Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA)

The Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) is a pivotal Canadian law designed to safeguard personal information.
Enacted in 2000, PIPEDA establishes guidelines for how businesses collect, use, and disclose personal data, ensuring the respect of individuals’ privacy rights.
As global digital interactions continue to grow, the importance of robust data protection measures has become increasingly evident.
In this article, we will discuss the critical provisions of PIPEDA, its impact on organizations and consumers, and how your business can comply with the law.
So, let’s dive in!
What is the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA)?
To begin with, the basics of PIPEDA, which stands for Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act, is a Canadian federal law governing the collection, usage, and disclosure of personal information.
It aims to balance individuals’ right to privacy with private organizations’ need to collect and use personal data for ethical business purposes.
The law applies to all businesses operating in Canada and handling the personal information of Canadian residents, ensuring individuals’ control over their data.
Principles of PIPEDA
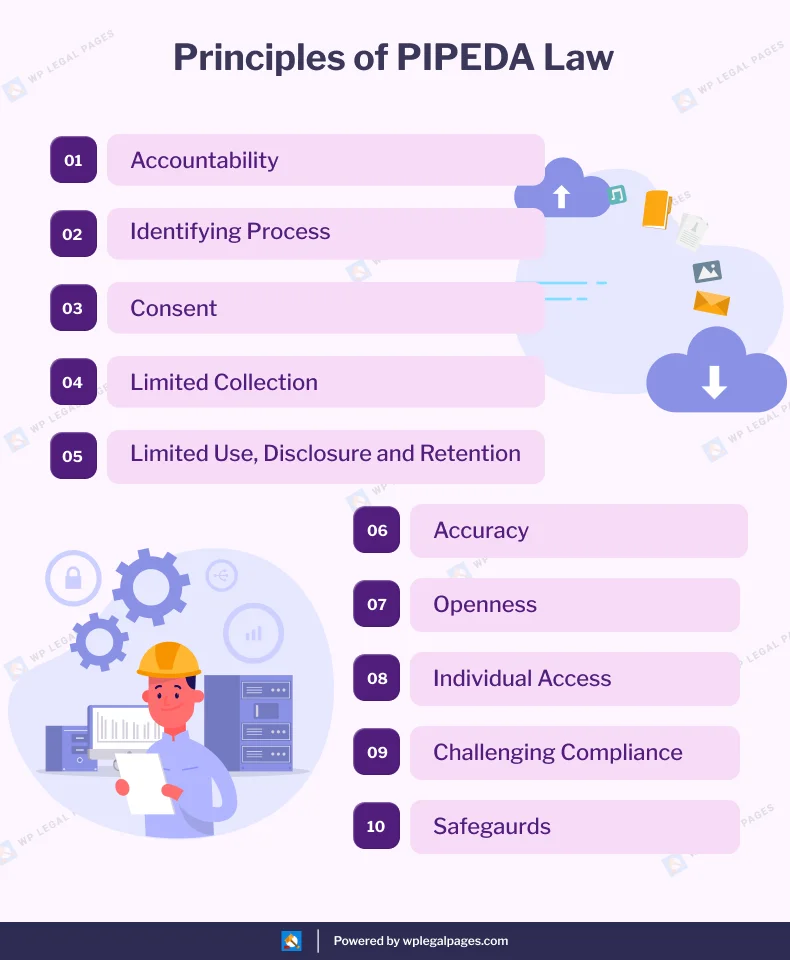
PIPEDA is built on ten core principles that guide the handling of personal information:
1. Accountability
Organizations must designate individuals responsible for compliance with PIPEDA. It ensures that personal information is managed properly and that there are clear lines of responsibility.
Organizations must implement policies and practices to protect personal data and respond to privacy-related inquiries or complaints.
2. Identifying Purposes
Organizations must identify the purposes for which personal information is being collected at or before the time of collection. This requires you to:
- Clearly state the purpose of data collection.
- Communicate purposes at or before collection.
- Ensure purposes are legitimate and specific.
3. Consent
Organizations must obtain informed consent from individuals to collect, use, and disclose their personal information.
Consent must be voluntary and can be withdrawn at any time. This empowers individuals by giving them control over their personal data and how it is shared.
4. Limiting Collection
Organizations should only collect personal information that is necessary for the identified purposes. This principle requires you to:
- Collect only necessary personal information.
- Use fair and lawful means for collection.
- Avoid excessive data gathering.
5. Limiting Use, Disclosure, and Retention
Personal information can only be used or disclosed for the purposes for which it was collected, and it must be retained only as long as necessary.
Organizations must have clear policies for data retention and disposal, minimizing the risk of misuse or unauthorized access.
6. Accuracy
Organizations are responsible for ensuring that personal information is accurate, complete, and up-to-date. Regular reviews and updates should be conducted to maintain data quality.
It also requires you to correct inaccurate information that can lead to inappropriate decisions and harm individuals.
7. Safeguards
Adequate security measures must be implemented to protect personal information from loss, theft, or unauthorized access. Organizations should use physical, technological, and administrative safeguards to ensure data security.
8. Transparency
Organizations must be transparent about their policies and practices regarding personal information. This openness includes making information about how their data is handled accessible to individuals.
9. Individual Access
Individuals have the right to access their personal information held by organizations, this includes to:
- Allow individuals to access their personal information.
- Provide a process for requesting corrections.
