What is Data Subject Access Request? A complete Guide

Summary
It covers DSAR rights under GDPR and CCPA/CPRA, types of data requests, response deadlines, penalties for non-compliance, and shows how website owners can manage DSARs easily using the WPLP Compliance Platform.
How do you know what personal data your website has collected about a visitor?
You don’t, until they ask for it.
That request is called a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR). It’s how users legally demand to know what data your website stores about them, how it’s used, and who it’s shared with.
Under privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA/CPRA, every website that collects personal data is required to recognize, process, and respond to these requests. When handled correctly, DSARs build transparency and trust. When ignored or mishandled, they can lead to fines, complaints, and reputational damage.
- What is a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR)?
- What Information must you provide in a DSAR Response?
- Type of Data Subject Access Requests
- Who Can Submit a DSAR?
- Deadline for Responding to the DSAR
- Penalties for Not Responding to a DSAR
- How to Handle Data Requests Using the WPLP Compliance Platform
- Can You Refuse To Respond to a DSAR?
- FAQ
- Conclsuion
What is a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR)?
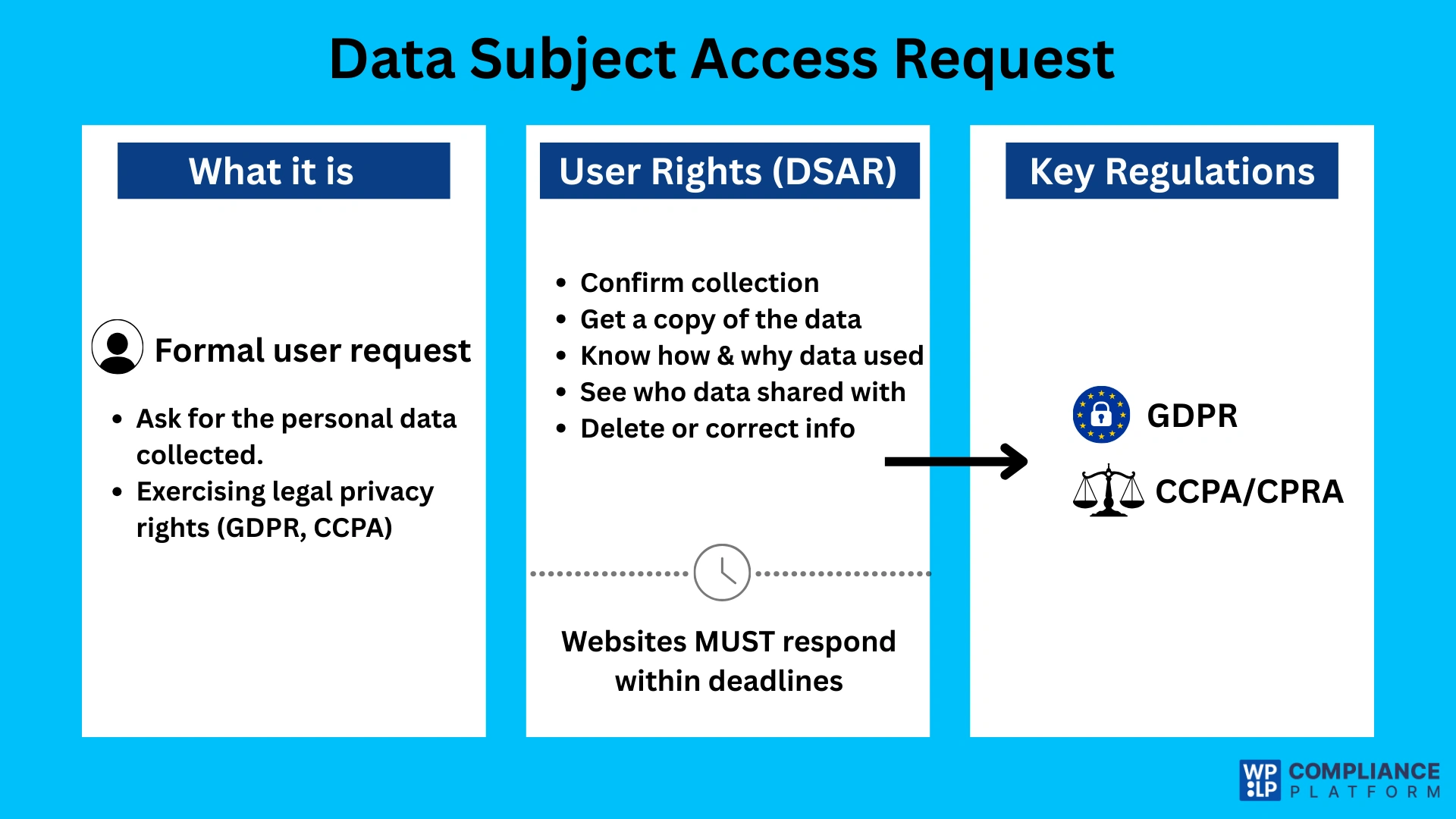
A Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) is a formal request made by a user asking a website or organization to disclose the personal data it has collected about them.
