What is Data Privacy? – Everything You Need To Know

Are you thinking about what data privacy is?
Data Privacy safeguards private and sensitive data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. It includes regulating data storage, sharing, using, and determining who can access and modify the data.
In the digital world, websites collect and use data in the form of cookies, leading to data breaches. Hence, safeguarding individuals’ data privacy is very important.
Online privacy protection plays a very important role in data privacy. Many governing bodies have formed data protection laws to safeguard the digital data privacy of individuals.
This article will share a detailed guide to what is data privacy and the solution for online privacy protection.
So, let’s dive right in!
- What is Data Privacy?
- Why is Data Privacy Important?
- Data Privacy vs Data Security
- What are the Laws Governing Data Privacy?
- Benefits of Data Privacy Compliance
- Challenges Users Face When Protecting Online Data Privacy
- Challenges Businesses Face When Protecting User Privacy
- How Businesses Can Protect User Privacy
- FAQ
- Conclusion
What is Data Privacy?
Data privacy, also known as information privacy, is an area of data protection that covers sensitive data handling and addresses the proper storage, access, retention, and security of sensitive data.
It handles personally identifiable information (PII), such as names, addresses, social security numbers, and credit card numbers, which are generally linked to data privacy. The concept, however, also applies to other private or sensitive data, such as financial, intellectual, and health-related data.
Many data protection laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act in the California province, aim to protect individuals’ online privacy. Both these data protection policies are legally obliged to uphold data privacy rights.
In general, data privacy consists of the following six components:
- Legal Framework: Data privacy laws regulate and govern issues related to data privacy. They ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and security of personal data.
- Data Protection Policies: Companies have developed many data protection policies to protect the privacy of workers’ and users’ data.
- Data Privacy Practices: Best practices have been established to govern data privacy, security, and IT infrastructure.
- Third-party Associations: Any external organizations that handle data, including cloud service providers.
- Data Management: Standards and procedures for accessing, storing, and securing data.
- Global Requirements: Compliance requirements among legal jurisdictions such as CCPA Compliance in the U.S. and GDPR Compliance in the European Union (EU).
Data protection is a broad concept that includes data privacy. It contains data security and traditional data protection measures like data backups and disaster recovery planning.
Data protection guarantees the security and privacy of vital data while maintaining its availability, consistency, and immutability.
Why is Data Privacy Important?
Data protection laws are in place to preserve privacy, which is seen as a fundamental human right in many nations. Data privacy is crucial because people must be confident that their personal information will be handled carefully before interacting online.
Organizations use data privacy practices to show users they can trust us with their personal information.
Data privacy is crucial for the following main reasons:
- Trust and Confidence: Building trust between people and organizations.
- Protection of Personal Information: Keeping sensitive information safe by preventing unwanted access to individuals’ personal information.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Implementing a data protection policy to safeguard individuals’ rights for their personal information.
- Preserving Individual Autonomy: Empowering people to keep control over their personal data, like choosing how the data is gathered, used, and distributed.
This are the areas where data protection laws apply. Data privacy will remain a critical problem as technology advances and the digital landscape shifts.
It is imperative to remain informed about new regulations, emerging dangers, and best practices to guarantee the ongoing safety of personal data.
Data Privacy vs Data Security
Although they are frequently used synonymously, data security and data privacy are two different ideas. Let’s look into each one carefully.
Data Privacy: It describes how sensitive data should be handled, including when and how personal information can be gathered and shared. It concerns using data ethically and responsibly.
Data Security: It is the process of protecting information from theft, alteration, and unwanted access. It includes procedures and instruments such as network monitoring, password management, and encryption.
Hacking can pose risks both internally and externally. An IT team can employ various strategies to safeguard data on various platforms and applications, including hashing, tokenization, encryption, and other techniques.
What are the Laws Governing Data Privacy?
Over the years, improvements in data-gathering technology have led governments worldwide to impose regulations on businesses handling personal information.
Multiple global and regional data protection laws govern how organizations collect, process, and protect information.
Let’s examine a few of the most well-known data privacy laws:
1. California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) controls how personal information about customers is gathered and handled. Businesses operating inside or outside California and providing goods and services to Californian customers are subject to the state’s privacy laws.
CCPA also allows opt-out, guaranteeing that companies will not sell customers’ personal information. To uphold these rights, businesses are required to enable the Do Not Sell My Information button on their website.
2. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is the world’s most strict and comprehensive privacy and data protection law. It is based on fundamental rights and considers individuals’ personal information privacy.
According to GDPR, the law permits individuals can delete their personal data that is received by them.
3. Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados Pessoais (LGPD)
The Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados Pessoais (LGPD) has established ten legal bases for the authorized processing of personal data and has also outlined nine privacy rights for individuals whose data is processed. Additionally, companies must conduct data protection impact assessments (DPIAs) upon the request of the Brazilian Data Protection Authority (ANPD).
Furthermore, the LGPD mandates that companies hire a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to supervise the law’s implementation and advise top management on complying with the LGPD.
4. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of the United States governs how you should handle an individual’s personal health information.
Benefits of Data Privacy Compliance
An organization can benefit greatly from strong privacy practices. This includes reducing losses from data breaches and building customer loyalty and trust. Let’s take a look at some of the benefits of data privacy.
- Adherence to Regulations: Companies that prioritize data privacy and protection can avoid common mistakes like collecting or disclosing personal data without adequate legal justification and also avoid facing severe penalties for noncompliance.
- Data Security: Information breaches that could threaten sensitive data can be managed using safeguards that maintain personal information throughout the information lifecycle and threat prevention and mitigation.
- Boosting Brand Recognition: Companies that prioritize protecting the data privacy of their clients and staff gain more understanding and loyal customers, improving their reputation and brand value.
- Trust: Businesses risk losing customers after a breach, but those that prioritize information security have increased access and usage of customer data.
Challenges Users Face When Protecting Online Data Privacy
Protecting user privacy is an essential aspect. Here are the many challenges that a user faces when dealing with online data privacy:
- Internet tracking: User activity is frequently monitored online. Users may not be aware of the extent to which cookies record their activity, even though most countries require websites to notify users when cookies are being used. Cookies frequently record a user’s activities.
- Losing control of data: People may be unaware of how their data is shared beyond the websites they use and may have no say in what happens.
- Lack of transparency: Users frequently must give personal information, such as their name, email address, phone number, or location, to utilize web applications. At the same time, the privacy policies linked to those programs may be complex and challenging to comprehend.
- Social media: Social media posts may reveal more personal information than users realize, and it’s now easier than ever to find someone online utilizing these platforms. Furthermore, consumers sometimes are unaware of how much data social media networks collect.
- Cybercrime: Attackers are increasingly trying to steal personal data to conduct fraudulent activities or sell it on illegal marketplaces. They use phishing attempts or try to hack into businesses’ internal systems. It’s important to protect sensitive information.
Challenges Businesses Face When Protecting User Privacy
Ensuring user privacy is a paramount concern for businesses in today’s digital landscape. Here are some of the challenges they face in protecting user privacy:
- Communication: Companies may find it difficult to explain to their users what personal information they are gathering and how they plan to use it.
- Cybercrime: Attackers target specific users and companies that gather and retain user data. Additionally, the attack surface grows as more elements of an organization are linked to the Internet.
- Data breaches: If personal information is disclosed, a data breach can result in a serious invasion of user privacy, and hackers are always improving the methods they employ to carry out these breaches.
- Insider threats: If data is not sufficiently secured, internal staff members or outsiders can get unauthorized access to it.
Understanding these challenges is crucial for businesses aiming to safeguard user privacy.
How Businesses Can Protect User Privacy
Creating privacy policies for your website is crucial to safeguard users’ data privacy. WP Legal Pages is a free privacy policy generator that allows you to create legal pages for your website, prioritizing data privacy easily and efficiently.
With pre-designed policy templates, you can comply with data privacy laws such as GDPR, CCPA, e-privacy, and more without hassle.
To obtain explicit consent from users to collect their data, you can use Consent Management Platforms (CMS) like WP Cookie Consent. These tools present the users with a cookie banner and ask them for their consent to opt in or opt out of sharing their data. You can select the law to display the cookie notice on your website.