- Respond to requests promptly.
10. Challenging Compliance
Individuals can challenge an organization’s compliance with PIPEDA and seek remedies for violations.
Organizations must have procedures in place to address these challenges effectively. This requires oganizations to:
- Establish procedures for addressing complaints.
- Ensure individuals can challenge compliance issues.
- Investigate and respond to challenges appropriately.
Who Must Comply With the PIPEDA Law?
PIPEDA applies to all private sector organizations in Canada that collect, use, or disclose personal information during commercial activities. This includes businesses, non-profit organizations, and associations.:
PIPEDA states that any business, regardless of size, that engages in commercial activities and handles personal information must adhere to PIPEDA. This includes retailers, service providers, and online platforms.
In addition, non-profits that collect personal data for fundraising, membership, or other activities related to their operations are also subject to PIPEDA.
Furthermore, organizations that operate under federal jurisdiction, such as banks, telecommunications companies, and transportation services, must also comply with PIPEDA when handling personal information.
Also, businesses that operate across provincial or national borders and handle personal information must comply with PIPEDA, as it governs the collection and use of data in a broader context.
However, PIPEDA does not apply to personal information collected, used, or disclosed by government institutions governed by separate privacy laws. Also, non-profits and charities located in Quebec, Alberta, and British Columbia are exceptions to the law.
How Businesses Can Comply With PIPEDA Regulations
Complying with the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) is crucial for businesses operating in Canada.
To ensure your business is PIPEDA compliant, you must first familiarize yourself with the principles and obligations outlined in PIPEDA. This includes understanding individuals’ rights regarding their personal information and your organization’s responsibilities.
Next, your will need to create a clear and comprehensive privacy policy that outlines how your organization collects, uses, and discloses personal information.
Adding a privacy policy for your website is crucial as it helps you comply with PIPEDA and safeguards your business from other global privacy laws.
There are various methods that you can use to create a PIPEDA-compliant privacy policy; you may choose the one that suits you best:
1. Self-Drafting A Privacy Policy
If you have legal experience or are eager to learn, you can research best practices for creating PIPEDA-compliant privacy policies. Alternatively, you can start from scratch, outlining the major components you wish to include and gathering references from peers.
While this method is highly customizable, it necessitates a deep understanding of legal terminology and its ramifications. You may have to go through a long learning and implication process.
Key Elements You Must Include In PIPEDA Compliant Privacy Policy
Here are a few key elements to include in your PIPEDA-compliant privacy policy:
- Contact Information: Provide clear contact details for the individual responsible for privacy within your organization.
- Purpose of Data Collection: Clearly outline the specific purposes for which personal information is being collected.
- Types of Personal Information Collected: Specify the types of personal information you collect, such as names, addresses, email addresses, financial information, and any other relevant data.
- Consent Mechanisms: Describe how you obtain consent from individuals for data collection, use, and disclosure.
- Use and Disclosure of Personal Information: Detail how you will use and disclose the personal information to third parties.
- Data Retention Practices: Explain how long will you retain the personal information and the criteria you will use to determine retention periods.
- Data Security Measures: Outline the security measures to protect personal information from loss, theft, and unauthorized access.
- Access and Correction Rights: Inform individuals of their right to access their personal information held by your organization and the process for requesting corrections if the information is inaccurate or incomplete.
- Openness and Transparency: State your commitment to being open about your privacy practices.
- Complaint Process: Provide information on how individuals can file complaints regarding your organization’s handling of their personal information.
- Third-Party Links: If applicable, disclose any links to third-party websites and clarify that your privacy policy does not apply to those external sites.
- Policy Review Date: Include the date the privacy policy was last reviewed or updated.
2. Hiring A Legal Professional
Businesses with specific legal requirements can also seek the advice of a legal professional. A lawyer can create a PIPEDA-compliant privacy policy tailored to the company and ensure compliance with applicable laws.
Furthermore, if you have an existing legal arrangement, a legal professional can analyze it to ensure it is still relevant and legally sound.
However, hiring a legal specialist may be costly and time-consuming, resulting in delays and decreased operating efficiency.
3. Using A Privacy Policy Generator
Using a privacy policy generator is one of the simplest processes to create a PIPEDA-compliant privacy policy for your site.
A privacy policy generator is a tool that automatically creates customized privacy policy statements for users based on users’ requirements.
While various privacy policy generators are available and offer free and paid solutions to create website privacy policies, we recommend you use the WP Legal Pages plugin. It is a free privacy policy generator that allows you to custom-create a privacy policy tailored specifically for your business.
The plugin is very simple to use and supports an intuitive wizard that helps you to design a privacy policy template from start to finish.
WP Legal Pages allows you to easily create a customized privacy policy that is PIPEDA compliant and also complies with other legal regulations such as CCPA and GDPR.
Furthermore, it allows you to develop policy templates in various languages, including English, French, German, Portuguese, Italian, and others.
Steps To Create A Privacy Policy For Your Website
To generate a privacy policy for your website, follow the following steps:
1. Installing The WP Legal Pages Plugin
Navigate over your WordPress Dashboard and click on Plugins > Add New.
Search for WPLegalPages in the search bar.
Click on the Install Now Button.
Click on the Activate button and activate the plugin.