From a website owner’s perspective, a DSAR is how users exercise their legal rights under privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA/CPRA. When someone submits a DSAR, they may ask your website to:
- Confirm whether you are collecting their personal data
- Provide a copy of the data you have about them
- Explain how and why that data is used
- Show who the data is shared with
- Delete or correct their personal information
If your website collects data through contact forms, cookies, analytics, user accounts, or marketing tools, you must receive, process, and respond to DSARs within specific deadlines.
DSARs and Major Data Protection Regulations
While the fundamental right is similar globally, the exact terminology, requirements, and deadlines can vary depending on the specific regulation. The two most prominent regulations governing DSARs are the GDPR (Europe) and the CCPA/CPRA (California, US).
DSARs and the GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which applies across the European Economic Area (EEA), is the foundational law for DSARs. The right of access is explicitly detailed in Article 15 of the GDPR.
Under the GDPR, the request must be fulfilled free of charge unless the request is manifestly unfounded or excessive (e.g., repetitive). If the data subject makes the request by electronic means, the information should be provided in a commonly used electronic format.
DSARs and the CCPA/CPRA
In the United States, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), as amended by the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA), grants California consumers similar rights. The CCPA/CPRA refers to these as “Requests to Know.”
What Information must you provide in a DSAR Response?
The organization must confirm data processing, provide a copy of the personal data, and explain the following:
In addition, the response should clearly explain:
- Explain why you are processing the data
- Specify who you share the data with, if anyone
- List the types of personal data you are processing
- State where the data came from, if you didn’t collect it directly from the individual
- Indicate how long you will keep the data
- Disclose whether you use automated decision-making or profiling
- Inform individuals of their data protection rights, such as the right to correct or delete their data
When responding to a DSAR, the organization must include a copy of the personal data and all required details.
Type of Data Subject Access Requests
In this section, we’ll look at the five most common types of data requests businesses receive and how to manage each one promptly.
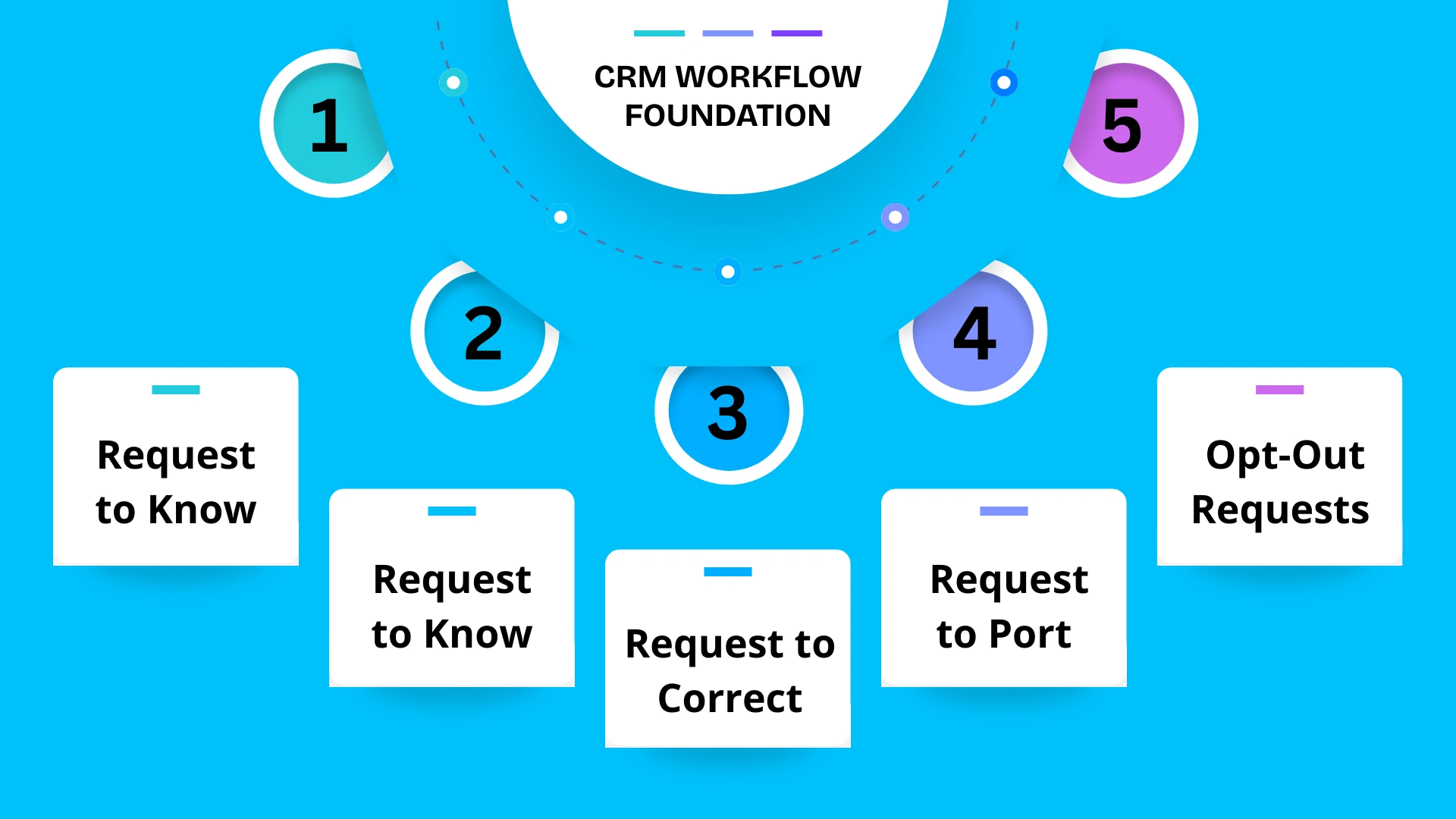
Request to Know
This is the most common type when users want to understand what data you’ve collected about them. They want to know how their personal information is stored, the reason for the collection, and how it’s shared with others.
