The California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA)

As a business owner, are you aware of what is CPRA compliance?
As we all know, California has multiple laws to protect California consumers’ personal information in terms of data breaches, data deletion requests, and maintaining correct personal information.
The California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) was enforced in November 2020 following the 2018 California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) expansion.
The CPRA law was enacted on January 1st, 2023; while its enforcement is global, its primary application and implementation focus on California.
California Privacy Rights Act law helps to protect the privacy of California residents and helps them limit the amount of information businesses can collect.
In this article, we will examine CPRA law and how a business owner must comply with it to maintain users’ personal information securely.
What is the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA)?
The California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) modified the CCPA and introduced new privacy regulations. This act is more small-business friendly than its predecessor, but it also:
– Gives customers more rights
– Creates a body to enforce and protect the CPRA
– Imposes additional conditions on organizations
The revisions were initially intended to take effect on January 1, 2023, with a lookback to January 2022. However, the California Privacy Protection Agency (CCPA) did not finalize the official enforcement guidelines until much later.
As a result, California courts extended the enforcement deadline to March 29, 2024, and only the statutory criteria were fully implemented on July 1, 2023.
Who Must Comply With the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA)?
Profit-earning organizations that meet one or more of the following criteria while operating in California are subject to the CPRA:
- The gross revenue was $25 million for the previous year as of January 1.
- Sell, purchase, or exchange 100,000 Californian consumers’ personal information.
- Obtained at least half their income from selling or sharing personal data (as yet specified).
Due to these new levels, certain small enterprises are exempt from CPRA restrictions.
However, the rule further broadens its application to businesses that receive at least 50% of their revenue from the exchange of personal data.
The CPRA will also apply to the following kinds of entities:
- If each company owns at least 40% of the other companies in partnerships or joint ventures, they will treat them as one independent company.
- Commonly controlled entities are entities that:
- Have access to the personal data of the covered business’s customers;
- Sharing a common brand with the business is an example of a commonly controlled company.
- Manage or manage a covered business,
- Any company that wants to abide by the CPRA, even if it doesn’t meet the aforementioned requirements
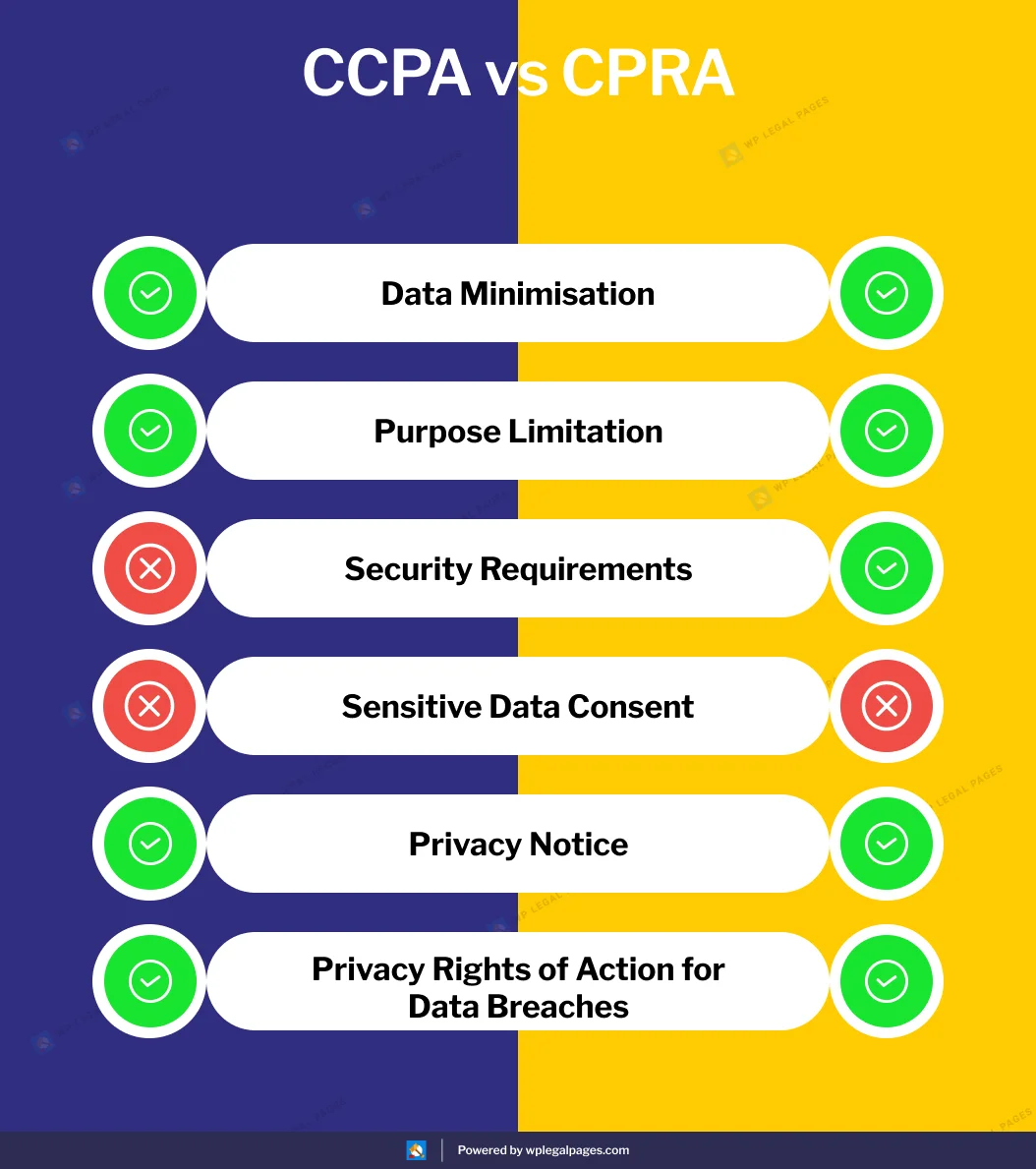
CCPA vs CPRA – Key Differences
In this section, let’s delve into the key differences of CCPA vs CPRA laws.
These two privacy laws, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), aim to protect Californians’ personal information.
However, there are a few significant variations between the two:
| Aspects | CCPA | CPRA |
| Scope | Offers privacy protection for personal info | Expands privacy protections and establishes the California Privacy Protection Agency |
| Sensitive Information | Does not clearly define “sensitive” data | Defines and adds protection for sensitive data |
| Data Minimization | Encourages minimal data collection | Mandates minimal data collection and sharing |
| Contractual Obligations | No specific requirement | Requires data processing and protection clauses |
| Consumer Rights | Provides certain rights for consumers | Introduces additional rights and limitations |
In general, the CPRA expands on the framework established by the CCPA to offer stronger privacy protection for California residents and places additional obligations on businesses that handle personal information.
How Business Can Comply With CPRA Regulations
To comply with CPRA (California Privacy Rights Act) regulations, businesses must enhance their data protection practices. Here are some steps to help comply with CPRA regulations:
- Data Inventory: Start by conducting a comprehensive inventory of the personal data your business collects, processes, and shares. Understand where the data is stored, how it is used, and who can access it.
- Update Privacy Policy: To ensure compliance with CPRA requirements, please update your privacy policy. Specifically, provide clear information about the categories of personal information collected, the purposes for collecting it, and the rights of consumers under CPRA.
- Consent Management: Implement robust consent management practices to ensure users provide explicit consent for collecting and processing their personal information. Clearly communicate the use of cookies and obtain consent using cookie consent tools.
- Data Security Measures: Strengthen your data security measures to protect the personal information you collect. This can include encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments.
- Data Subject Rights: Establish processes to accommodate data subject rights, including the right to access, delete, and correct personal information.
- Third-Party Contracts: Review and update contracts with third-party service providers to ensure they comply with CPRA requirements when handling personal data on your behalf.
- Employee Training: Provide comprehensive training on data privacy, security practices, and handling personal information.
- Data Retention and Deletion: You should establish data retention and deletion protocols to ensure that personal information is not retained longer than necessary and can be securely deleted upon request.
- Regular Audits and Compliance Checks: Conduct audits and compliance checks regularly to identify and address any gaps in your data protection practices.
- Stay Informed and Updated: Stay informed about any changes in privacy regulations and adjust your practices accordingly.
By following these steps, businesses can work towards compliance with CPRA regulations. By using WP Legal Pages and WP Cookie Consent Plugins:
WP Legal Pages