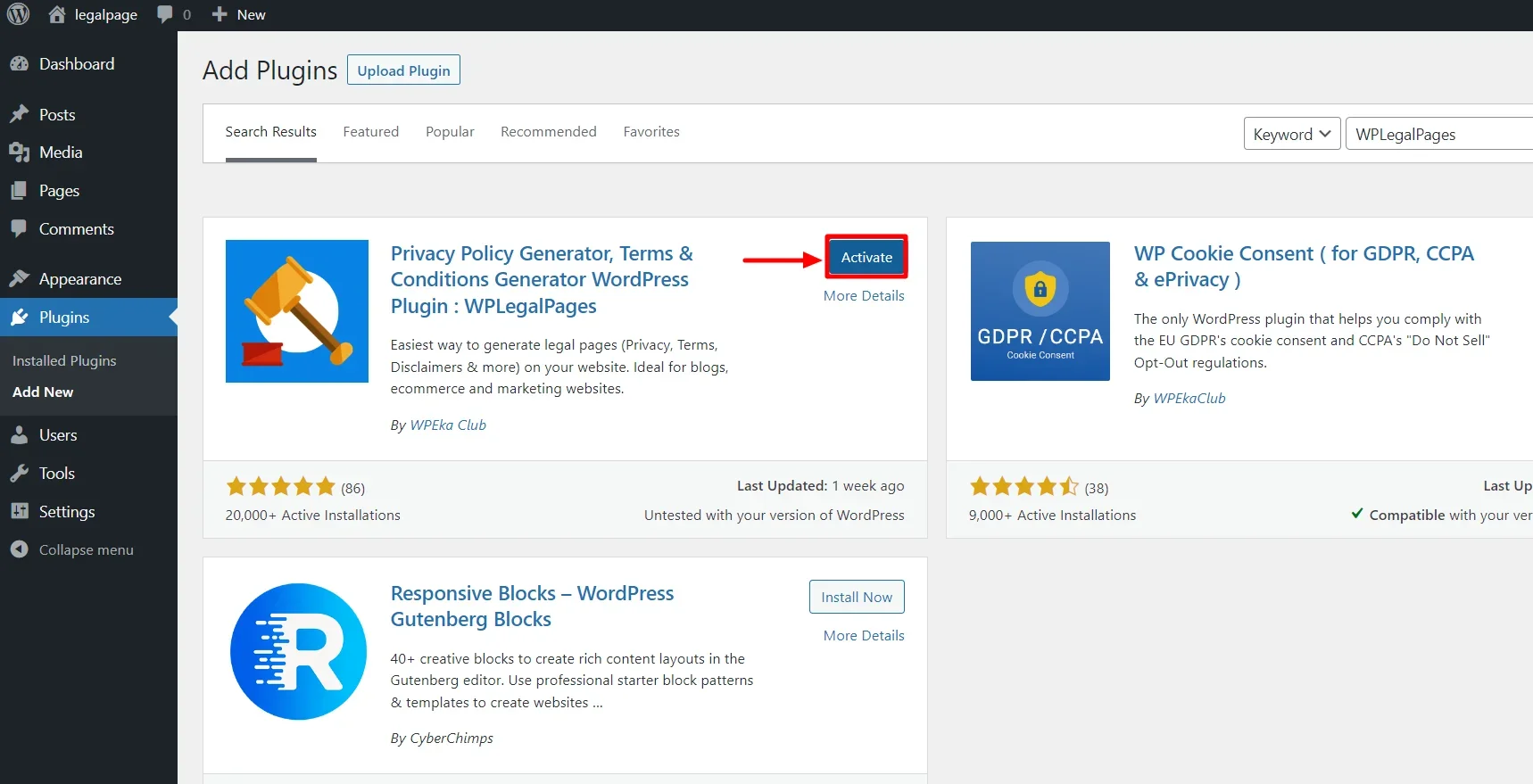
Once the plugin is active, you can directly access it from your WordPress Dashboard.