The user’s motive here is that they want to make sure that their personal information is in safe hands. Nobody wants others to misuse their data. And, when you respond to those requests, it’ll show that your business values openness and respects the users’ privacy.

Request to Delete
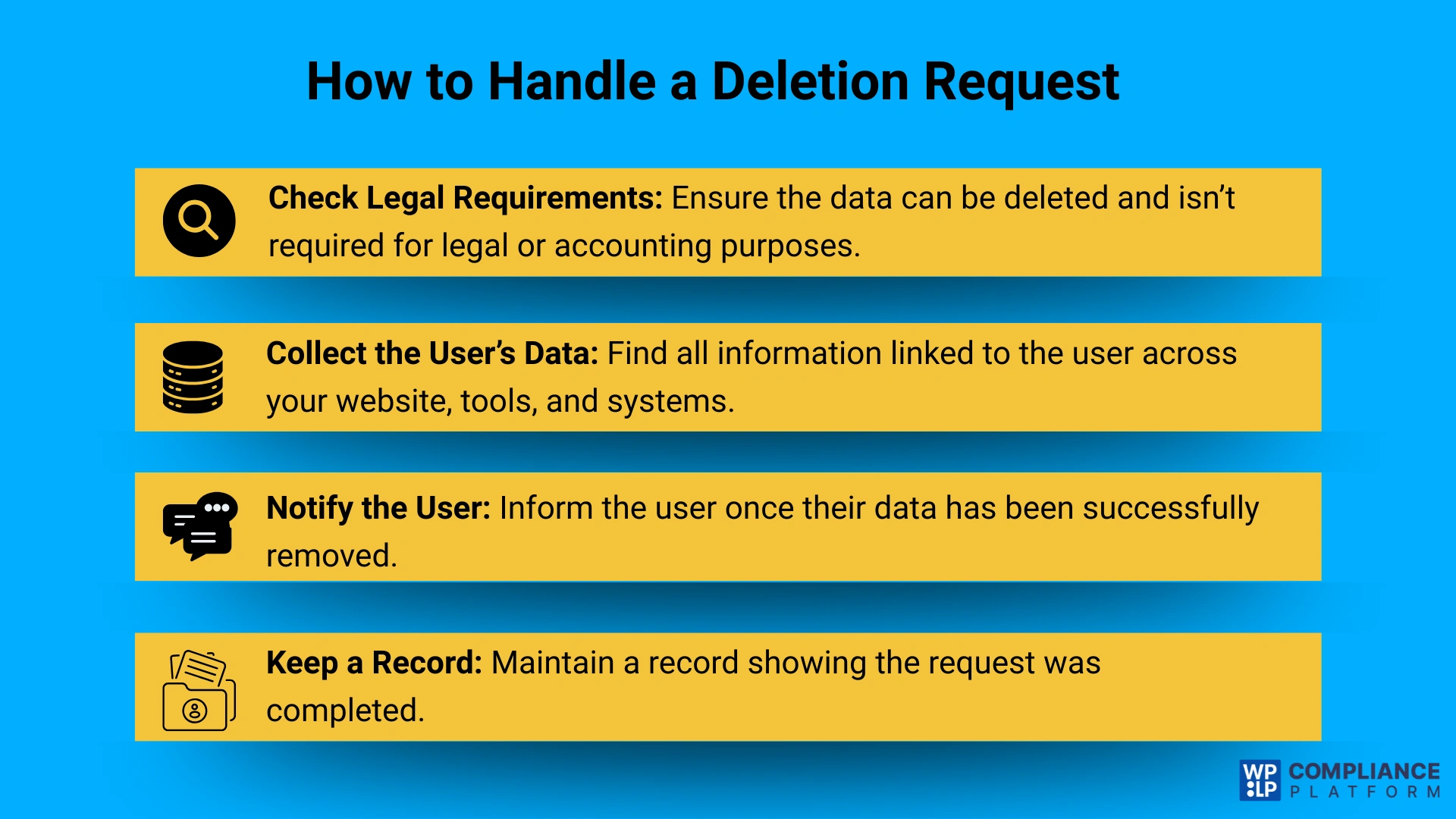
There’s a chance that users may ask to delete their personal data. This means they want all information you’ve collected about them removed from your records.
