How to Master GDPR Data Minimization & Stay Compliant
Have you found yourself questioning what exactly GDPR data minimization means and why it matters to you as a company?
We live in a world driven by data. This has led organizations to collect huge amounts of personal information, especially in efforts to improve services or grow a business. With lots of information comes a lot of responsibility under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
One of the core principles of GDPR is data minimization. This principle is critical in protecting people’s privacy. However, it can also minimize the risk of data breaches and improve overall compliance.
Through this blog, we will explore what GDPR data minimization means, why it is important when considering ethical data practices, and some actionable steps to help you implement it in your organization.
Regardless of whether you are a business owner, data protection officer, or privacy-minded professional, principles of data minimization are essential to building trust and ensuring compliance.
- What is GDPR Data Minimization?
- The Role of Data Minimisation in GDPR Compliance
- Benefits of Data Minimization
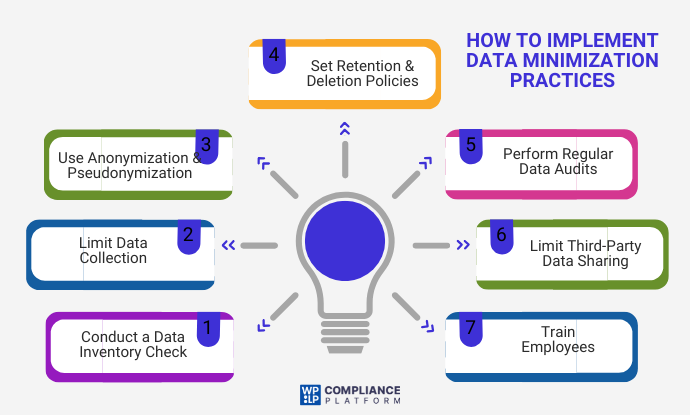
- How to Implement Data Minimization Practices
- Step 1: Conduct a Data Inventory Check
- Step 2: Limit Data Collection to What Is Necessary
- Step 3: Incorporating Data Anonymization and Pseudonymization Methods
- Step 4: Apply a Data Retention and Deletion Policy
- Step 5: Regular Data Audits and Reviews
- Step 6: Review and Limit Data Sharing with Third Parties
- Step 7: Employee Training and Awareness
- Data Minimization Tool
- FAQ
- Conclusion
What is GDPR Data Minimization?
GDPR data minimization is one of the original General Data Protection Regulation‘s main principles, which sets the value of only collecting and processing individuals’ personal data to serve a precise goal, and only as much of it as needed to do so. Article 5(1)(c) of the GDPR requires that personal data be:
- Adequate: The data is adequate for the purpose for which you are collecting it.
- Relevant: Information that is pertinent to the reason you are gathering it.
- Limited:The amount of data being gathered is confined to what is needed to attain the purpose.
This rule is crucial to organizations as it assists in ensuring that they respect the privacy of people by not gathering more personal information than required. For example, it minimizes the dangers of gathering personal information in general, e.g., data breaches or the possibility of a fine for non-adherence, by not having to deal with personal data records whatsoever.
Take an example of required data collection through an e-commerce site; if they are collecting personal information for the purpose of order processing, it could involve a customer’s name, address, and payment details. But it would not be necessary to collect a customer’s age.
Key Principles of GDPR Data Minimization
In order to comply with the data minimization requirements of the GDPR, organizations should focus on the following fundamental principles:
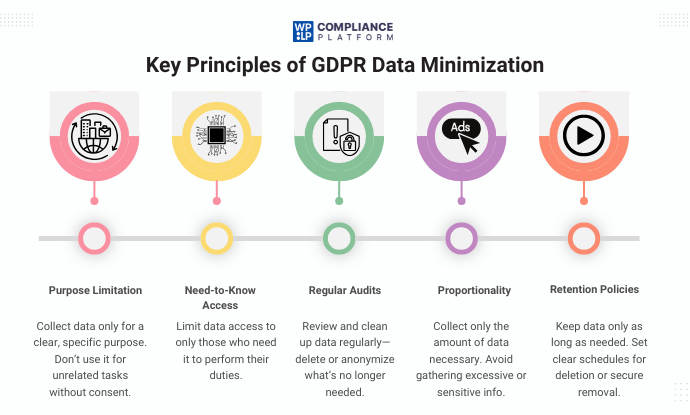
- Purpose Limitation: Establish a purpose for collecting the data and collect only what is required to fulfill that purpose. Do not repurpose data for unrelated activities without proper consent.
