What Are Functional Cookies? Definition & Examples

Curious about the role functional cookies have in your website?
Cookies expedite modern websites’ functionalities and user experience. Functional cookies, as a group of cookies, are essential in making sure websites function and provide users with an optimal user experience.
However, with privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA evolving quickly, knowing how to manage functional cookies has never been more important.
Functional cookies can provide a smoother and tailored experience by remembering user choices like language, logged-in user, and even website-specific configurations.
While functional cookies are a convenience, they create unique privacy and data use issues.
In this guide, we will look at functional cookies in full light and give you actionable advice on how to use functional cookies and manage them in consideration of privacy regulations worldwide.
- What Are Cookies?
- What Are Functional Cookies?
- Advantages of Functional Cookies
- How Do Functional Cookies Work?
- Global Laws That Affect Functional Cookies
- 1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – European Union
- 2. California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) – United States
- 3. ePrivacy Directive (Cookie Law) – European Union
- 4. Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados (LGPD) – Brazil
- 5. Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) – Canada
- 6. Data Protection Laws in Other Regions
- Do You Need Consent to Use Functional Cookies?
- Manage GDPR Functional Cookies With WP Cookie Consent
- FAQ
- Conclusion
What Are Cookies?
Cookies are small text files that are stored on a user’s device by websites. These cookies are made to remember information about a user and aspects of their experience on the site. Experiencing such as logging in, user preferences, and previous activity, so that the user’s experience is easier and better on subsequent visits.
Cookies can perform a variety of functions, and can be categorized in a variety of ways, such as:
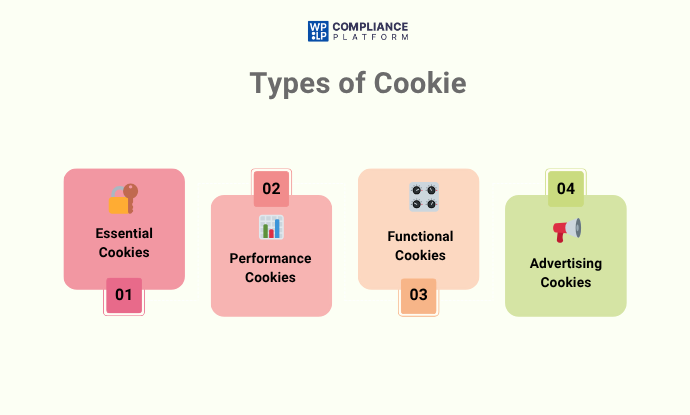
- Essential Cookies: Cookies that are necessary to help the basic function of a website. For example, enabling secure and authenticated user logins and processing transactions.
- Performance Cookies: Cookies that collect data to help website owners understand how a new user is interacting with the site. Although these cookies are often used for analytics, many website owners may elect not to use the data for analysis.
- Advertising Cookies: Cookies that can be used for marketing purposes, as well as tracking preferences across sites.
- Functional Cookies: These cookies help the user by remembering preferences, such as controlling a language selection or theme selection, so that a user’s experience is more customized.
By categorizing cookies by their function and remembering that they serve various purposes, the website owner can better understand the functionalities of different types of cookies and how to comply with global privacy regulations.
What Are Functional Cookies?
Functional cookies provide a way for websites to remember information about users’ preferences, choices, and settings for a more effective user experience.
Unlike essential cookies that are critical to the basic functions of a website, functional cookies provide an enhanced, smooth, and personalized interaction with the website.
Functional Cookies Compared to Other Cookies
Below is a comparison table of functional cookies compared to other types of cookies:
| Cookie Type | Purpose | Examples | Requires Consent? |
| Essential Cookies | Essential for core functions of sites such as security, Authentication, navigation, etc. | Session handling, secure login, and checkout operations. | No, they are essential for the website to function. |
| Performance Cookies | Collect data around user behaviour to improve the performance of the website. | Analyzing page load times, click tracking, and heat and mouse maps. | Yes, under GDPR and other relevant EU legislations. |
| Advertising Cookies | Track user behavior in order to serve targeted ads and measure their impact. | User segmentation in retargeting ads for campaigns. | Yes, it always requires the consent of the user. |
| Functional Cookies | Facilitate usability by remembering user preferences and settings. | User language preferences, shopping cart items, and their selected, customized theme or layout. | Yes, unless the feature is requested explicitly by the user (i.e, selecting their language preference) |
This table illustrates the nature of functional cookies and how they vary from other functional cookie types by providing another layer to usability and personalization functionality, as opposed to the critical operational requirements of essential cookies or analytics cookies.