Users often do this when they no longer use your services or want more privacy.
Data deletion is one of the most crucial user rights under privacy laws. It gives users control over their own data and allows them to manage how it’s used.
Not just that, deleting data also helps your business keep databases organized. It reduces storage costs and lowers the risk of keeping outdated or unnecessary information.
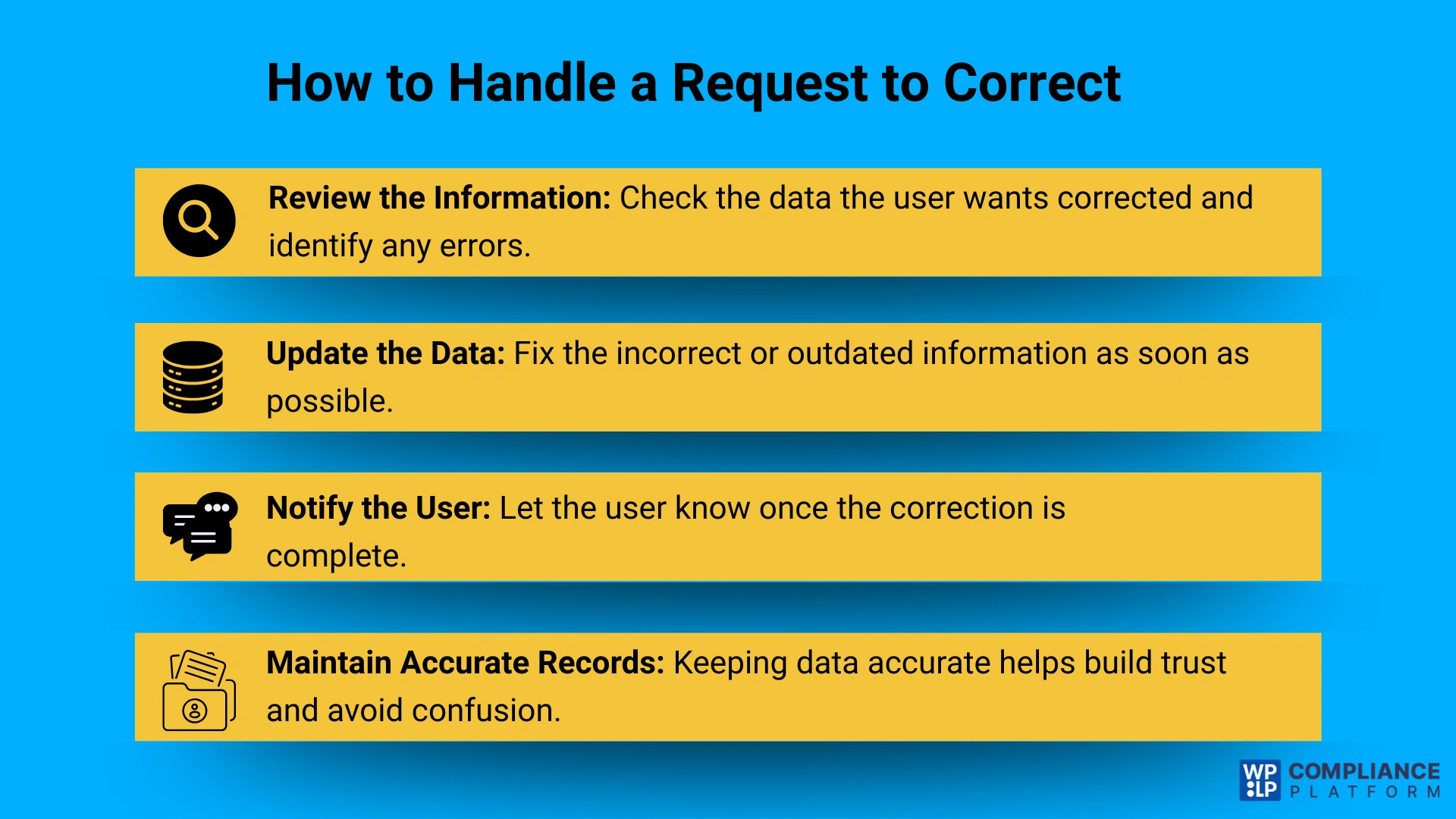
Request to Correct
Sometimes users notice that the information stored about them is incorrect or outdated. They totally have the right to fix it.
This is called a request to correct. It ensures your data remains accurate and reliable. This kind of request shows that users are aware of their personal information and want it to stay private.
It’ll also come in handy for you. It’ll help your business maintain the records of user information in a correct way, while avoiding mistakes. Doing this will improve communication and service quality significantly.
Request to Port
Your website’s users can request a copy of their data in a common format at any time. The reason might be that they’d want to move it to another platform or service.
Data portability gives your users the free hand to share their personal information across different services. It also makes switching between services, websites, or apps easier and more transparent.
For example, a user may ask for their profile, saved contacts, or order history details so they can upload this data to a new account on another website or app.