- Need-to-Know Basis: Restrict access to workers or systems that only need it to perform one or more specific tasks, reducing the exposure of personal data to risks.
- Regular Audits: Regularly examine the data one collects and processes, and delete or anonymize data that is no longer necessary or relevant.
- Proportionality: Always ensure that the extent and detail of data collected are appropriate to the purpose. It is poor practice to over-collect sensitive or unnecessary information.
- Retention Policies: Establish clear retention schedules regarding personal data. Only hold onto data for as long as it is required for its intended purpose, and after you have delivered the purpose, remove it securely.
How Data Minimization Aligns with GDPR Compliance
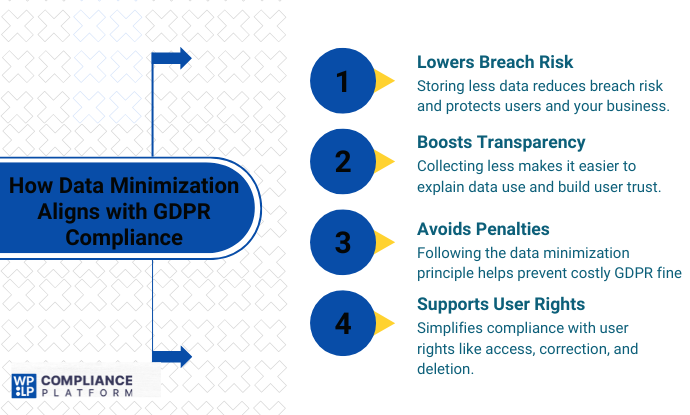
Applying data minimization is part of becoming and staying compliant with the GDPR, and here’s why:
- Decreasing Data Breach Risk: Storing only the data that is required means that you are decreasing the sensitive information at risk in case of a data breach, helping to keep your organization and individuals safe.
- Enhancing Transparency: When your organisation’s collection of data is reduced, it becomes simpler to be open with users about the use of their data, as well as establishing trust with people and proving accountability.
- Reducing Fines and Penalties: If your organisation is failing to follow the data minimisation principle, it can result in heavy fines. Demonstrating compliance with this principle reduces the risk of regulatory inquiry.
- Enhancing Data Subject Rights: Incorporating data minimisation into practice will naturally assist organisations in meeting GDPR requirements under data subject rights, such as access, rectification, and erasure.
Incorporating data minimisation into your organisation’s activities gives the right to comply with the GDPR, and promotes a more ethical and privacy-conscious organisation.
The Role of Data Minimisation in GDPR Compliance
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a revolutionary regulation that protects personal data and privacy for individuals in the EU. Data minimization is an important principle to comply with under the GDPR.
This requirement means organizations must collect, process, and store only the data that is relevant and necessary to carry out a specific purpose. In keeping with this requirement, organizations can fulfill their regulatory requirements, build trust with their customers, and take away several risks while processing any data.
How GDPR Data Minimization Reduces Legal Risks
Promoting data minimization will reduce legal and financial risk. Less data equals less risk. When organizations limit what data they collect, they also limit their chance of processing data that is irrelevant or unnecessary, which is probably also non-compliant.
Data minimization strategies should also reduce an organization’s surface in the event of a breach as well. The less data an organization collects, the less data it exposes. Finally, data minimization eases compliance as well.