Advantages of Functional Cookies
Functional cookies offer a variety of advantages that improve user experience as well as website functionality. Below are the most important benefits:
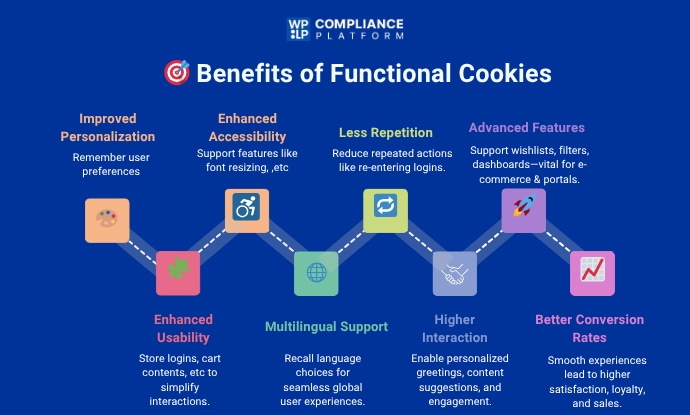
- Improved Personalization: Functional cookies enable websites to recall user-specific preferences like language settings, currency options, or preferred layouts. This makes for a more personalized and interactive user experience, so users feel that they belong to the website.
- Enhanced Usability: These cookies facilitate interactions by allowing features such as storing login information, remembering shopping cart contents, or keeping form input. Users have an easier time accessing websites without the need to re-perform actions.
- Enhanced Accessibility: Functional cookies aid accessibility features such as font size changes, high-contrast modes, or choosing alternate navigation means. Enhancements make websites more accessible for people with varying needs.
- Effective Multilingual Support: For global-user websites, functional cookies assist in remembering users’ language preference, so they do not need to choose the language each time they visit.
- Decrease in Repetitive Activities: Storing user-specific information, functional cookies reduce repetitive activities such as asking users to enter login details or location preferences repeatedly. It enhances overall satisfaction and reduces time.
- Higher Interaction: Functional cookies promote user interaction through dynamic content suggestion, personalized salutations, and other interactive aspects customized for specific users.
- Facilitation of Advanced Functionality: Functional cookies allow advanced website features such as wishlist saving, content filtering, and user dashboards. These provide immense value to e-commerce sites, educational portals, and customized services.
- Better Conversion Rates: Functional cookies, by ensuring a smooth and pleasurable browsing experience, can have a positive impact on user behavior, resulting in increased conversions, repeated visits, and loyalty from customers.
They fill the gap between bare usability and a tailored, high-quality user experience. They are critical for companies looking to keep users coming back, increase engagement, and be competitive in an ocean of web space.
How Do Functional Cookies Work?
Functional cookies save little bits of data on a user’s device that can be accessed by the website every time a user initiates a new interaction with the website. The purpose of a functional cookie is to make a user’s experience on the website, allowing the user to easily and effectively interact with the website.
Functional cookies are typically initiated by the user’s action or explicit choice and not just a method to track users for advertising.
Here is a detailed explanation of how functional cookies work:
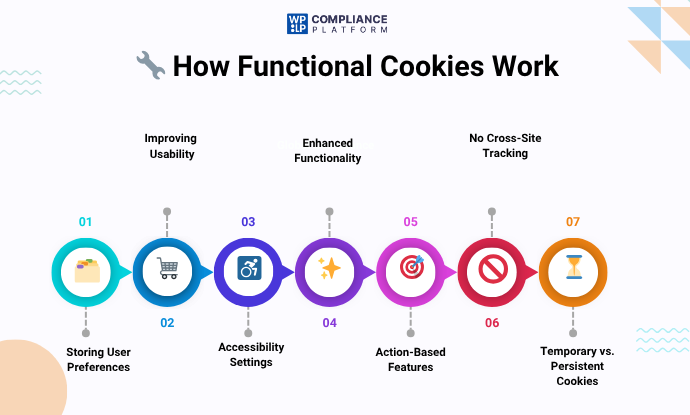
1. Storing user options
Functional cookies can store user selections (for example, language preferences, bookmarks, theme preferences, or currency preferences). When a user returns to the same website, the website can retrieve user options accordingly and provide an outcome the user would expect.