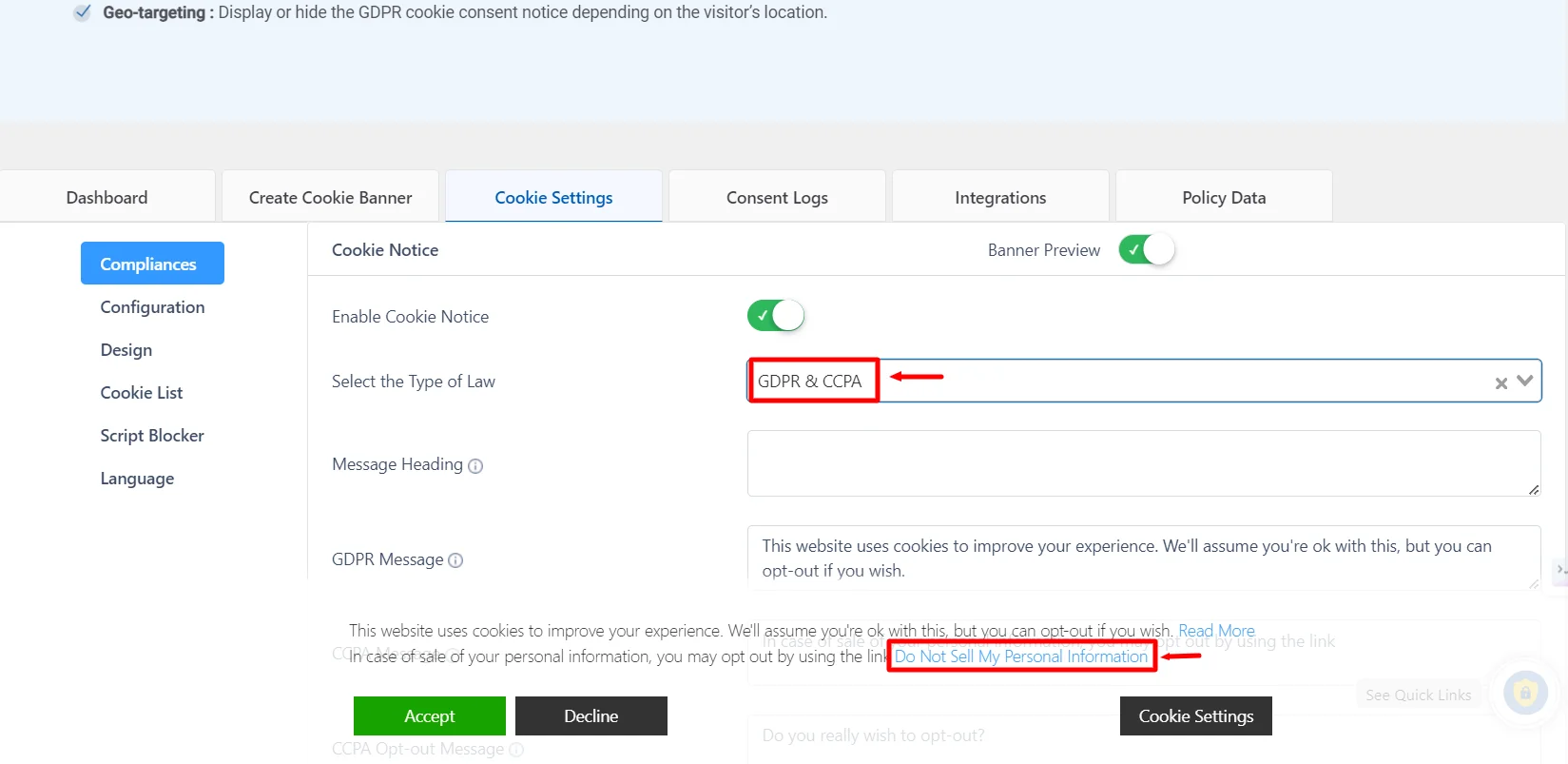
Furthermore, you can add a data request form to your privacy settings and enable a consent forwarding feature to obtain user consent on one site and count it for selected sites in the network.
