacy over the Internet.
Both regulations combined form a “regulatory ecosystem”. They determine the prospects of data privacy and how businesses deal with user data within technological platforms.
Rights of Individuals Under GDPR
Data protection is a critical right represented under Article 8 of the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights. It establishes that each individual has a degree of control over their information.
This principle is significant from the standpoint of compliance with the GDPR. It once again brings forth the interrelationship existing between GDPR and the ePrivacy Directive. They are two dominant instruments of data privacy law in the digital age.
Every person has the right to, as cited in Article 8:
- The protection and fair processing of their personal data for defined and legitimate reasons.
- Accessing the information and requesting amendments for any inaccuracies.
- An independent specialist has control over the data in order to guarantee its handling.
In compliance with Article 6 of GDPR, organizations need to have a validated, legitimate reason for processing personal data.
The following are the six lawful grounds for processing data;
- Consent – Explicit consent for data processing has been provided by the person.
- Contractual Necessity – Performance in contract requires processing.
- Legal Obligation – Data processing is important in order to be compliant with laws.
- Vital Interests – Processing of data is necessary to guard someone’s life.
- Public Interest – Necessary for the performance of tasks in the public interest.
- Legitimate Interests – Any organization can defend a reason for processing data as long as it does not violate the rights of individuals.
With ePrivacy Directive vs GDPR, it is critical to understand these legal grounds. GDPR forms the foundations of data protection, while the ePrivacy Directive narrows down to privacy in electronic communications.
Together, they help develop contemporary data security and privacy compliance.
ePrivacy Directive vs GDPR – Key Differences

Two of the most important regulations regarding data protection and privacy in the EU are the ePrivacy Directive and the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
While both have some things in common, they do differ in some ways. We discuss the key differences between the two below in this table.
ePrivacy Directive vs GDPR
| Sr. no. | Type | ePrivacy Directive | GDPR |
| 1 | Scope of Regulation | Particular components of electronic communications, such as cookies, direct marketing, and the confidentiality of digital interactions, fall under the ePrivacy Directive. It governs these areas too. | On the other hand, personal data processing in all sectors falls under GDPR which ensures data protection and privacy of individuals. |
| 2 | Legal Basis For Data Processing | The relevant legal framework for the ePrivacy Directive is consent which is the basis of the user data collection, specifically cookies, and other tracking technologies. | On the contrary, GDPR is one of the legal frameworks that allow data processing under multiple valid reasons such as legitimate interest, necessary contracts, or legal obligation compliance. |
| 3 | A Tracking Technologies Focus | Cookies and tracking tools that advertisers and websites use are heavily regulated in the ePrivacy Directive which requires websites to obtain consent before they can store or access cookies. | While GDPR focuses on regulating the collection, storage, and processing of personal data which does include cookies, it adopts a broader approach. |
| 4 | Geography (Regional Scope) | The ePrivacy Directive is applicable to providers of electronic communication services based in the EU. | On the other hand, GDPR has a more pronounced impact as it touches on any organization dealing with the personal information of residents of the EU irrespective of where the company is situated. This expanded coverage of GDPR makes it a critical issue of compliance for multinational firms. |
| 5 | Implementation and Penalties | The ePrivacy Directive is subject to interpretation by each EU country and so is interpreted by the relevant state ePrivacy Directive Enforcers, leading to some lack of consistency. | In contrast, direct applicability regulations such as GDPR, governing the entire EU territory is dealt with in a uniform manner and accompanied with stiffer penalties for breach of regulations—€20 million or 4% of the total annual revenue of the company globally. |
The Impact of the ePrivacy Directive and GDPR on Businesses
Selecting the right strategy and dealing with the complexity of relations ePrivacy Directive and GDPR is important for many international companies and businesses operating within the EU.
Both regulations strive for privacy, although they treat compliance differently. Knowing what is ePrivacy Directive and what is GDPR is vital for businesses, because any miscalculation may lead to financial penalties.
Compliance Obstacles for Businesses
Businesses are caught in a complicated web of conflicting legislations which makes maintaining compliance with both the GDPR and the ePrivacy Directive seems impossible.
The ePrivacy Directive requires unequivocal consent of users for online tracking and the use of cookies, whereas the GDPR has stronger limitations on the collection and processing of personal information.
The constant regulatory changes require companies to adopt comprehensive solutions for data protection and reliable auditing trails, which is a strict requirement of both regulations.
Impact On Marketing And Advertising Campaigns
The ePrivacy Directive has great significance in the area of advertisement and marketing and the usage of cookies, email marketing and targeted advertising.
Businesses must obtain user consent before collecting behavioral data, which can lead to user inactivity and limit precise target marketing.
Moreover, GDPR forces businesses to provide reasonable rationale for information retrieval, adequate locks on storage and allows people more freedom over their personal details.
Data Protection Requirements for Websites and Apps
Websites and mobile apps must observe the privacy requirements of the ePrivacy Directive and GDPR.
The ePrivacy Directive deals with the protection of electronic communications and the use of cookies, whereas GDPR oversees the processing of personal data and the rights of the user.
Businesses need to adopt strategies to comply with GDPR, which includes disclosing privacy policies, installing cookie consent banners, and implementing secure data storage systems.
ePrivacy Regulation: The ePrivacy Directive Will Be Changed in the Forthcoming Future

What is the ePrivacy Regulation?