WP Legal Pages is a plugin that can help you create and maintain a compliant privacy policy. It provides templates and guidance to ensure your policy meets legal requirements, including GDPR, CCPA, eprivacy Directive, and CPRA laws.
WP Cookie Consent

WP Cookie Consent is a plugin designed to help websites comply with cookie consent requirements.
It allows you to display customizable cookie consent banners, manage cookie settings, and obtain user consent, aligning with CPRA requirements for cookies and user consent.
By using WP Legal Pages and WP Cookie Consent plugins, businesses can streamline the process of ensuring their website’s legal compliance with CPRA regulations, particularly in maintaining a compliant privacy policy and managing cookie consent in a user-friendly manner.
CPRA Penalties and Fines for Non-Compliance

An amendment to the CPRA has included a new penalty: deliberate breaches or violations concerning the personal information of individuals under sixteen may result in administrative fines of up to $7,500.
Additionally, the 30-day cure period that starts automatically after a person is accused of a violation will be eliminated under the CPRA. Rather, the amount of time you have to make corrections is determined by the CPPA. They will consider the following aspects:
- Whether or not you intended to break the CPRA
- Whether you tried to remedy the alleged infraction
- Even for accidental infractions, there is still a $2,500 maximum penalty.
These fines may also extend up to $7,500 (USD).
FAQ
Cookie banners are essential for businesses because they help protect user privacy and comply with privacy regulations worldwide.
Cookie banners are notification popups on websites informing website owners about using cookies.
An implied cookie banner is a type of cookie popup or notification not clearly or explicitly displayed to users.
Explicit Cookie banners are clearly or transparently shown to users on a website or mobile application.
To create a cookie banner for your website, you can use a free consent management platform like WP Cookie Consent plugin.
Conclusion
The CPRA Law is an updated and strengthened version of the CCPA. With CPRA, customers have more privacy rights and can prevent companies from using sensitive personal data, such as financial or health information.
Additionally, CPRA privacy prohibits companies from disclosing a customer’s whereabouts to third parties without that customer’s knowledge or consent. Furthermore, the California Consumer Protection Act (CPRA) creates a new agency to safeguard consumer rights by allowing consumers to retain authority over their own data and enhancing overall transparency.
To create a privacy policy, we recommend using WP Legal Pages, and to show explicit consent banners to users, we recommend using WP Cookie Consent and the WP Legal Pages plugin. Both these plugins will help you stay compliant with data privacy laws.
If you’ve liked reading this article, don’t forget to check out our other engaging articles:
- CPRA vs CCPA – A Detailed Comparison
- Best Consent Management Platforms – An Ultimate Guide
- What Is A Cookie Banner And Why Do You Need One For Business
Want to create a unique cookie consent banner for your WordPress website? Grab the WP Cookie Consent plugin!
