Texas Data Privacy and Security Act (TDPSA): A Quick Summary

Summary
Non-compliance can result in fines up to $7,500 per violation. Businesses must update privacy policies and cookie consent banners to stay compliant. Tools like WP Legal Pages simplify compliance.
Does your business comply with the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act (TDPSA)?
The TDPSA will modify how you manage consumer data to align with the stricter privacy laws of other states.
With growing concerns about privacy and consumer rights, it is imperative for every business operating in the state to understand what the TDPSA law entails.
But how does it compare with other U.S. data privacy laws? And what does it mean for consumers?
Let’s look at the primary factors regarding the Texas regulation and how it affects businesses.
- What is The Texas Data Privacy and Security Act (TDPSA)
- Who Must Comply With the Texas Data Privacy Act?
- What Are The Consumer Rights Under TDPSA Law
- How Businesses Can Comply With TDPSA Regulations
- Other Unique Provisions in The Texas Privacy Law
- TDPSA Penalties and Fines for Non-Compliance
- FAQ
- Conclusion
What is The Texas Data Privacy and Security Act (TDPSA)
The Texas Data Privacy and Security Act (TDPSA) is designed to provide consumer protection by imposing specific obligations on businesses and by granting consumers certain data-related privacy rights.
The TDPSA was signed into law on June 18, 2023, and became effective on July 1, 2024. However, the universal opt-out mechanisms will come into force six months later, on January 1, 2025.
With California, the largest-population state and the first in the nation to enact a state-level privacy, Texas now becomes the second most populous state with a similar data privacy act.
The TDPSA establishes conventions concerning the collection, use, processing, and handling of consumers’ data. Businesses subject to the Act that fail to comply with any provision of the Act are liable to civil penalties.
The TDPSA is modeled after other contemporary privacy laws, especially after the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act. It seeks to protect Texas residents’ privacy and personal data rights while restricting companies’ use of that data.
The Texas Privacy Act grants residents various recognized data privacy rights, including, but not limited to, the following:
- Confirmation of whether a controller and access to that data are processing their personal data.
- Correction of inaccuracies in their personal data.
- Erasure of personal data in relation to them.
- Obtain a copy of their personal data in a format that is technically feasible and easy to use.
- Opt-out from processing of personal data for purposes of targeted advertising, sale of personal data, or profiling.
The TDPSA officially became effective on July 1, 2024, but the provisions relating to global opt-out technology came into force on January 1, 2025. Accordingly, businesses are now required to recognize universal opt-out signals, including the Global Privacy Control, thus enhancing the consumer’s power over their data privacy.
Who Must Comply With the Texas Data Privacy Act?
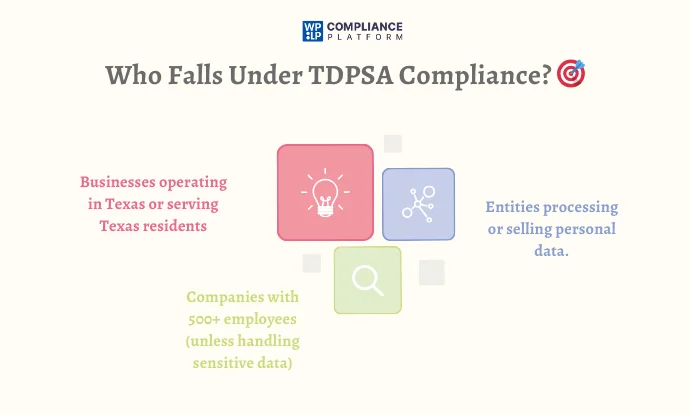
As per Sec. 541.002 in the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act (TDPSA), your business is bound to follow this Act if it meets any of the following requirements:
- Conducting business in Texas or producing goods or services consumed by residents of the state.
- Processing or selling personal data.
- It is not a small business according to the definition of the United States Small Business Administration (SBA)—i.e., it should have less than 500 employees unless the business sells sensitive personal data.
This unique legal scope is distinct from the other data privacy laws in the U.S., which have traditionally relied primarily on specific monetary and data processing thresholds.
What Are The Consumer Rights Under TDPSA Law
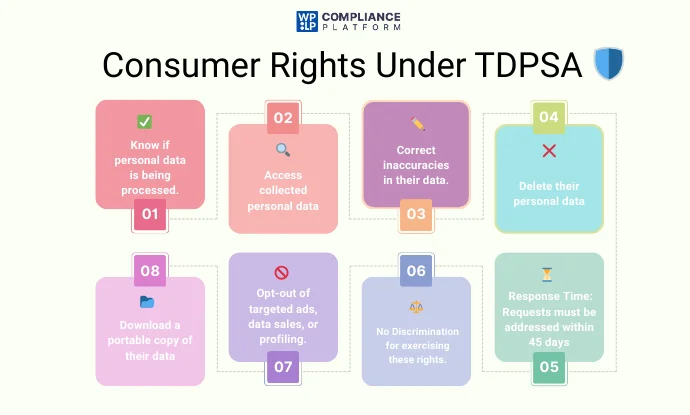
Under the TDPSA, consumers can request controllers at any time to exercise their rights actively. A legal guardian may duly make requests on behalf of a well-recognized child as per 541.051 the law.
Rights available for consumers to submit requests include:
- To check if a controller is processing personal data
- To get access to the personal data collected about them
- To rectify inaccuracies in their data, given the accuracy of the data and the purpose of its processing
- To have the data provided by or about the consumer removed
- To get a portable copy of their data when it is in a digital form
They are also entitled to protection from discrimination and to opt out of the processing of their data for targeted advertising, sale, or profiling.
Authenticated consumer requests are to be complied with promptly and within 45 days, with the possibility of extending the time further.
How Businesses Can Comply With TDPSA Regulations
For TDPSA compliance, the website should have a privacy policy and cookie consent banner to meet TDPSA requirements.
Businesses can comply with Texas data privacy law in the following ways.
1. Privacy Policy
First, a privacy policy should be generated that covers the legal requirements contained by the law. If you already have a privacy policy, you should ensure it is updated.
You can use a privacy policy generator like the WP Legal Pages plugin to create a privacy policy for your website. This plugin will also help you create other policies for your website.