The new ePrivacy Regulation will apply in its place and will update the existing ePrivacy Directive to be more consistently compliant with GDPR. It will add new restrictions on:
- User privacy in electronic communication – Safeguarding the rights and freedoms of individuals using emails, texts, and social media.
- Processing of communication content and metadata – Regulators will oversee how businesses handle metadata, such as call duration, location, and recipient.
- Protection of end-user devices – Regulators will govern how businesses collect and process data from user’s devices. It includes cookies and tracking technologies.
- Publicly available directories – Authorities will control personal data in online directories to prevent unauthorized use.
- Direct Marketing Regulations – Businesses must obtain consent before sending unsolicited marketing or promotional messages.
Differences Between ePrivacy Directive and ePrivacy Regulation
While distinguishing the ePrivacy Directive vs GDPR is important, businesses must take note of the change from the ePrivacy Directive to the forthcoming ePrivacy Regulation.
Both seek to advance the protection of online privacy, but there is a difference in enforcement, scope, and GDPR alignment for compliance.
| Sr. no. | Type | ePrivacy Directive | ePrivacy Regulations |
| 1 | Legal Framework and Enforcement | The ePrivacy Directive acts as a framework where it is up to individual EU member states to enforce it through national laws. | This is in contrast to the ePrivacy Regulation, which will have direct applicability in all EU countries and uniform enforcement, in the same manner as GDPR. |
| 2 | Advanced Scope of Regulation | ePrivacy Directive shift is closer to the principles of GDPR compliance. | The ePrivacy Regulation will apply to a wide variety of digital communication services such as VoIP, messaging and social media. |
| 3 | More Restrictive Measures Regarding Cookies and Tracking Technologies | The ePrivacy Directive requires consent for cookie placement, while the regulation will streamline consent processes and increase tracking control. | The ePrivacy Regulation will implement more restrictive measures regarding the use of cookies and tracking online. |
| 4 | Reinforced Alignment with GDPR | One of the main aspects that set apart ePrivacy Directive vs GDPR is that GDPR has jurisdiction over personal data in general while the ePrivacy Directive limits it to electronic communications. | The ePrivacy Regulation seeks to narrow this gap to have a consistent relationship with GDPR and the ePrivacy Directive on issues of consent and data processing. |
How It Will Work Alongside GDPR
It is evident from the comparison between the ePrivacy Directive vs GDPR that both regulations seek to safeguard user privacy yet differ in scope.
Most businesses have already adapted to GDPR compliance, while the ePrivacy Regulation will complete the data protection puzzle by focusing on electronic communications.
1. Collaborative Regulations Relating to Privacy and Data Protection
ePrivacy Regulation will increase the scope of online privacy violations under GDPR by including issues such as cookie compliance, metadata processing, and direct marketing.
While the GDPR serves as the overarching law concerning the collection and processing of personal data, the ePrivacy Regulation will oversee the use of electronic communications and monitoring technologies by businesses.
2. Alignment and Change in Consent Requirements
Both GDPR and the ePrivacy Regulation emphasize consent of the user for data processing. However, the latter enhances consent requirements in relation to online tracking.
According to ePrivacy Regulation, businesses must retrieve permission to use cookies and other tracking devices. This creates a stronger link between GDPR and ePrivacy Directive.
3. Enforcement and Compliance Overlap
Similarly to the GDPR, the ePrivacy Regulation will have direct applicability throughout the EU, lessening variation fragmentation divergence between national transpositions of the ePrivacy Directive.
Organizations which already observe GDPR will have to adjust their privacy policies to comply with more stringent rules on digital communications.
FAQs
1. How do ePrivacy Directive and GDPR affect the businesses?
GDPR regulates personal data processing and ePrivacy Directive regulate electronic communications like cookies and more.
2. Do businesses need separate consents to comply with GDPR and ePrivacy Regulations?
Yes, since GDPR and ePrivacy regulations regulate different things, businesses will need to get separate consents from each entity respectively.
3. How are GDPR and ePrivacy Regulations related in terms of enforcement?
National authorities regulate GDPR, and national law enforces the ePrivacy Directive. The ePrivacy Regulation will centralize laws like GDPR.
Conclusion
The comparison between the ePrivacy Directive and GDPR highlights the efforts modern society is taking toward data privacy.
While ePrivacy Directive concerns itself with electronic communications, the GDPR has a wider scope of dealing with personal information.
Businesses still need to focus on compliance with GDPR while preparing for the transition to the ePrivacy Regulation.
In order to comply with both the ePrivacy Directive and the GDPR, strong data protection mechanisms need to be established.
Understanding the correlation within both frameworks will help businesses tackle compliance as well as user privacy protection issues.
WPLP Compliance Platform
Please check out our ePrivacy directive compliance for more detailed information on effective compliance strategies.
Businesses can ensure secure data processing using AI, Big Data, cloud computing, and compliance tools like WP Cookie Consent and WP Legal Pages.
If you like this article, you might also like:
- Best GDPR WordPress Plugins
- Top GDPR-Compliant WordPress Themes For Your Website
- What is GDPR Data Minimization and How to Do It?
Are you looking to process your cookie data automatically? Grab the WP Legal Pages Compliance Platform for easy operations!