All the businesses that support data portability show respect for user rights.

Opt-Out Requests
Opt-out requests typically relate to marketing emails, analytics, and advertising cookies. Many users don’t want their data tracked and used for marketing or analytics.
When they send an opt-out request, they’re asking you to stop processing their data for such purposes. This request is quite common, especially for websites using tracking tools.
Opt-out requests help users control their online privacy. They can choose which messages or ads they receive and how their data is used for analytics.
Honoring opt-out preferences can help in reducing spam complaints and building a cleaner brand image. It’s a simple way to show that your business puts privacy first.

Who Can Submit a DSAR?
Anyone whose personal data an organization processes can submit a DSAR and request a copy of their data, without giving a reason. It can be submitted by:
- The Data Subject Themselves: Any individual about whom an organization processes data.
- A Third Party Authorized by the Data Subject: This includes legal guardians on behalf of children, or a lawyer acting on instruction. Under the CCPA/CPRA, this person is called an ‘authorized agent.’
- Legal Representatives: In some cases, and depending on the jurisdiction, a legal personal representative (e.g., executor of an estate) may be able to make a request on behalf of a deceased individual.
Key Note on Verification: Organizations must take reasonable steps to verify the identity of the person making the request to ensure they do not disclose personal data to the wrong person (a significant security breach). The level of verification should be proportionate to the sensitivity of the data.
Deadline for Responding to the DSAR
