Consent Management: A Guide to Compliance & Best Practices

Did you know that without proper consent management, your website could face legal fines under GDPR and CCPA?
Each time a website prompts you to accept or decline cookies, does it really matter?
Because of growing concern for user privacy, organizations have a duty to collect, store, and handle user consent by regulations.
GDPR, CCPA, and Quebec Law 25 are a few of the numerous global regulations requiring data collection openness.
This is where a Consent Management Platform (CMP) steps in. One of its roles is to help websites manage cookie consent correctly while ensuring compliance with privacy laws.
This article will explain what a consent manager is, why consent management matters, and how organizations can create a good consent strategy. Read on to discover how to stay compliant and build user trust!
What Is Consent Management?
Consent management involves the acquisition, storage, and handling of the consent of users to gather and process personal information.
This allows organizations to stay in line with global legislation related to privacy, like the GDPR, CCPA, and Quebec’s Law 25, which are transparent regarding which organizations gather and allow individuals to have control over their data.
Among the first things users of the site will notice is typically a pop-up to obtain permission for cookies. Cookie consent is among the most important components of consent management. It enables end-users to accept, refuse, or set preferences on sharing their personal data.
Organizations without a consent management system will be facing hefty fines and would most likely scare users away from trusting them.
To make this process efficient, businesses employ a Consent Management Platform (CMP), which is a system meant to automate and handle user consent in an efficient manner. A consent manager assists websites in tracking user preferences, revising them when necessary, and presenting legally compliant consent banners. It also offers extensive audit logs to establish compliance in case of need.
Thus, consent management is more than just complying with the law; it does contribute to user experience and transparency.
When businesses give the user control of data, they establish trust and credibility. When you have an e-commerce store, a SaaS application, or a website, imposing rigorous adherence to the implementation of a consent management tactic is one form of compliance, and it provides assurance of customer trust.
In an evolving digital age, with a growing cloud of data and privacy legislation, a consent management approach equates to a penalty-free zone and better ethical treatment of users.
Key Principles of Consent Management
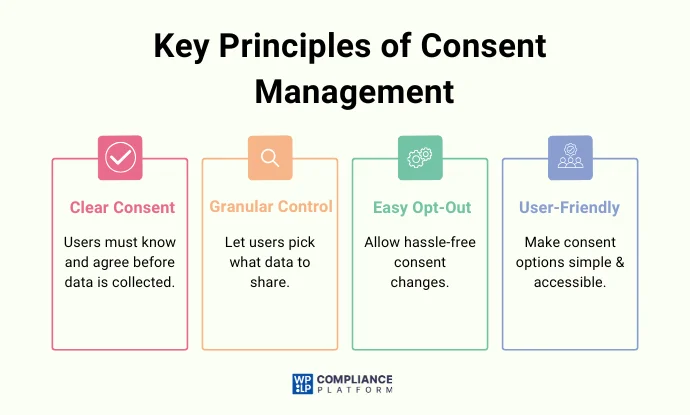
- Explicit & Informed Consent — Users need to be made aware of data collection and explicitly give consent before data about them is processed.
- Granular Consent Choices — Users need to have control over what kinds of data they consent to share and not be forced to choose “all” options.
- Simple Withdrawal of Consent – Users need to be able to alter or withdraw consent whenever they want without hassle.
- User-Centric Interface – Consent banners and preference settings need to be user accessible, readable, and useable.
Adhering to these guidelines, companies can act in accordance with the legislation and maintain user trust.
Why Websites Need Consent Management for Compliance?
Consent management in the modern digital world is not a statement of law but, to a great extent, a gateway to user trust and data openness.
In a situation where GDPR, CCPA, and Law 25 of Quebec are imposing severe regulations, businesses have to conduct proper diligence on the collection, storage, and treatment of user consent; arguably, non-compliance would be too heavy a price in terms of fines, lawsuits, and reputational harm.
On the one hand, it’s the law; on the other hand, handling consent fosters user trust. Businesses that are open regarding the information they collect and how it is processed cause their users to feel more at ease and believe they control their data.
The CMP (consent management platform) comes in handy by allowing organizations to present clear consent notices, manage user settings, and log audit trails that reflect compliance. The second important reason for using a consent manager is to escape monetary fines.
The bodies responsible for enforcing compliance will impose outrageously high fines on organizations that misuse user data. A consent manager can thus help organizations present evidence of compliance with regulatory requirements and mitigate the risk of costly non-compliance lawsuits.