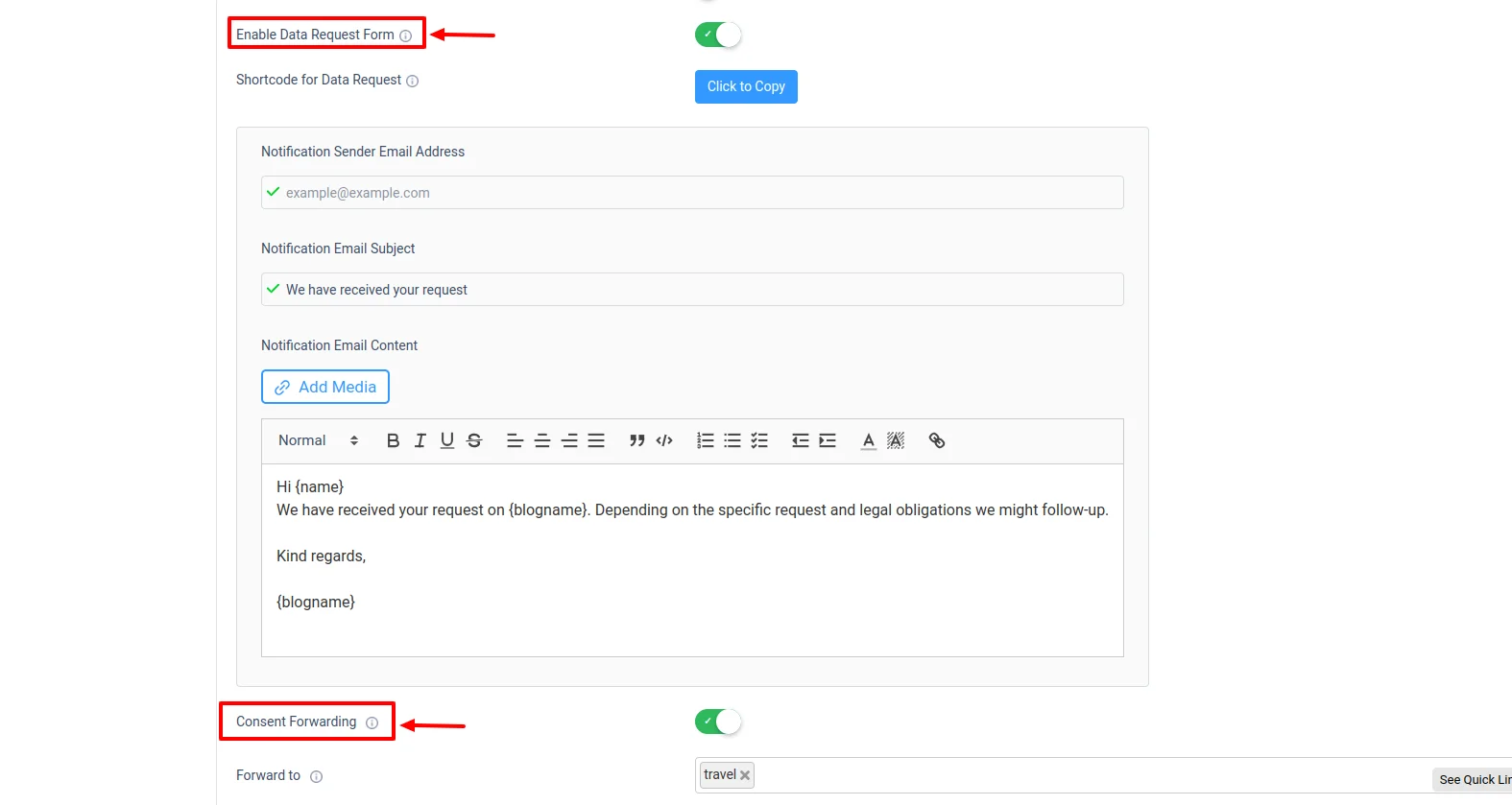
WP Cookie Consent allows you to access these settings directly from the WordPress dashboard.
Therefore, if you’re a website owner, then creating a privacy policy as well as implementing a cookie consent banner for your website is an ideal choice.
FAQ
Data privacy is managing and safeguarding personal data, including personally identifiable information (PII) and personal health information (PHI).
The key data protection laws are GDPR in the European Union, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in California, the state in the USA, and many other laws.
The best CMS tool to protect users’ data privacy is WP Cookie Consent as it helps to get explicit consent from users, thereby collecting data with permission.
Conclusion
Any business that collects, manages, and uses personal customer information should prioritize data privacy.
Businesses benefit from obtaining private user data. It enhances the customer experience, helps with customer retention, marketing, and research, and when new products and services are developed, it more closely aligns with the needs and preferences of your target market.
But the user data you gather needs to stay out of the hands of dishonest people, and your business can only utilize it for safe, legal, and appropriate purposes.
You can prioritize data privacy using WP Cookie Consent and WP Legal Pages compliance solutions. These plugins ensures that everyone can access the Internet safely.
If you liked reading this article, don’t forget to read our other engaging articles:
- Most Common Privacy Policy Issues To Avoid
- Best Terms And Conditions Generators – A Detailed Review
- Digital Markets Act: What Website Owners Need to Know
Are you excited to create a privacy page for your website? Grab WP Legal Pages now!
