What is the Digital Services Act (DSA)? Explained

Are you wondering what the EU’s Digital Services Act (DSA) is and how it impacts your business?
Look no further! This article will help you get covered.
The DSA is a key regulation passed in the European Union to create a safe digital environment that protects users’ fundamental rights. It introduces new obligations for digital services, particularly online platforms, to ensure accountability and transparency.
This article will help you get into the intricate details and understand the essentials of the Digital Services Act (DSA) and its implications for your business operating in the EU.
So let’s get started!
What is the Digital Services Act (DSA) of the EU?
First, let’s start with the fundamentals so that we can understand what the Digital Services Act, or DSA, is.
The Digital Services Act is a powerful piece of legislation passed in the European Union that ensures users’ data privacy. It aims to transform the digital space to provide a safer and more transparent environment within the European Union.
It places responsibilities on digital services, especially online platforms, to act in the best interests of their users, concerning their fundamental rights and equality.
Specifically, the DSA requires companies to take preventive measures related to content moderation, transparency reporting, and the protection of user rights.
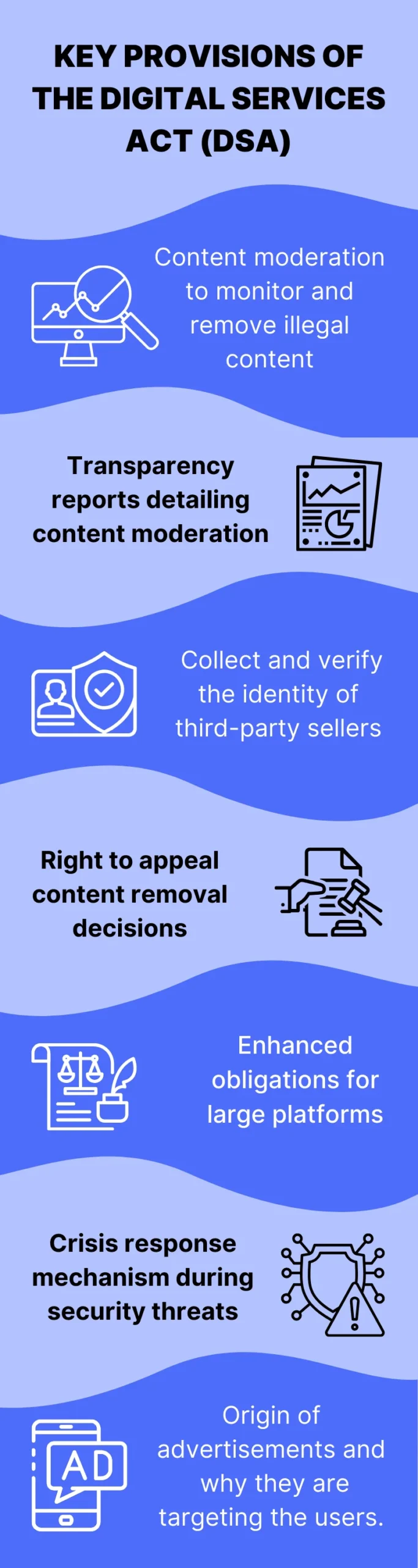
Key Provisions of the Digital Services Act (DSA)
While the above was just a brief description of DSA, let’s now get into its details to understand each of its components.
Each of these provisions aims to promote a higher level of safety and transparency in the digital space, protect users’ rights, and foster the responsible use of platforms.
The key provisions of DSA are as follows:
Who Must Comply with the EU’s Digital Services Act (DSA)
The Digital Services Act (DSA), which governs digital service providers in Europe, impacts all sizes of providers offering services to users in the EU – think from small, nascent companies to large multinational corporations.
Here are the broad categories of businesses that the DSA will apply to:
- Online Platforms: Covers all social networking sites, content-sharing sites, online marketplaces, etc.
- Hosting Services: Companies providing web hosting, cloud storage, or similar services.
- Internet Infrastructure Services: Internet service providers, domain name registrars, and other infrastructure service providers
- E-commerce Platforms: Online retailers and marketplaces that offer third-party sellers.
- Collaborative Economy Platforms: Platforms providing peer-to-peer services, for example, peer-to-peer ride-hailing or home-sharing platforms
Consequences of Non-Compliance with the DSA
Failure to comply with the Digital Services Act (DSA) can result in serious ramifications for businesses operating in the European Union.
Additionally, businesses face reputational damage from non-compliance, which can result in a loss of customer trust.