For example: A person visits an e-commerce site and selects English as the language and USD as the preferred currency. The functional cookie stores this selection as a functional cookie, so the person will not have to select their options during their future visits.
2. Improving usability
One of the purposes of these cookies is to improve the user’s actions by providing functions that remember login and password information, retain items in the shopping cart, and remember the whole or parts of the completed form.
For example: If a person adds products to the cart and navigates from the site without checking out, the functional cookies will keep the cart if the person returns, which will allow the person to continue where they left off rather than starting all over again.
3. Accessibility settings
Functional cookies are also necessary to establish accessibility settings with cookies that will also remember selection options such as larger text size, high contrast mode, and user voice assistance.
For example: A visitor who is visually impaired changes the overall site look by changing contrast and font size, then a functional cookie would hold that visual adjustment in place when that user returns.
4. Enhancements to functionality
Many websites offer features that, when supported by functional cookies, allow for better functionality to enhance the overall experience. For example:
- Holding a wishlist/favorites.
- Holding filters (ex., price, product types).
- Providing individual personalized dashboards of previously viewed items.
For example: A learning platform may have functional cookies that provide users with a list of courses they previously viewed.
5. User Actions and Features
Functional cookies are intended to link specific user actions when on the site, with functional aspects of that site. These cookies will not collect user personal data other than what is necessary to support any intended features.
For example: A user enables dark mode while browsing a site, and the functional cookie recalls that preference to provide the dark mode design on subsequent browsing days.
6. No Tracking of Non-Personalized Data
Functional cookies are not able to track the use, like advertising cookies, across sites. The general design of functional cookies only sets out to enhance the function of each site for a logged-in user.
For example: A content site allows a user to designate the news sections they want to view while they are on the site. The same user, upon logging back in, will see their selected news sections.
7. Temporary Cookies vs. Persistent Cookies
Functional cookies can be either:
- Temporary (session-based): Deleted when the user leaves the browser.
- Persistent: Stored on the user’s device for longer and can ensure preferences are also remembered over time.
For example: A session-based cookie might track a user’s actions during a shopping session while a persistent cookie may track login information for weeks.
Technical Functionality
Functional cookies are retained via browser-based storage technology. A cookie is created and sent to the user’s machine by the site server, and the browser uses this information to store and retrieve the cookie based on future activity.
- Setting a cookie: When the user acknowledges an option, the website sets the cookie to store the option.
- Retrieving a cookie: When the user revisits the site, the cookie is stored by the browser and will be sent back to the server. The server will read the cookie to customize the user’s experience.
Functional cookies may use JavaScript or server-side scripting to make the process more efficient.
Functional cookies are an essential aspect of modern web experiences, allowing a website to cater to users’ individual preferences and provide a seamless experience online.
However, the use of functional cookies must be done within the privacy regulations in the world, and usually that is done with informed consent from the user. Balancing compliance and user preferences is key.
Global Laws That Affect Functional Cookies
Functional cookies are necessary to improve user experience, but they are governed by numerous privacy legislations around the world.
Privacy legislation views cookies as a means to protect and promote the privacy of users, which means privacy legislation focuses on managing cookies to offer privacy protection, transparency, and ensure that users have the power to allow or deny how information is collected and stored.
Here’s an in-depth look at the major laws affecting the use of functional cookies:

1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) – European Union
The GDPR has applications in the European Union and other parts of the global landscape because it is one of the most comprehensive pieces of privacy legislation in the world.