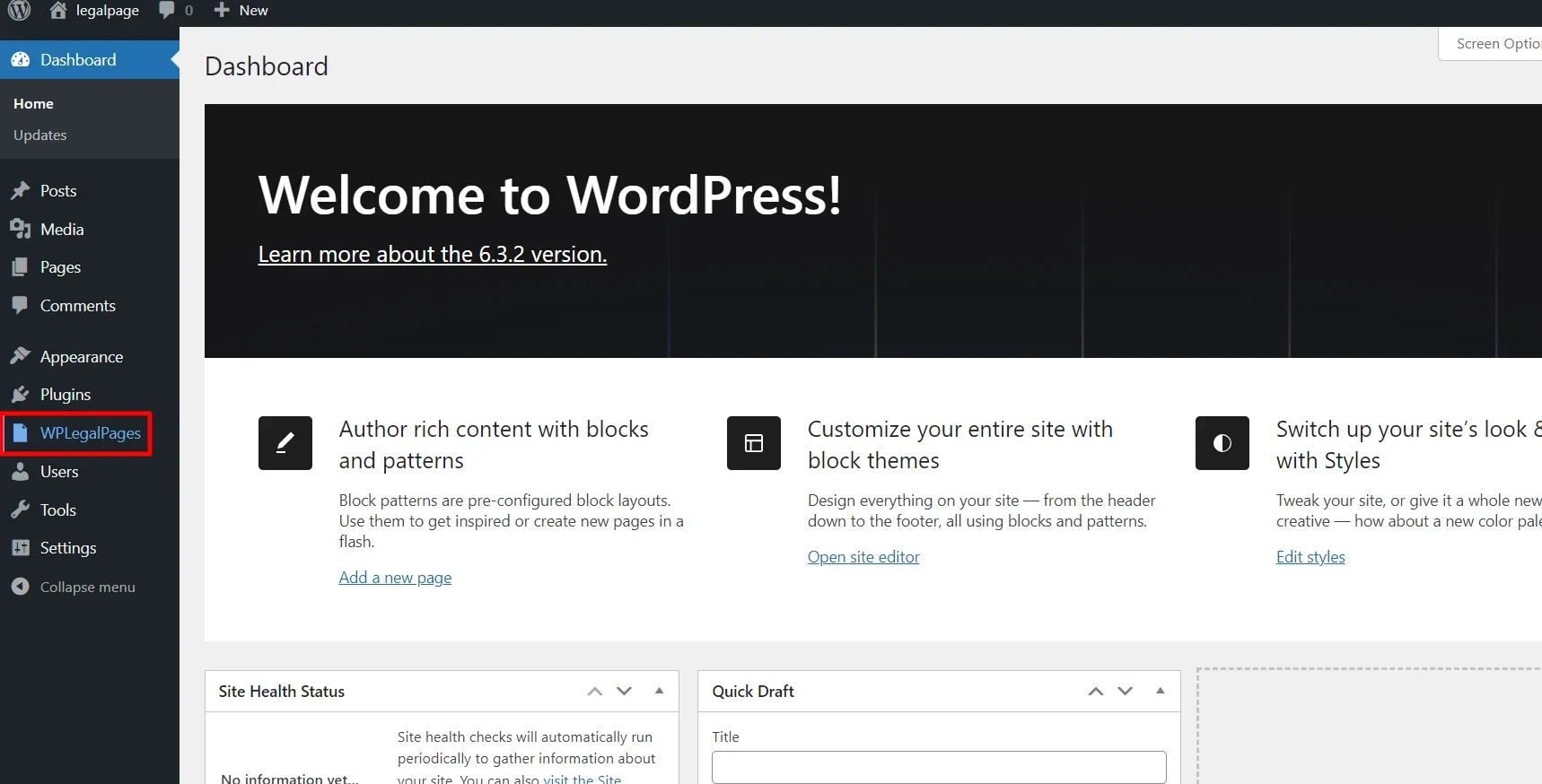
2. Creating a Privacy Policy For Your Website
From WPLegalPages, click Accept to create your legal pages.
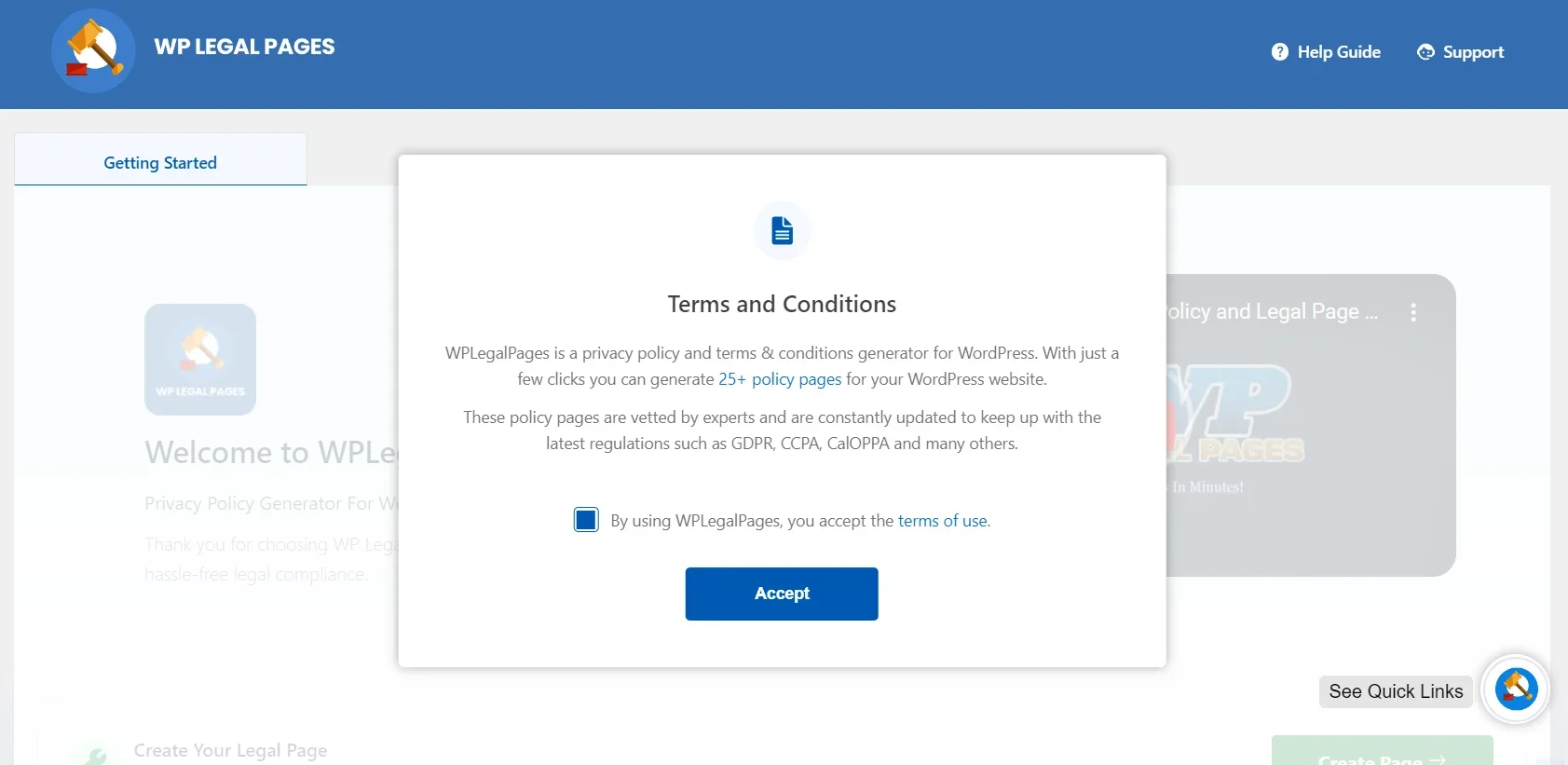
To create a Privacy Policy for your website, click Create Legal Page from the WP Legal Pages menu.