Non-compliance can also mean increased regulatory scrutiny and administrative resources, as well as increased compliance costs. Increased regulatory scrutiny can inhibit business activities, as businesses will need to make substantial changes to their business processes and, in some cases, suspend business operations all together.
Difference Between DSA and GDPR
The Digital Services Act (DSA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) are two significant pieces of legislation within the European Union that aim to regulate the digital environment.
However, both of them focus on different aspects and have distinct purposes.
| Aspect | General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) | Digital Services Act (DSA) |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Protects personal data and privacy rights of individuals in the EU. | Regulates digital services to ensure a safer and more transparent online environment. |
| Objective | Ensures stringent data collection, processing, storage, and transfer requirements. | Focuses on content moderation, transparency, and accountability for online platforms. |
| Year of Introduction | Came into effect in 2018. | Proposed in 2020; expected full implementation by 2024. |
| Applicability | Applies to any organization processing the personal data of EU residents, regardless of location. | Targets digital service providers, platforms, and intermediaries operating within the EU. |
| Key Focus | User consent, rights to data access, rectification, and deletion. | Protecting users from harmful content and ensuring fair marketplace practices. |
| Key Provisions | Data Protection Principles: Lawfulness, fairness, transparency, etc.User Rights: Access, rectify, erase, restrict processing, portability, objection. Accountability: Requires DPOs and DPIAs for compliance. | Content Moderation: Detect, remove, and prevent illegal content. Transparency Requirements: Reporting on moderation actions, algorithms, and ads. User Protection: Appeal mechanisms for content removal reporting illegal content. Enhanced Obligations: Stricter rules for very large platforms (VLOPs). |
| Enforcement | Non-compliance can result in fines of up to 4% of global annual turnover. | Penalties for non-compliance can reach up to 6% of global annual turnover. |
The GDPR and DSA both intersect in their goal of ensuring protected users and data; however, while the GDPR focuses on data privacy and protection, the DSA is about regulating content and making platforms responsible for creating a safe digital environment.
Both regulations must be understood and complied with by businesses in the EU. Utilizing both regulations together is a way to meet the rigorous data protection standards and digital service transparency required in the EU.
What is the Digital Service Act Package?
As we continue in the context of the Digital Services Act (DSA), we must recognize that the DSA is only one part of a more extensive legislative program also known as the Digital Services Act Package.
The broader Digital Services Act Package is focused on modernizing the EU’s digital services landscape to create a safe, realistic, and competitive online environment.
How Can Your Business Comply With DSA Regulations?
Ensuring your website or online platform complies with the Digital Services Act (DSA) is crucial for maintaining transparency, accountability, and user trust.
While there are many ways to comply with DSA regulations, the best and most affordable way we recommend is to use legal compliance plugins such as WP Legal Pages.

WP Legal Pages allows you to create comprehensive and customized privacy policies that meet the DSA’s requirements. The plugin allows you to include detailed data collection, usage, sharing, and protection sections. This ensures users are well-informed about managing their data, aligning with the DSA’s emphasis on transparency and user rights.
Additionally, the plugin provides templates for terms and conditions, which can outline the rules and guidelines for using your website. These documents can specify the procedures for content moderation, clearly stating how illegal content is detected, reported, and removed, as mandated by the DSA.
FAQ
The DSA aims to create a safer, transparent digital space by enhancing accountability, protecting user rights, moderating illegal content, and ensuring fair practices among digital service providers and online platforms operating within the EU.
The DSA applies to digital service providers, including online platforms, hosting services, internet infrastructure providers, and very large platforms (VLOPs), as well as small businesses operating within or targeting users in the EU.
Non-compliance can lead to fines of up to 6% of global annual turnover, legal actions, operational disruptions, and reputational damage, severely impacting the business’s financial stability and customer trust.
The DSA focuses on content moderation, transparency, and platform accountability, while the GDPR emphasizes data privacy and protection. Both aim to safeguard users but address distinct aspects of the digital environment.
Conclusion
The EU’s Digital Services Act (DSA) is a transformative regulation that ensures a safer, more transparent digital ecosystem for digital service providers.
Compliance with the DSA regulations is not only essential for your business to avoid significant penalties but also helps build trust and credibility.
Alongside the Digital Markets Act, the DSA reflects the EU’s commitment to creating a fair, secure, and competitive online space.
Further, if you liked this article, you can also consider reading:
- Oregon Consumer Privacy Act: An Overview of OCPA
- Best GDPR WordPress Plugins
- DPIA: An Overview of Data Protection Impact Assessment
Grab the WP Legal Pages and stay complied with all the global laws!