The standard rule is that you must respond without undue delay and at the latest within one calendar month of receiving the request.

How to Calculate the Deadline:
The DSAR response deadline starts the day you receive the request. Normally, it’s one month later, but if the date falls on a weekend or holiday, it moves to the next working day. For end-of-month requests, the deadline is the last day of the following month if that month has fewer days.
In certain situations, you can extend the response time by up to two additional months, making the total response period three months. This extension applies if the request is complex or if multiple requests come from the same individual. However, you must inform the requester within the first month, explaining why the extension is necessary.
Penalties for Not Responding to a DSAR
If you don’t respond to a DSAR on time, you could be subject to fines, legal action, or other penalties depending on which data privacy regulations apply.
I compiled a list of penalties for all privacy laws mentioned in this guide, which you can find in the table below.

How to Handle Data Requests Using the WPLP Compliance Platform
Now, let’s look at how you can use the WP Cookie Consent plugin inside the WPLP Compliance Platform to manage data requests easily.
First and foremost, you’ll have to install the WP Cookie Consent plugin and open its dashboard.

Inside the WP Cookie Consent dashboard, you’ll see the cookie settings section. In that section, you’ll find an option called “Enable Data Request Form.” Simply toggle it on.
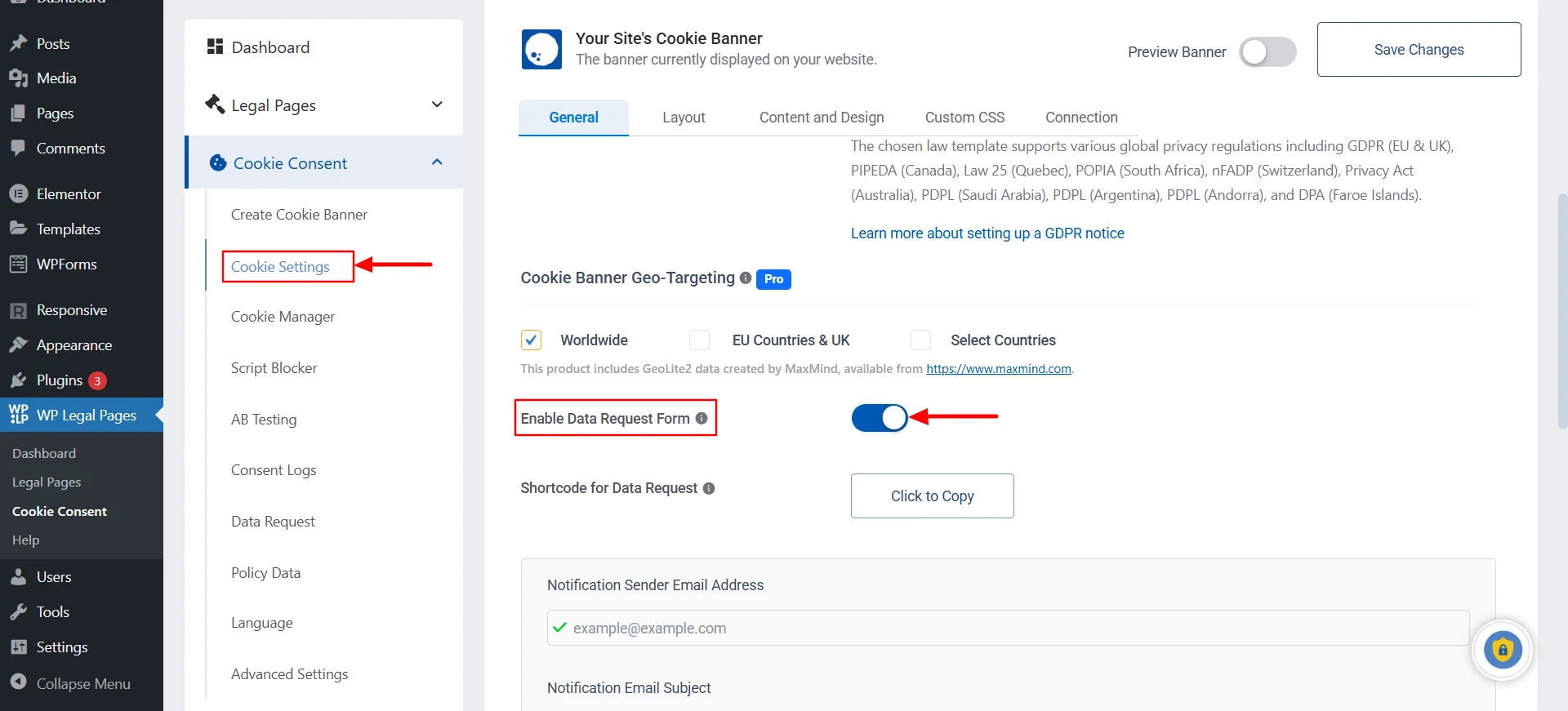
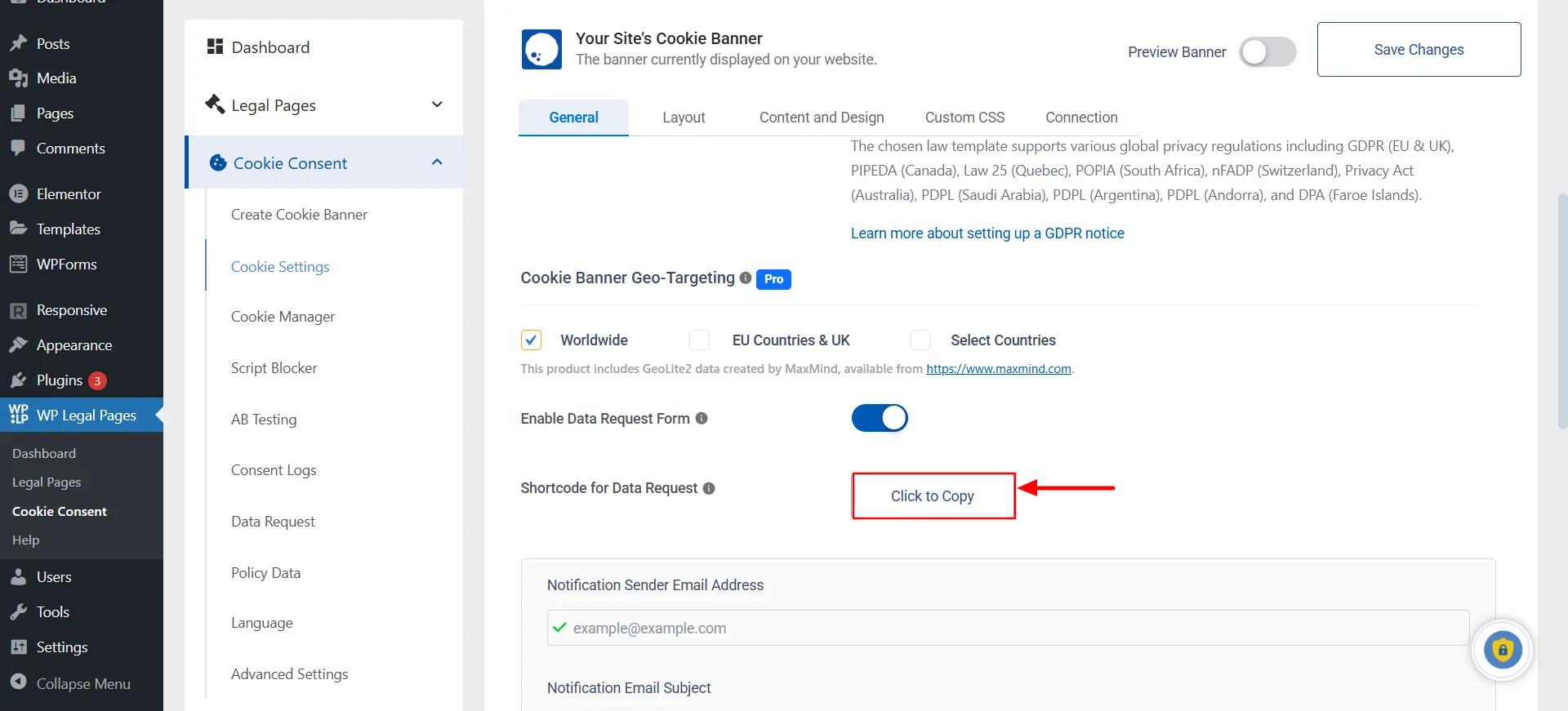
Right under that, you’ll find an attribute called “Shortcode for Data Request.” Click on the “Click to Copy” button beside it.