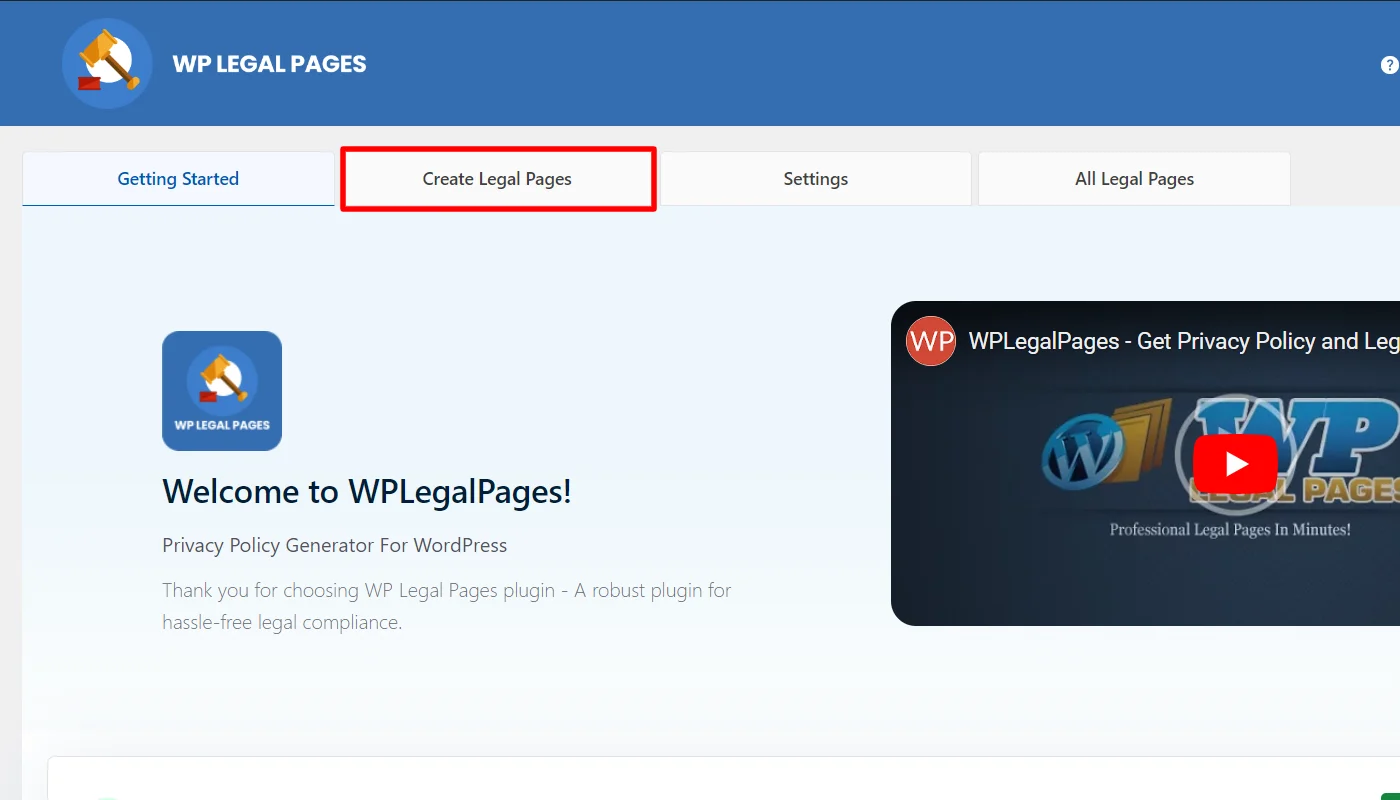
You will now see four templates available in the free version. Click on the Standard Privacy Policy option to create a website privacy policy.