When some data is no longer in the stream of co-mingling data, it becomes easier for organizations to maintain accuracy, security, and ongoing permissible legal processing of any remaining data.
This minimizes the possibility of regulatory scrutiny, penalties, and reputational harm with regard to insufficiently protecting personal data. Also, not collecting information when not needed shows respect for individual privacy and may cultivate customer trust and loyalty.
As an example, an online retailer generally needs the customer’s name, shipping address, and payment information to complete an order.
Collecting other information, such as date of birth or personal interests, without a legitimate and legally permissible purpose, may contravene the data minimization principle and expose the company to compliance risks.
Consequences of Failing to Implement Data Minimization
The ramifications for not following data minimization principles can be catastrophic under the GDPR. Non-compliance with the GDPR includes administrative monetary penalties of up to €20 million, or 4% of the organization’s worldwide turnover, whichever is higher. There are also reputational implications, in addition to economic implications.
Organizations that fail to preserve customer data jeopardize stakeholder trust, which undermines customers’ confidence in those stakeholders, which may disproportionately cause all lost business. Beyond this, gathering excessive unnecessary data increases the chances of a data breach, which can have devastating consequences in the form of federal and/or civil penalties, fines, and/or attorney fees.
If a breach occurs and that organization continues to have excessive data retention, the organization may face additional ramifications if they are unable to demonstrate justification for possession of certain data in the first place.
Additionally, if there were no data minimization concepts in place, it may be far more difficult for that organization to comply with a data subject request, such as an erasure or access request, and to answer/comply as timely as possible, without further complicating the matter.
Benefits of Data Minimization
Data minimization has various benefits for organizations, from elevating privacy protection to developing customer trust. By only collecting and processing relevant information, organizations can also improve efficiency, all while demonstrating a serious commitment to protecting personal data.
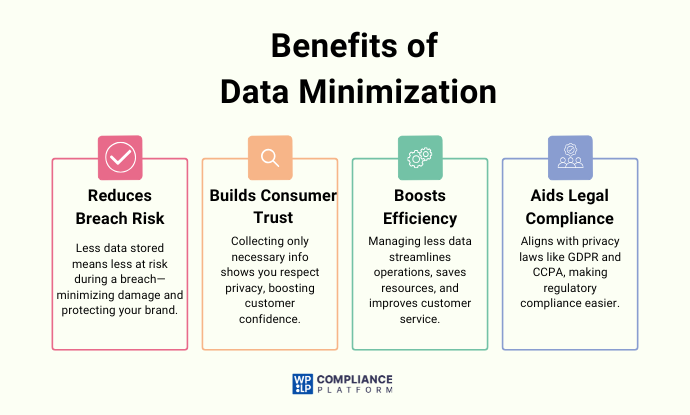
1. Less Risk of Data breach
Think of any prominent corporation that is often the headline of the national news. If they experience a data breach, there will likely be serious repercussions. The corporation will suffer severe losses for its company data and may expose personally identifiable information of its employees and customers.
Data minimization minimizes harms because the corporation only retains relevant information. While the corporation can work to protect its critical data, it can also minimize the fallout if a data breach occurs.
Since a data breach can cause irreversible harm to a brand, this strategy is particularly important for corporations seeking to avoid negative headlines.
2. Develops Consumer Trust
At a time when privacy scandals and data breaches are making national headlines, consumers are more cognizant than ever about who they can trust with their personal information.
By only obtaining and retaining the minimum information needed to process a financial transaction, the company is illustrating the importance of protecting consumer privacy. There is untold value in building trust in an industry where protecting private financial information is critical.
3. Improves Operational Efficiency
Imagine an online retailer that deals in millions of consumer information every day. They are using a data-minimisation method of practice meaning they will only collect information to the extent that is needed to process an order, maintain a customer account and provide recommendations.