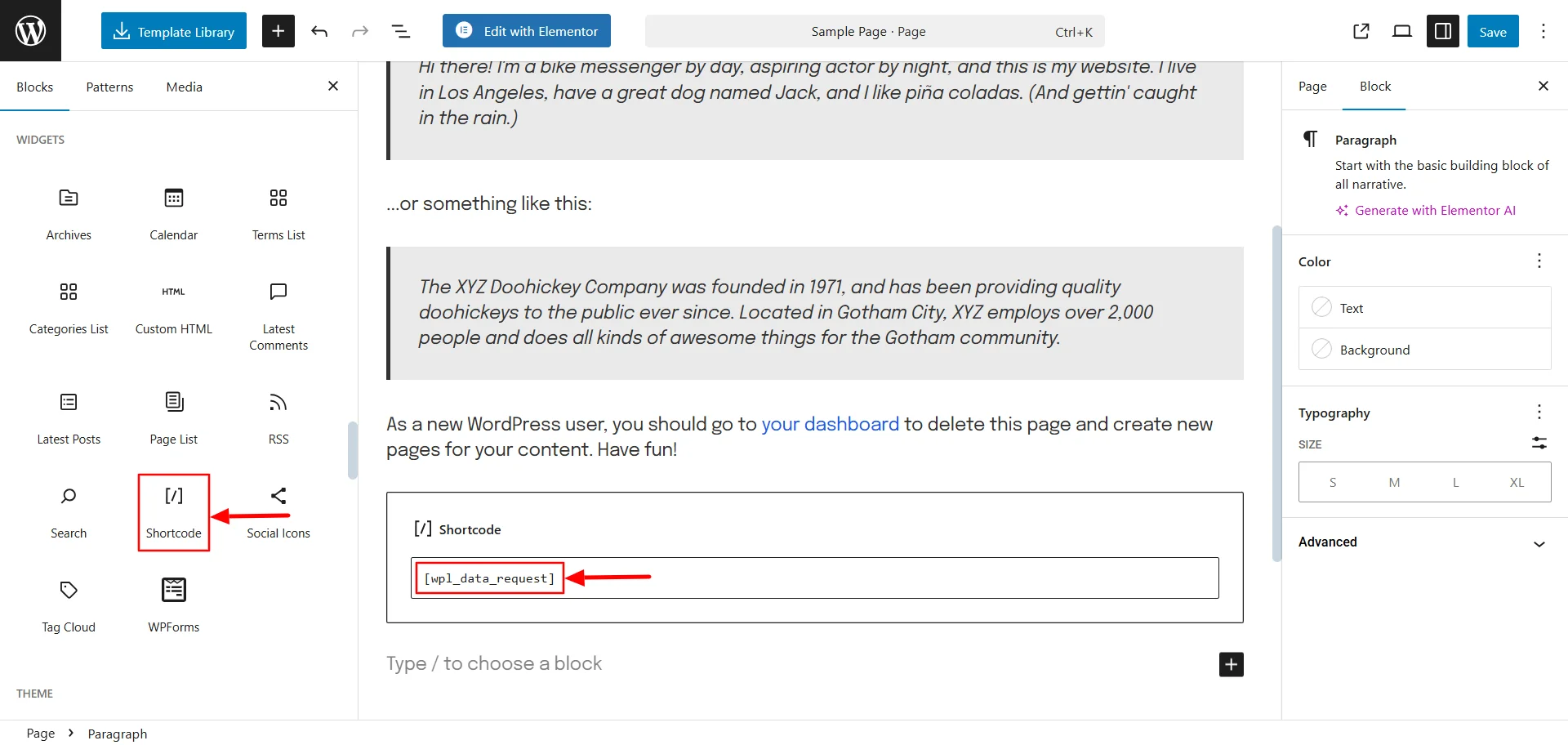
Now, you can paste this code anywhere on your website where you want the data request form to appear. This could be on your privacy page or contact page.
Once users start submitting their requests, you’ll receive them inside the same dashboard. Under the “Data Request” section, you’ll find a simple table that displays all user submissions.