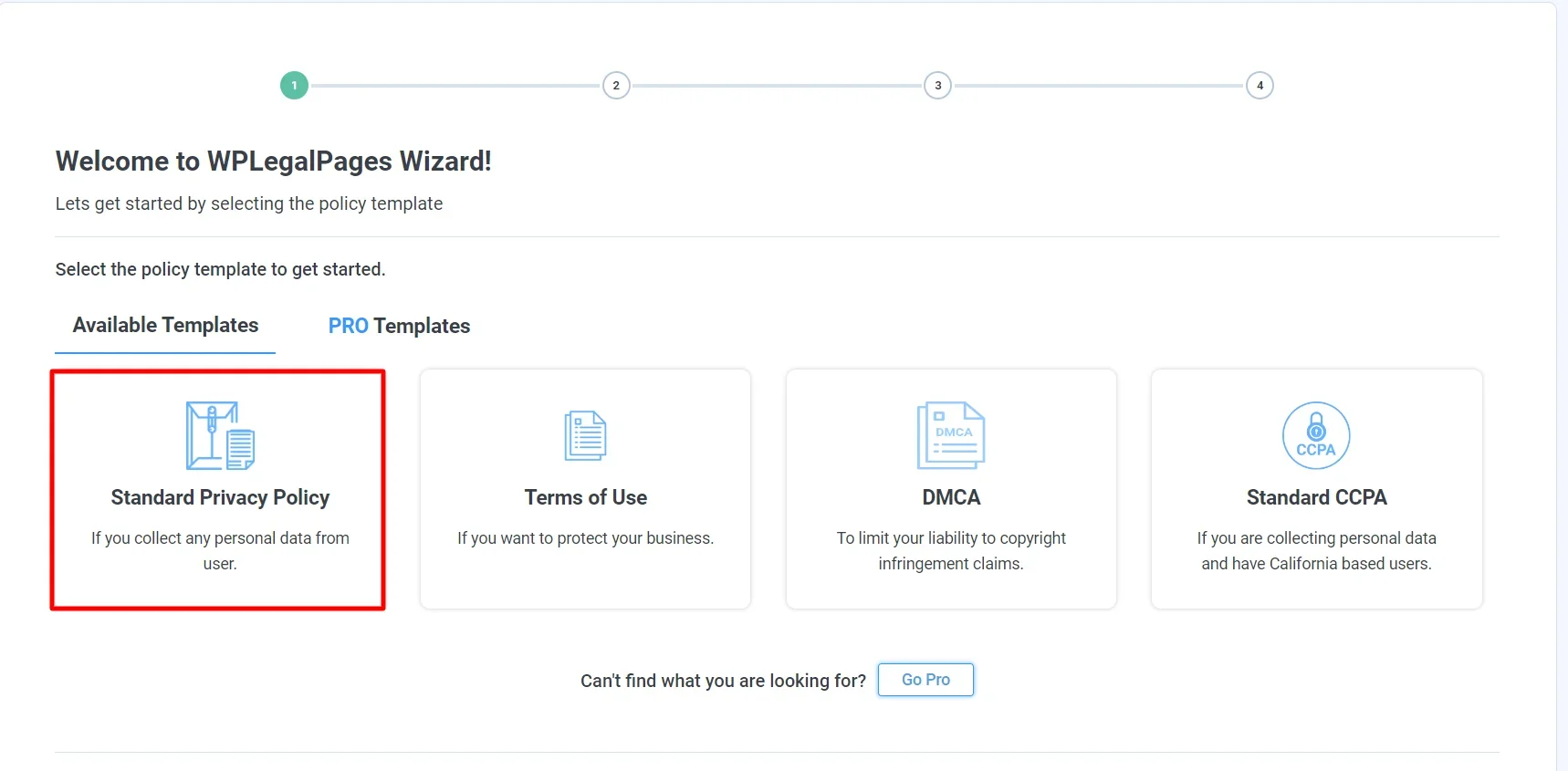
Fill in the Basic Details and click Next.
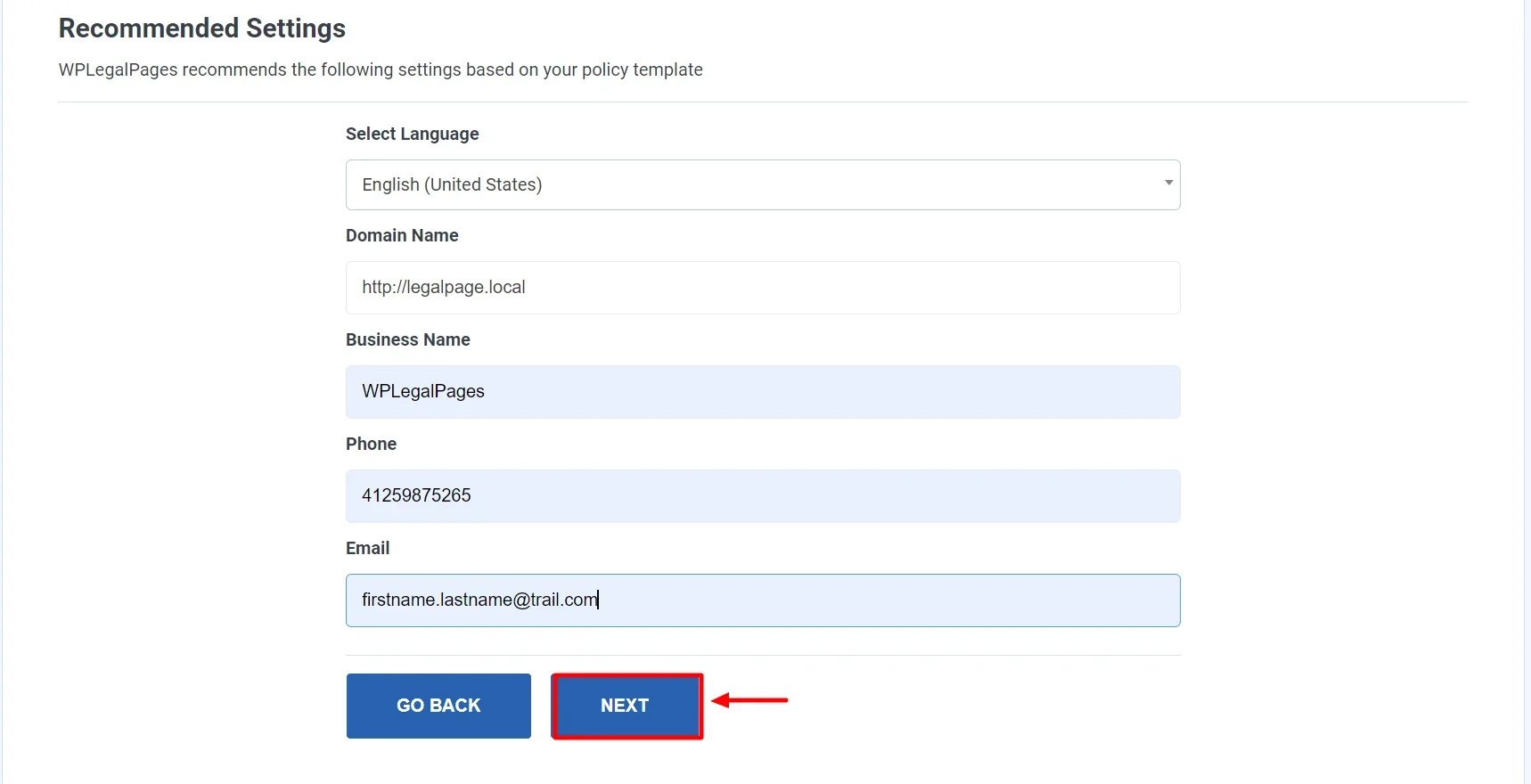