It contains restrictions on cookies (and functional uses of cookies) by requiring that information used relating to the user’s information is presented clearly and appropriately.
Major provisions that apply to functional cookies:
- Consent: Functional cookies are characterized as non-essential under the GDPR, therefore, consent has to be given by the user in order for those to turn on. Cookies that relate to basic site functionality are exempt from this requirement.
- Transparency Requirements: Website owners have to provide an explanation of functional cookies to users in the form of a cookie policy.
- What do the cookies do?
- What data do the cookies collect?
- For how long will the cookies be in effect?
- Withdrawal of consent of the user: When a website uses functional cookies to store user preferences for dark mode or which language they want, consent of the user must be obtained to store these cookies.
2. California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) – United States
The CCPA is a comprehensive privacy law providing California residents with rights to their data. Although its core focus includes matters of transparency and opting out, it can also impact functional cookies taking personal data into account.
Important Provisions Related to Functional Cookies:
- Right to Know – websites need to tell users when they are using cookies, including functional cookies, as well as what type of data is being collected.
- Right to Opt-Out – if functional cookies collect personal data, users must have the ability to opt out of them.
- Broad Definition of Personal Data – any data that ties back to an individual, including their preferences stored in functional cookies, fall within the definition of personal data under CCPA.
Example: A functional cookie that saves the user’s preferred currency on an e-commerce site may be classified as personal data under the criterion that it remembers that preference for that user.
3. ePrivacy Directive (Cookie Law) – European Union
The ePrivacy Directive (also known as the “Cookie Law”) builds upon GDPR by providing an explicit focus on electronic communications and cookies.
Key Provisions Pertaining to Functional Cookies:
- Prior Consent: Prior informed consent will be required for functional cookies, unless the cookie is absolutely necessary to provide a service at the request of the user.
- Aligned with GDPR: The ePrivacy Directive is consistent with the GDPR but emphasizes cookie-specific requirements, including the following:
- Mechanisms of consent for non-essential cookies.
- Communicating to users that cookies are being used and how they are being used.
For instance, a website providing multi-language options does not need to receive consent from users for a cookie to remember language settings.
4. Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados (LGPD) – Brazil
The Brazilian LGPD contains many query aspects of the GDPR and applies to those residing in Brazil. LGPD has a strong emphasis on transparency and allowing individuals to control their personal data collected through cookies.
Key Provisions Related to Functional Cookies:
- Consent: Functional cookies that collect personal data need to have user consent.
- User Rights: Brazilian users have the right to know how and what is done with their data, and to have it erased.
- Data Minimization: Websites should only collect the amount necessary to carry out a function.
For Example: A functional cookie that saves preferences for a user’s order on a Brazilian e-commerce site will need to comply with LGPD from an aspect of consent and transparency.
5. Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) – Canada
PIPEDA regulates the collection, use, and disclosure of personal information in Canada. While it does not define the term cookies, its principles apply to the functional cookies that process personal data.
Key Provisions Relevant to Functional Cookies:
- Implied Consent: PIPEDA could allow implied consent to the collection of non-sensitive data where consumers are sufficiently informed and afforded a right to choose not to provide their consent.
- Accountability: Organizations should have a procedure in place to manage a functional cookie’s compliance with PIPEDA’s principles.
Example: A functional cookie that stores a user’s preferred layout on a Canadian news website is likely implied consent if adequately disclosed in the context and the data is non-sensitive.
6. Data Protection Laws in Other Regions
- Australia (Privacy Act): Functional cookies that are used and that collect personal information, require compliance with the Australian Privacy Principles, emphasizing transparency and control for the user and consumer.
- India (Proposed Data Protection Bill): India’s emerging data privacy DPDP is likely to impose more duties and restrictions in terms of consent and storing data, not limited to functional cookies.
- South Africa (POPIA): The Protection of Personal Information Act, POPIA, requires the operator of the organisation’s website to notify users when cookies are employed, with a user opt-in thereafter.
Global privacy laws are constantly changing, making it imperative for businesses to stay on top of them and be ahead of changes in the laws. With the knowledge of privacy laws and regulations, website owners can remain lawful and build trust with their users on their websites.