This effective approach brings operational efficiencies to the manufacturer in many functional areas, such as data processing, order processing and customer service.
If there is less data to manage or maintain, the organisation is able to manage its resources effectively so they can concentrate on the most important aspect of their business – delivering an incredible client experience.
4. Compliance with Other Regulations
Any international organisation must comply with laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) of the European Union (EU).
Data minimisation is a principle of the GDPR that requires organisations to collect only the data needed, and under what conditions it needs to be processed. This makes it easier for organisations to operate under these stringent laws.
How to Implement Data Minimization Practices
Data minimization is one of the key principles of the General Data Protection Regulation, (GDPR). It requires organizations to limit the collection, use and processing of personal and/or any other data to the minimum required to fulfill a specific purpose.
Implementing simple practices of data minimization can increase compliance, reduce risk and increase consumer confidence. Steps that can be implemented to employ data minimization in an organization are:
Step 1: Conduct a Data Inventory Check
- Identifying Data that you Collect:- The first step to data minimization is understanding what your organization is really collecting. Develop an inventory of all the information in your organization to understand what types of data have been captured, both structured (i.e., databases) and unstructured (i.e., emails).
- The exercise should include customer data, employee data, and any other personal identifiable information (PII).
- Categorize and Prioritizing Data within Need:- After identifying each data type, then you will categorize the data based on your purposes and needs.
This will lay the groundwork for eliminating duplicate data, while also focusing your attention on the possible decisions surrounding legitimate data.
Step 2: Limit Data Collection to What Is Necessary
- Understanding the “Minimal Data” Principle: The GDPR limits the usage of personal data to fulfill a specified and lawful purpose. In this spirit, think about how you collect data through your various channels; does all data being collected have an explicit and lawful purpose?
- Reviewing Your Data Collection Practices: Review each data collection form, online survey, and every other customer touchpoint where you are collecting data, to make sure that only the minimum data is being collected (the minimum necessary). As a general example, only ask a customer for their date of birth if you require it for age verification.
- Developing Clear Data Collection Policies: Develop and implement policies on data collection that limit data collection to what is necessary. Record the reasons why an organization collects different data points, and share this information with all affected business units for a consistent approach and shared accountability for how data collection is managed.
Step 3: Incorporating Data Anonymization and Pseudonymization Methods
- Definitional Delineation and Benefits of Anonymization vs. Pseudonymization:– Anonymization means either removing or altering information so that the subject can no longer be identified from the data.
- Pseudonymization means replacing identifiable information with a pseudonym, with the intent to reverse this process. Both methods lower risks by removing the possibility of recovering the sensitive data when exposed in a breach.
- When Data Anonymization or Pseudonymization: – Anonymize data when it is no longer needed in identifiable form, as in for statistical analysis.
Pseudonymize data when identifiable data is needed in the context of a business, but should be secured. For any period of time, at all times, exploit the resources and tools available to make the data anonymization or pseudonymization process easy.
Step 4: Apply a Data Retention and Deletion Policy
- Data Retention Periods: By Necessity:- Identify retention periods for each category of data in order to determine the period of time necessary to meet a given objective.
- Best Practices for Data Deletion:- Engender methods of automatic deletion for data that is past its designated retention period; this will reduce reliance on human notice of length of time. If you don’t, your organization will end up with vast amounts of redundant data over time.
Step 5: Regular Data Audits and Reviews
Routine Audits Implementation:- Implement a consistent routine of audits to assess compliance with the data minimization policy. Audit data collection, data processing, and data storage. The audit does not need to be regimented but it must ensure that data is collected and retained appropriately and in compliance with relevant regulations and organizational priorities.
When conducting audits, the auditor will be identifying opportunities for improvement related to data minimization. When gaps are identified, take appropriate corrective measures – for example, updating processes, logging use of past tools, and retraining employees as appropriate.