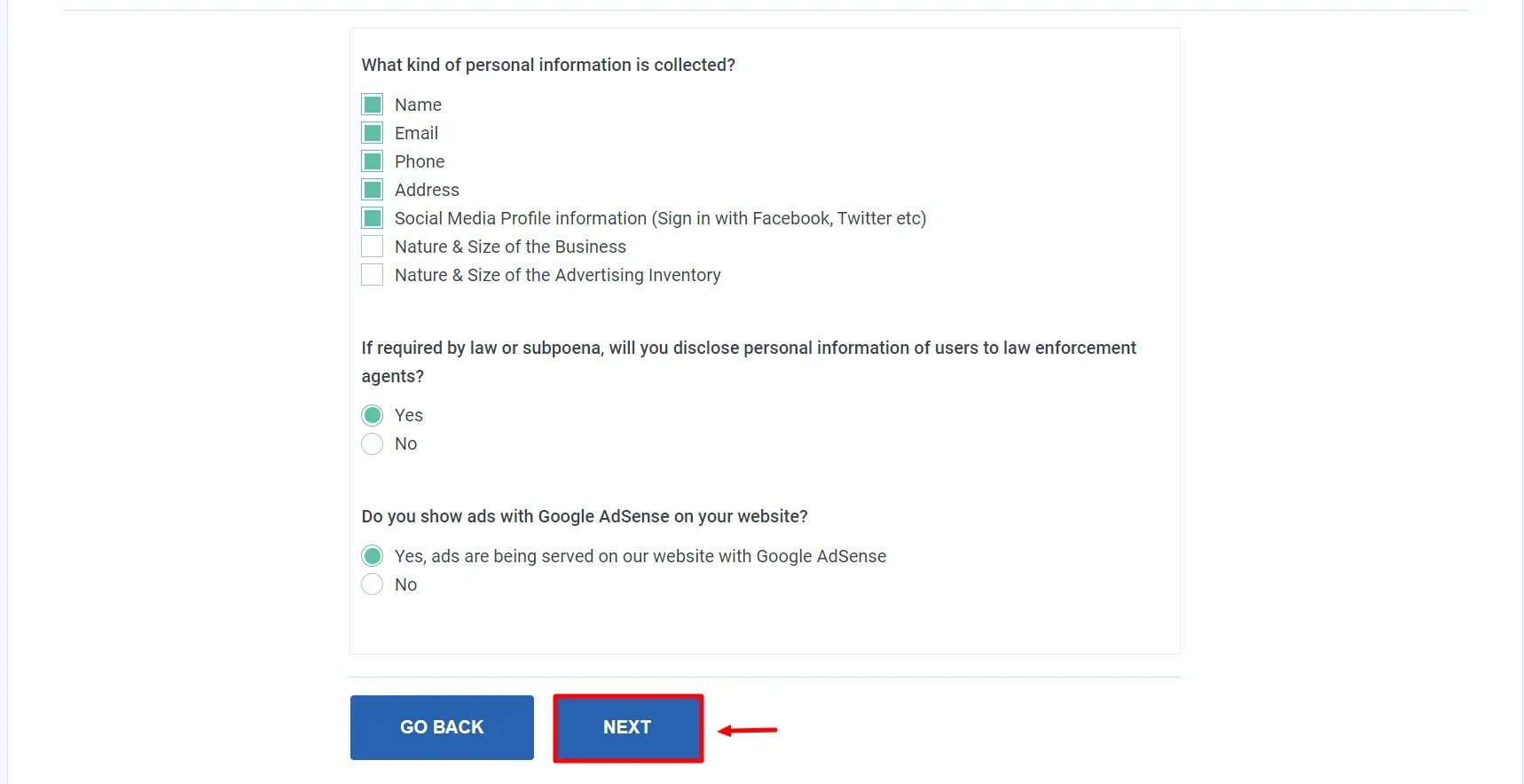
Select the appropriate section for your legal policy, then click Next.