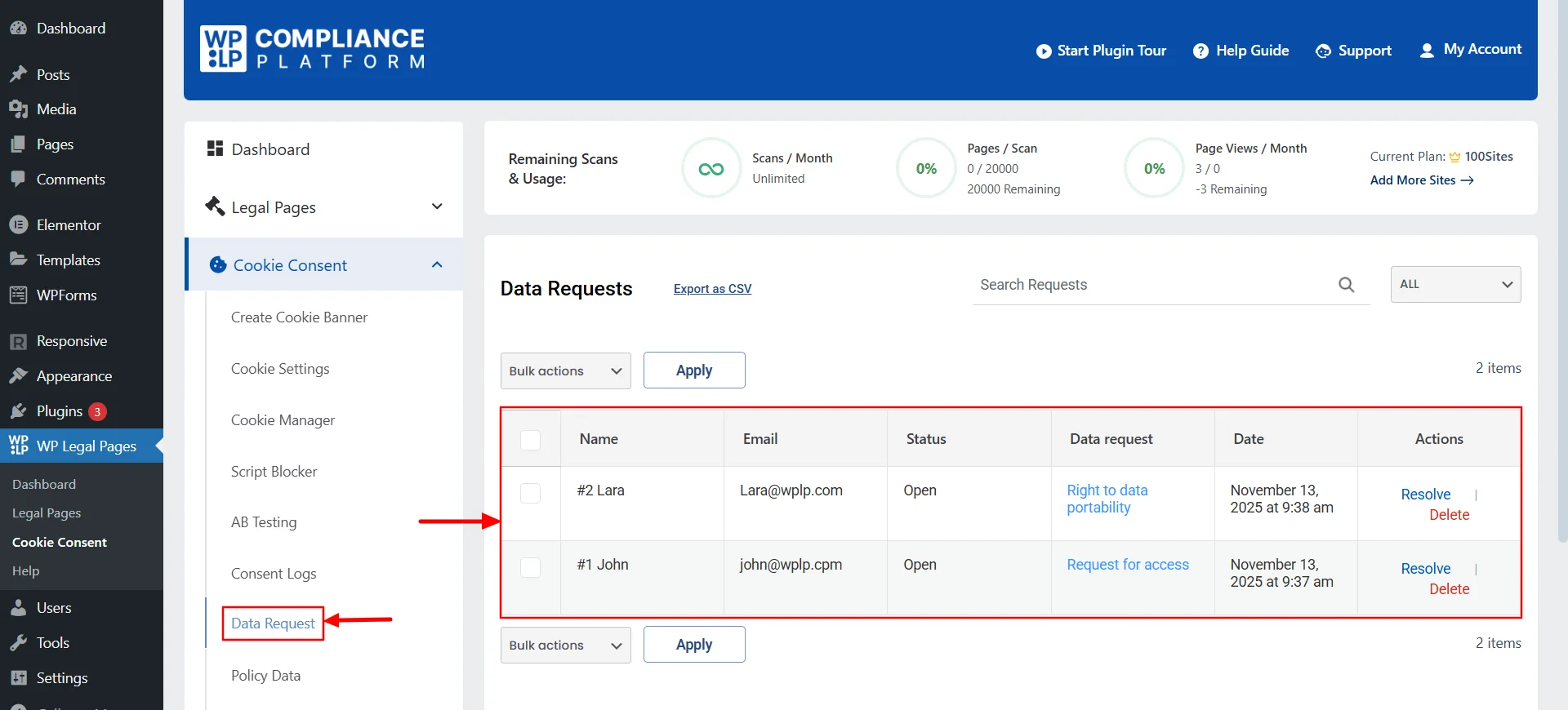
You can review each request and respond directly through the platform. Everything is organized and easy to manage. You don’t need to handle emails or external spreadsheets.
This setup makes the process seamless. You can manage DSARs without extra effort, stay compliant with privacy laws, and build trust with your users.
The WPLP Compliance Platform, with its WP Cookie Consent plugin, truly makes DSAR management effortless and reliable.
Also, make sure not to expose DSAR results publicly. This can cause major security concerns. Try delivering the data securely to the users.
Can You Refuse To Respond to a DSAR?
Yes, depending on the law, you may refuse to respond to a DSAR under certain circumstances and in specific situations, but you must always do the following:
- Inform the individual of your choice
- Explain why you’re denying their request
- Provide them with a way to appeal your decision
For example, you can refuse to honor a DSAR if it’s malicious in nature, for legal reasons, to fulfill a contract, or if the request breaches another individual’s privacy.
GDPR: “If you deny a DSAR, inform the requester, explain why, and tell them how to appeal, complain, or take legal action.”
CCPA: “If you deny a DSAR, notify the consumer, give the reason, and explain how they can appeal.”
Additional data privacy laws, like the VCDPA and CPA, follow very similar guidelines as the GDPR and the CCPA when it comes to denying a DSAR from an individual.
FAQ
No. A user does not need to give any reason at all. They can make a request at any time. You cannot ask for an explanation. You must handle the request in a fair and respectful way, even when no reason is provided.
It’s a request under the GDPR that allows a user to ask for all personal data a business holds about them. The user can see the purpose of the data use and the places where the data is shared. It helps the user understand how their information is used and stored.
You can refuse a request only in rare cases. You must inform the user about the refusal and explain the reason for the decision in a polite way.
Conclsuion
Handling DSARs properly means you earn the trust of your users and show them that you honor their privacy. When people see that their data is safe, they feel confident about your business. And, responding to requests quickly also helps avoid legal issues while keeping your process clean.
The best way to manage these requests is by using the right tools. The WPLP Compliance Platform helps you stay organized and respond on time. We make DSAR management simple and smooth. You can track, respond, and stay compliant without stress.
If you found this blog helpful, you should also take a look at the following.
- From GDPR to AI Regulations: The Future of Data Privacy.
- How to Manage WordPress Privacy With User-Generated Content.
- Understanding Privacy Centers For Better Compliance.
So, take the next step today! Use the WPLP Compliance Platform to simplify privacy compliance for your business.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational and reading purposes only and does not constitute legal advice.