Do You Need Consent to Use Functional Cookies?
The basic issue is whether these cookies process personal data or do something more than the functionality that is requested only by the user.
Consent Requirements by Region:
1. GDPR (European Union)
In most cases, consent is required for functional cookies unless they are strictly necessary to deliver a service explicitly requested by the user (for example, saving cart items in an online store during an active shopping session).
Websites must:
Disclose the use of functional cookies in their cookie banners.
Obtain explicit user consent before enabling those cookies.
Make the privacy policy reflect what functional cookies do, what data they store, and how a user can manage their consent.
2. CCPA (California)
Functional cookies are a type of “personal information” if they retain user preferences or actions that can be linked to identifiable people.
While consent is not an explicit requirement, users must be able to opt out whenever their data is being sold or shared.
3. ePrivacy Directive (EU)
Requires that users are given informed prior consent, unless the functional cookies are “strictly necessary” for a service requested by the user.
4. LGPD (Brazil)
This regulation, like the GDPR, states that transparency and consent must be acquired when functional cookies involve the processing of any personal data.
5. More Regions
Other countries, such as Canada (PIPEDA) and Australia, may require transparency and, in some instances, implied or explicit consent for functional cookies.
Manage GDPR Functional Cookies With WP Cookie Consent
Maintaining compliance and usability with GDPR functional cookies can be a challenge, especially given ever-changing privacy laws. The WP Cookie Consent plugin was created so that WordPress website owners can manage functional cookies conveniently and responsibly.

Key Features of WP Cookie Consent:
- Customisable Cookie Banners: User-friendly banners that clearly communicate the use of functional cookies can be created. Designs can be customised to your site branding for a seamless experience.
- Granular Cookie Settings: Users can switch functional cookies on and off, independently of other cookie categories (i.e, performance cookies, advertising cookies). The user experience and understanding can be simplified by breaking cookie categories down.
- Multi-Language Options: Automatically detect user location for cookie consent banners and have them displayed in the preferred language. Great for merchants with international audiences.
- Consent Tracking: Protocols to keep detailed records of user consents so you can demonstrate compliance in an audit. Offline reporting to track overall cookie consent activity for the admin.
- Automatic Cookie Blocking: Block functional cookies until consent is acquired. To comply with regulations like GDPR and the ePrivacy Directive, a website is unable to employ functional cookies prior to consent.
- Integration With Other Tools: WP Cookie Consent can easily be integrated with other analytics or third-party tools for full cookie management.
By leveraging WP Cookie Consent, you can balance enhancing user experience and ensuring legal compliance.
FAQ
Functional cookies are browser cookies designed to improve website usability by remembering user preferences and settings, such as language selection, theme choices, and shopping cart contents.
Yes, consent is required in most jurisdictions, including the EU (under GDPR) and other regions with robust data privacy laws, unless the user explicitly requests the functionality.
Essential cookies are necessary for a website’s core operations, such as security and session management. On the other hand, functional cookies enhance usability and user experience but are not mandatory for website operation.
Functional cookies can store personal data, such as preferences linked to a user profile or device. This is why many privacy laws require transparency and user consent for their use.
Non-compliance with cookie laws can lead to fines, reputational damage, and loss of user trust. Adopting compliance tools like WP Cookie Consent can help mitigate these risks.
Conclusion
Functional cookies are crucial for producing customized, user-friendly, and accessible websites. They are important from an instrumental perspective when it comes to improving user experience, but their use of must also comply with global privacy laws.
When website owners know the distinctions in functional cookies (and the value that they offer), and can even manage them with tools like WP Cookie Consent, it is possible for website owners to provide a smooth browsing experience without worrying about legal issues.
Moving into the future, in 2025 and beyond, cookie compliance will continue to be complex but should be a key benefit of an ethical website.
If you liked this article, you can also consider reading:
- What Is Privacy Management and Why Is It Important?
- Top CCPA Fines for Non-Compliance: Key Cases and How to Avoid Penalties
- What is the EU’s Digital Services Act (DSA)?
Want to stay compliant while offering a great user experience? Try WP Cookie Consent today.