Step 6: Review and Limit Data Sharing with Third Parties
- Limit Data Sharing with Third Parties : When sharing personal data to make it available to a third party, share only the data necessary to deliver the service; this strategy minimizes exposure of personal data.
- For example, you can share shipping addresses when using logistics providers, but do not need to share individualized per-customer information related to the shipping address.
- Validation of Third Party Vendors Activities Related to Data Minimization: – If your organization is assessing third party vendors, in addition to GDPR compliance, consider that alignment with data minimization principles should also be reviewed.
- Outline Appropriate Data Sharing Agreements: – Organizations should have an outline for data sharing agreements that address what type of engagements are appropriate.
Step 7: Employee Training and Awareness
The most critical aspect of a successful data minimization process is employee awareness. Regular training sessions should be developed for employees on GDPR, data minimization principles, and their role in meeting the GDPR compliance obligations.
Employees need to know how to act responsibly with data, report any inconsistencies they may discover, and understand the policies and procedures that you have put in place.
Data Minimization Tool
Data minimization is a crucial step toward complying with the GDPR, and the right tools can make it a lot quicker and easier than you think.
Compliance platforms are incredibly valuable tools that assist organizations to effectively manage data collection, data retention and data protection in addition to meeting legal requirements.
Data Minimization Tools and Platforms
The WP Legal Pages compliance platform provides your business with everything it needs to achieve compliance on the website. And it consists of two powerful plugins. The plugins are WP Legal Pages and WP Cookie Consent plugin, that work together to help you manage legal documents, privacy policies, cookie banners and consent.
WP Legal Pages Plugin: The WP Legal Pages plugin enables businesses to create GDPR-compliant legal pages, including privacy policies, terms of service, and disclaimers. When you clearly disclose the data you collect and how you process it, you ensure compliance with data minimization principles.

WP Cookie Consent Plugin: The WP Cookie Consent plugin manages your cookie consent banners for you. For businesses operating a site with cookies, you want to collect only the cookies you need to operate the site and allow the user to determine how they accept or reject cookies.

Using this plugin will fulfil your GDPR obligations as well as your ePrivacy Directive obligations.
Automating Data Collection and Retention Processes
The WP Legal Pages compliance platform automates data collection through embedded consent mechanisms, ensuring your site captures only the necessary data. It also enables managed workflows for data retention policies and can show compliance via audit logs.
Using encryption and masking methods to protect information
The WP Legal Pages compliance platform supports transparency and consent practices as a means to use encryption and masking tools to protect sensitive information. In addition to data minimization, encryption can protect against data breaches and unauthorized access.
Using the WP Legal Pages compliance platform and plugins, a company can easily implement data minimization protocols and ensure compliance with GDPR or other data protection regulations.
FAQ
The seven main principles of GDPR are lawfulness, fairness, transparency, purpose limitation, data minimization, accuracy, storage limitation, integrity and confidentiality (security), and accountability.
Data minimization is essential because it ensures legal compliance, enhances security, reduces costs, and builds customer trust.
Businesses can implement it by clearly defining data purposes in their privacy and cookie policies, limiting access, and deleting unnecessary data.
Conclusion
Data minimization is a way to ensure that only necessary information is collected and stored. By keeping only what’s essential, it reduces risks like data breaches. This approach helps businesses protect privacy while still growing.
By avoiding unnecessary data collection, companies can innovate and improve security efficiently. To comply with GDPR data minimization, we recommend using the WP Legal Pages Compliance Platform.
It will simplify compliance with privacy laws like GDPR, CCPA, LGPD, and more with features like automated policy generation and seamless integration with WordPress. It will save time, ensure accuracy, and keep your website legally secure.
If you liked this article, you can also consider reading:
- What Is Privacy Management and Why Is It Important?
- Florida Digital Bill of Rights (FDBR) — A Complete Guide
- Best GDPR WordPress Plugins
Are you ready GDPR data minimization for your website? Grab WP Legal Pages Compliance Platform now!