Your Privacy Policy Template Preview is ready.
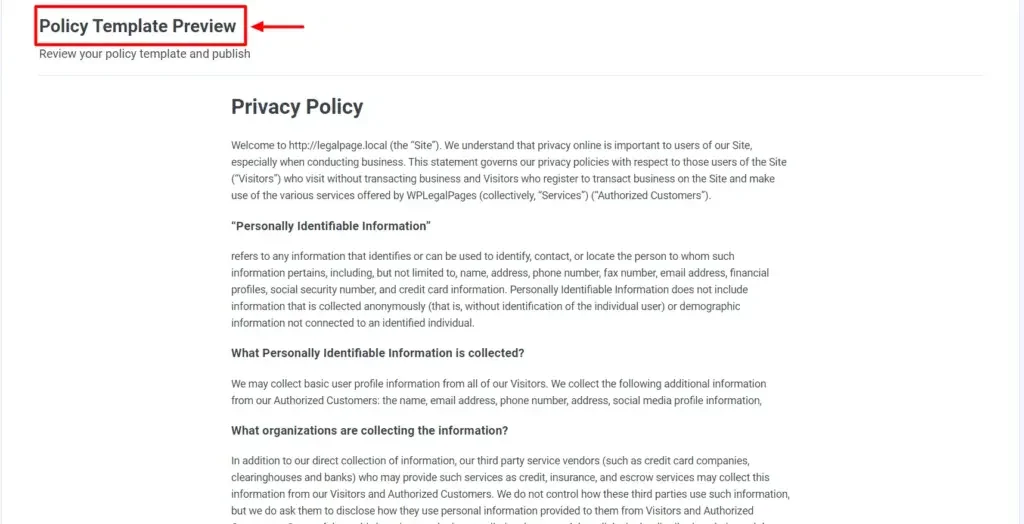
3. Customize your Privacy Policy
Click on the Create and Edit option to edit or add any additional information to your privacy policy.
After you have made the necessary changes, click on Publish.
There you go with a customized privacy policy template tailored for your website.
PIPEDA Penalties and Fines for Non-Compliance
The enforcement of PIPEDA is primarily overseen by the Office of the Privacy Commissioner of Canada (OPC). It investigates complaints and ensures adherence to privacy laws.
Non-compliance with the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA) can result in significant penalties and fines for organizations.
Here are the key aspects of penalties and fines associated with PIPEDA non-compliance:
- Investigations and Complaints: Individuals can file complaints with the OPC if they believe their privacy rights under PIPEDA have been violated. The OPC has the authority to investigate these complaints and determine whether an organization has breached PIPEDA.
- Recommendations: Following an investigation, the OPC may issue recommendations for organizations to rectify their non-compliance. While these recommendations are not legally binding, organizations must follow them to avoid further action.
- Court Orders: If an organization fails to comply with the OPC’s recommendations, the Commissioner can seek a court order to compel compliance. This can result in legal action, further damaging the organization’s reputation.
- Fines and Penalties: As of recent updates, organizations that have been found violating PIPEDA can face fines of up to $100,000 per violation. This is a deterrent against mishandling personal information and emphasizes the importance of adhering to privacy regulations.
- Reputational Damage: Noncompliance can lead to significant reputational harm beyond financial penalties. Organizations that fail to protect personal information may lose customer trust, which can have long-term implications for their business.
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: Organizations that are found non-compliant may face increased scrutiny from regulators in the future, leading to more frequent audits and reviews of their data handling practices.
FAQ
PIPEDA, the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act, is Canadian legislation that governs how private sector organizations collect, use, and disclose personal information in the course of commercial activities, ensuring individuals’ privacy rights.
PIPEDA applies to all private sector organizations in Canada, including businesses, non-profits, and federal workers. It covers entities that collect, use, or disclose personal information during commercial activities, regardless of their size.
Non-compliance with PIPEDA can result in fines up to $100,000 per violation, potential legal action, and reputational damage. Organizations may also face increased scrutiny and audits from regulatory bodies.
Businesses can comply by developing clear privacy policies, obtaining informed consent, and implementing strong data security measures to ensure adherence to PIPEDA requirements.
Conclusion
As privacy concerns continue to grow, prioritizing PIPEDA compliance safeguards personal information and enhances organizational reputation and accountability in an increasingly digital landscape.
By understanding the requirements, developing comprehensive privacy policies, and implementing robust security measures, businesses can protect individuals’ privacy rights while avoiding penalties.
We recommend using the WP Legal Pages plugin to create a standard privacy policy for your website.
If you liked this article, you can also read:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- What is EULA and How to Create One For Your Website
- The California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA)
Are you looking to make a privacy policy that complies with the PIPEDA law? Grab the WP Legal Pages now!