Another great practice is showing users a smooth cookie-consent experience.
The ease of use of a consent tool allows personalized data sharing with full user input, thereby building some level of loyalty and trust.
Effective consent not only fulfills legitimate marketing activities but also favors companies. By gaining informed user consent, a company can gather data legally to perform targeted marketing and deliver personalized experiences without breaching privacy legislation.
This enhances regulatory compliance and produces better marketing efficiencies since the intended audience will be communicated to in terms of permission-based data acquisition.
Data privacy is the buzzword today, organizations that can manage consent competently are seen as being ethical, trustworthy, and free from the risk of regulatory issues. A successful consent policy serves as the platform for lasting success, compliance, and customer satisfaction.
Key Components of Consent Management
Good consent management has several elements to ensure compliance and transparency, which foster data privacy. All the elements, from user consent to secure preferences storage, are crucial.
Let us find out what supports a robust consent management framework.
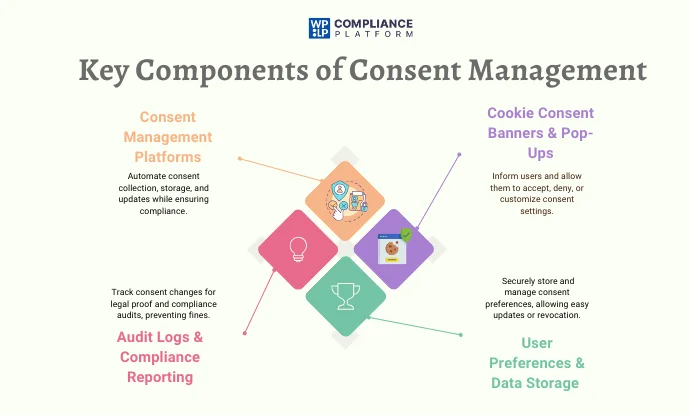
1. Consent Management Platforms (CMPs)
A Consent Management Platform (CMP) is software that can help companies capture, handle, and store user consent regarding data protection legislation.
They automate the consent processes so that sites can easily obtain a sufficient cookie consent notice, log user consent preferences, and modify those consent as needed.
CMPs also integrate into analytics and advertising, handling only permitted data.
2. Cookie Policy Consent Banner & Pop-Ups
Cookie consent pop-ups and banners are the initial interaction points in the consent process.
They inform individuals about how the web will manage their information and give them the choice to accept, deny, or control their settings.
3. User Preference and Data Storage
A fundamental component of consent management is securely storing and handling user consent preferences. A consent manager allows users to refresh or revoke consent when appropriate.
Companies must securely store consent records to be accessible for legal proof and compliance audit purposes. Proper data storage establishes transparency and trust between users.
4. Audit Logs and Compliance Reporting
Such evidence may be required upon audit or within a legal order.
Executing audit logs and compliance reports related to a Consent Management Platform is imperative in determining when and how the users provided, changed, or revoked consent.
These logs will assist the organization in proving compliance with privacy legislation while preventing massive fines due to noncompliance.
These important components provide organizations with a strong consent management system that ensures legal compliance, the best user experience, and long-term trustworthiness.
Privacy Laws and Regulations Governing Consent
With time, new data collection technologies have caused governments worldwide to adopt legislation for businesses dealing with personal data.
Many international and regional privacy laws specify how organizations must collect, use, and safeguard personal data.
Some of the most celebrated data protection laws are:
1. California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) governs the way businesses collect and use customers’ data. Any business, whether located in California or not, has to abide by this law if it sells services or products to California consumers.
One of the most significant features of the CCPA is the right to opt out, preventing businesses from selling personal information. To make it happen, companies need to have a “Do Not Sell My Information” button on their website.
2. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is one of the strictest privacy laws in the world. It is designed to protect individuals’ personal data and privacy rights.
Under the GDPR, people can request the deletion of the data businesses collect.
3. Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados Pessoais (LGPD)
Brazil’s primary data protection law is the Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados Pessoais (LGPD). It provides ten legal reasons for processing personal data and grants nine privacy rights to individuals.
Companies must also perform Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) if requested by Brazil’s data protection authority (ANPD). Additionally, businesses must appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to oversee compliance with the LGPD and guide the company in following the law.
4. Thailand’s Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA)
Thailand introduced the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) to regulate how personal data is collected, used, and shared within the country.
Since taking effect in 2020, this law grants individuals rights over personal data and sets guidelines for organizations and data processors to ensure proper data protection.