2. Cookie Consent Banner
You should also update or generate your cookie policy and include opt-out options when configuring your cookie consent banner. If you use cookies for targeted advertising, Texas consumers have the right to withdraw their consent for such data processing.
You must also start collecting user consent if you are collecting sensitive data.
3. Requests for Data Subject Access
To provide your Texas consumers with a suitable means to exercise their privacy rights, create a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR or SAR) form on your platform. Remember to link it to your privacy policy.
Using a Consent Management Platform, such as the WP Cookie Consent Plugin, can assist your website in meeting opt-in and opt-out obligations as well as handling requests for Data Subject Access.

4. Data Processing Agreement
Depending upon your role and the type of data you process, the performance of data protection assessments may be required.
If you share the information with others or rely on a third-party data processor, you should also create contracts meeting all TDPSA guidelines.
Other Unique Provisions in The Texas Privacy Law
The TDPSA is still deemed more business-friendly than privacy legislation in other states, such as California, Virginia, and Connecticut.
Many of these requirements require companies or entities selling sensitive or biometric information to add the following words: “NOTICE: We may sell your sensitive (or biometric) personal data.” This notice must be attached to the exact location, like the privacy notice.
In addition, businesses that sell personal data for targeted advertising must make additional disclosures and provide an opt-out provision for consumers about selling their data.
There is much more similarity between this act and Virginia’s privacy act than between Texas law and the California Privacy Rights Act. Still, in terms of defining the sale of personal data, the Texas Act is more in line with the California Privacy Rights Act than Virginia’s privacy law.
The act defines sale as “sharing, disclosing, or transferring personal data for monetary or other valuable consideration by the controller to a third party.”
The trait ‘controller’ thereby applies to every entity conducting business in the state and processing or selling personal data except for specifically exempted entities.
TDPSA Penalties and Fines for Non-Compliance
The Texas Personal Data Security Act (TDPSA), like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), does not give the consumer a cause of action against the violators. Enforcement is the sole business of the Texas Attorney General. Also, as contained in section 541.155, TDPSA permits businesses to remediate violations within 30 days of penalization.
- Penalties and Fines of TDPSA for Non-Compliance: Noncompliance with TDPSA entails serious legal and financial consequences:
- Cure Period of 30 Days: Companies are given 30 days to remedy violations before penalties apply.
- Civil Penalties: Organizations may be fined up to $7,500 per violation.
- Injunctions & Restaining orders: It empowers the Attorney General to seek court orders to stop the violation.
- Legal Fees: These could require businesses to pay the costs incurred from the Attorney General’s fees and investigations.
The Attorney General could undertake the above actions:
- Recovery of civil penalty.
- Restraining or enjoining the person from breaching the TDPSA.
- Seek injunctive relief.
- Recover attorney’s fees and all reasonable expenses incurred in the investigation.
Consumers covered by this law do not have a private right of action.
FAQ
TDPSA means Texas Data Privacy and Security Act. This act is a data privacy law for business owners for collecting, storing, and processing consumer data online.
TDPSA law or TDPSA compliance applies to any business that conducts business in Texas or collects, uses, sells, shares, or analyzes consumer personal data online.
Under Texas privacy law (TDPSA), if a business is seen as noncompliant, the business might face hefty fines from the government. Civil penalties of up to $7,500 per violation can be faced for non-compliance.
To comply with the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act (TDPSA law), Businesses must provide transparency, obtain consumer consent for sensitive data, and use a reliable compliance platform that provides privacy policy and consent management solutions all in one place. WP Legal Pages compliance Platform is best for business for TDPSA compliance.
Conclusion
To ensure your business complies with the Texas Data Privacy and Security Act, you must update or create your privacy policy and include opt-out options on its cookie consent banner displayed on your website.
Additionally, you must follow and maintain contractual obligations to work with third-party data processors. Lastly, a tool should be used to honor consumer requests for universal opt-out.
You could do it all by yourself and deal with the hassle — or save time by using the WP Legal Pages Compliance Platform, which includes our Privacy Policy Generator and Consent Management tools.
If you like this article, you might also like:
- Florida Digital Bill of Rights (FDBR) — A Complete Guide
- Oregon Consumer Privacy Act: An Overview of OCPA
- American Privacy Rights Act (APRA)
Are you looking to process your cookie data automatically? Grab the WP Legal Pages Compliance Platform for easy operations!