The PDPA aims to build public trust and align Thailand’s privacy regulations with global standards.
5. Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA)
Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) is a federal law that oversees how private businesses collect, use, and share personal data.
Enacted in 2000, PIPEDA establishes rules for obtaining consent, limits data use, and protects personal information from unauthorized access.
This law reflects Canada’s effort to balance privacy rights with businesses’ responsibility to handle data securely and ethically.
6. Digital Personal Data Protection Bill 2022 (DPDP)
India’s proposed Digital Personal Data Protection Bill 2022 (DPDP) safeguards individuals’ privacy and regulates how personal data is managed.
The bill focuses on data localization, ensuring data stays within the country, and plans to establish a Data Protection Authority for better oversight. Once implemented, the DPDP will define clear data protection principles and individuals’ rights over their information.
IAB GPP Support: The New CMP Baseline
Modern CMPs are no longer limited to cookie banners. IAB GPP (Global Privacy Platform) support has become essential.
The Interactive Advertising Bureau introduced GPP as a unified framework that allows businesses to manage consent and privacy signals across multiple regulations (GDPR, US state laws, global frameworks) using a single specification.
A CMP with GPP support enables:
- Standardized consent signals for ad tech and analytics vendors
- Better interoperability with advertisers and publishers
- Easier compliance across regions without multiple consent frameworks
Without GPP support, websites may face ad revenue issues, broken consent signals, or non-compliant data sharing.
How to Manage User Consent Effectively with Consent Management Platforms (CMPs)?
A Consent Management Platform (CMP) helps businesses collect, manage, and store user consent for data processing in compliance with global privacy laws like GDPR, CCPA, and LGPD.
These platforms ensure that websites and apps obtain user permission before collecting personal data, giving individuals control over how their information is used.
CMPs display a cookie banner or pop-up when a user visits a website. This banner informs users about data collection and provides options to accept, reject, or customize their consent preferences.
Once users select their preferences, the CMP records and stores the consent data, ensuring compliance with privacy laws.
Features of a CMP
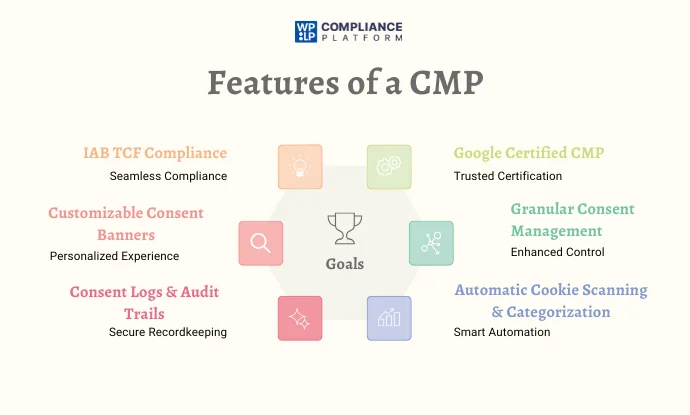
A good CMP offers various features to help businesses comply with privacy regulations and manage user consent effectively. Key features include:
- IAB TCF Compliance – Supports the Interactive Advertising Bureau’s Transparency & Consent Framework (IAB TCF), ensuring seamless compliance with advertising industry standards.
- Google Certified CMP – Some CMPs, like WP Cookie Consent, are Google-certified, allowing publishers to comply with Google’s consent requirements for ad monetization.
- Customizable Consent Banners – This lets businesses tailor cookie banners’ look, feel, and behavior to match their branding.
- Granular Consent Management – Users can selectively enable or disable cookies based on categories like marketing, analytics, and functional cookies.
- Automatic Cookie Scanning & Categorization – Detects and categorizes cookies used on the website, helping businesses stay compliant.
- Multi-Language Support – Ensures compliance across different regions by displaying consent messages in multiple languages.
- Consent Logs & Audit Trails – Keeps a record of user consent, which is essential for regulatory audits and compliance checks.
Integrating a CMP into Your Website/App
Adding a CMP to your website or app is a straightforward process:
- Choose a CMP – Select a CMP that meets your business needs and complies with global regulations.
(WP Cookie Consent is an excellent choice as it is Google-certified and supports IAB TCF 2.2 compliance.) - Install & Configure – If you are using WP Cookie Consent, you can install it as a GDPR WordPress plugin. Customize the banner, consent settings, and cookie categories.
- Enable Auto-Scanning – Allow the CMP to scan and categorize cookies used on your site.
- Publish & Monitor – Once set up, activate the CMP and monitor consent logs to ensure compliance with privacy laws.
Best CMP Tools in the Market
When choosing a Consent Management Platform (CMP), it’s essential to pick one that ensures compliance, is user-friendly, and integrates seamlessly with your website.
Among the top CMPs available, WP Cookie Consent is one of the best solutions, especially for WordPress users.
WP Cookie Consent – The Best CMP for WordPress

WP Cookie Consent is a powerful cookie consent management platform that is Google-certified and designed to help businesses comply with global privacy laws like GDPR, CCPA, LGPD, and more. It ensures that websites collect and manage user consent transparently and legally.
Why Choose WP Cookie Consent?
- Google Certified CMP
- WP Cookie Consent is a Google-certified CMP, meaning it meets Google’s requirements for Consent Mode v2 and works seamlessly with Google Ads, Analytics, and other advertising platforms.
- If you monetize your website using Google Ads, your ads will remain compliant with Google’s ad-serving policies.
- IAB TCF 2.2 Compliance
- It fully supports the Interactive Advertising Bureau’s Transparency & Consent Framework (IAB TCF 2.2), which is essential for websites that engage in digital advertising.
- Ensures advertisers and publishers properly collect and transmit consent signals for programmatic ads.
- Customizable Cookie Banners
- Offers a customizable cookie consent banner that blends with your website’s branding.
- Lets users modify text, design, colors, and layout to match their site’s aesthetics.
- Granular Consent Management
- Allows users to opt in or out of specific cookie categories such as Essential, Analytics, Marketing, and Functional cookies.
- Provides a user-friendly consent preference panel for easy modifications.

- Automatic Cookie Scanning & Categorization
- Automatically scans your website to detect, classify, and categorize cookies, ensuring your cookie policy stays current.
- Saves time by eliminating the need to identify cookies manually.
- Multi-Language Support
- Supports multiple languages, making it easy for websites catering to global audiences to display consent messages in different regions.
- Ensures compliance with privacy laws in various countries.
- Consent Logs & Audit Trails
- Keeps a detailed record of user consent, which is essential for compliance audits.
- It provides transparency by allowing businesses to track when and how users consent.
Why WP Cookie Consent is the Best Choice
- Easy to Set Up & Use – No coding skills required; simple setup within minutes.
- Optimized for Performance – Lightweight and optimized to prevent website slowdowns.
- Regular Updates – Continuously updated to stay compliant with evolving privacy laws.
- Reliable Support – Offers dedicated customer support for setup and troubleshooting.
WP Cookie Consent is one of the best choices if you’re looking for a reliable, feature-rich, and compliant CMP for your WordPress site.
It ensures compliance with global regulations, helps businesses avoid fines, and provides a seamless user experience.
Types of User Consent in Data Privacy
Consent is fundamental to data privacy, ensuring users control how their data is collected and used.
Different types of consent exist based on how users grant permission, each playing a critical role in compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and LGPD.
Explicit vs. Implicit Consent
- Explicit Consent: Users must agree to data collection and processing, usually through a checkbox, signature, or affirmative action.
- Example: A website asking users to check a box before subscribing to a newsletter.
- Regulations: These are required under GDPR for sensitive personal data.
- Implicit Consent: Assumes consent based on a user’s actions, such as continuing to browse a website or using a service.
- Example: If a user continues using a site after seeing a cookie banner, some websites treat this as implied consent.
- Regulations: Some laws (like CCPA) allow implicit consent in specific cases, but GDPR does not consider it valid for personal data processing.
Opt-In vs. Opt-Out Consent
- Opt-In Consent: Users must agree before their data is collected or processed actively.
- Example: A cookie banner that requires users to select preferences before tracking starts.
- Regulations: Common in GDPR-compliant websites.
- Opt-Out Consent: Assumes users agree to data collection unless they specifically decline or request to be excluded.
- Example: Websites that automatically track user data but provide a “Do Not Sell My Information” option (CCPA requirement).
- Regulations: These are used in CCPA and some advertising models where users must opt-out.
First-Party vs. Third-Party Consent
- First-Party Consent: Given directly to the website or service a user interacts with.
- Example: A customer signing up for an email list directly on a company’s website.
- Third-Party Consent: When a user’s data is shared with external parties, such as advertisers or analytics providers.
- Example: A website sharing visitor behavior with an ad network for targeted ads.
- Regulations: GDPR requires websites to disclose third-party data sharing and obtain user consent before tracking.
Challenges in Consent Management
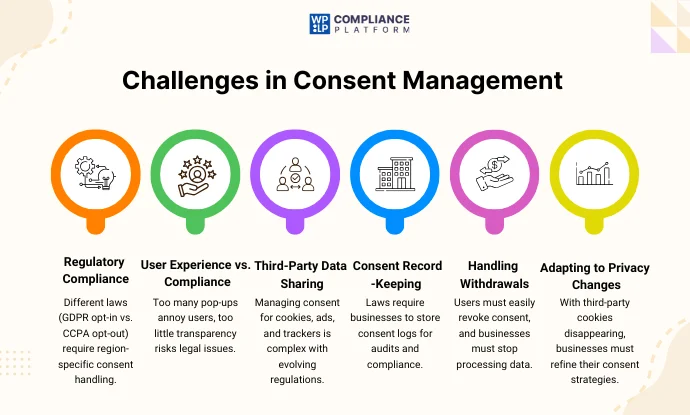
Managing user consent comes with various challenges, especially as privacy regulations evolve and businesses collect more data. Some of the key challenges include:
- Ensuring Compliance with Multiple Regulations
- Countries have different consent rules (e.g., GDPR requires opt-in, while CCPA allows opt-out).
- Businesses operating globally must implement region-specific consent mechanisms.
- User Experience vs. Compliance
- Balancing privacy compliance with a seamless user experience is tricky.
- Excessive consent pop-ups may annoy users, while too little transparency may lead to legal risks.
- Managing Third-Party Data Sharing
- Many websites rely on third-party cookies and advertising networks.
- Managing and obtaining consent for third-party tracking is complex, especially with evolving regulations and browser restrictions.
- Keeping Consent Records for Audits
- Regulations like GDPR require companies to store and manage consent logs as proof of compliance.
- Businesses need automated Consent Management Platforms (CMPs) to track and manage user consent history.
- Handling Consent Withdrawal Requests
- Users can withdraw consent anytime, requiring businesses to stop data processing and remove collected data.
- Organizations must implement easy-to-use consent preference settings for users to update their choices.
- Evolving Technology & Privacy Changes
- With Google phasing out third-party cookies and new privacy laws emerging, businesses must adapt their consent strategies continuously.
How to Overcome These Challenges
- Use a CMP (Consent Management Platform) – Solutions like WP Cookie Consent help businesses automate compliance and simplify consent tracking.
- Regular Compliance Audits – Businesses should frequently review and update their consent policies based on new laws.
- Provide Granular Consent Options – Users can control specific data categories rather than an all-or-nothing approach.
- Clear & Transparent Privacy Policies – Clearly explain how and why data is collected in an easy-to-understand language.
FAQ
Not complying with consent regulations has serious consequences in the form of large fines, lawsuits, and reputational losses. Organizations such as the GDPR (Europe), CCPA (California), and LGPD (Brazil) penalize companies for handling user data ineffectively or for not obtaining valid consent.
The number of times users are asked to provide consent depends on local laws and business practices:
GDPR does not set a strict time frame but suggests periodic renewing of consent (typically 6-12 months) to make sure consent is still effective.
CCPA does not require constant renewal of consent but dictates that companies need to have an opt-out solution for consumers.
When a business changes its privacy policy or collects data in some new way, it has to notify users and seek permission again.
Even small businesses must comply with data privacy laws if they collect or process user data. Even if a business does not directly sell products internationally, it may still receive visitors from regulated regions. A CMP ensures compliance and reduces the risk of fines.
Conclusion
Handling user consent has become an important component for data privacy compliance, enabling businesses to keep user information safe while following other regulations worldwide, such as the GDPR, CCPA, and LGPD.
Being a proper implementation, a Consent Management Platform (CMP) like WP Cookie Consent will cement compliance, enhance user experience and reduce legal risk.
As data privacy laws change quickly, companies need to stay updated on these changes, make periodic reviews of their consent policies, and ensure users enjoy sufficient controls of their data. Investing in the right tools will assure compliance and help build customer trust and credibility.
If you like this article, you might also like:
- Best GDPR WordPress Plugins
- Top GDPR-Compliant WordPress Themes For Your Website
- What is GDPR Data Minimization and How to Do It?
Need a reliable Consent Management Platform? WPLP helps you automate GDPR & CCPA compliance effortlessly. Get Cookie Consent Today
