What is Privacy Management: Why It Matters for Your Business?

In this technology age, we must know about data privacy management, but what is it?
Data privacy management is a set of best practices to support your organization’s compliance with international privacy legislation.
We are living in a data world as of 2021, where we are capturing and processing our own data every second to personalize the experience, so there are a lot of people considering privacy risks.
This is where privacy management sets in, a critical process for individuals and even for organizations, to travel safely and responsibly.
So, if you’re a business executive, a consumer who cares about your data, or a stakeholder keen on knowing the significance of privacy in the age of the internet, this guide is a one-stop portal.
So, let’s begin and discover what privacy management is all about!
What is Privacy Management?
The idea behind managing privacy is a broad approach to protecting an individual’s right to privacy while being responsible about how confidential information is collected, used, and disclosed.
It encompasses policies and practices, laws and regulatory regimes, and technology measures to protect personal information and build trust between businesses and consumers.
Implementing a robust privacy program is critical because compliance managers are always going to have to deal with regulatory requirements or technological developments. Privacy management serves a broader function than a simple compliance with the law and is vital for building and maintaining consumer trust.
At a time when data privacy is paramount, consumers want to be assured they can engage with a business that is committed to protecting their personal information. Such commitment helps ensure your consumer’s loyalty to your company and increases your brand’s image.
In addition, creating a commitment to privacy will position your business as a trustworthy and responsible steward of consumer data – something that counts for so much in today’s competitive environment.
The Basic Elements of Privacy Management

- Data minimization: Only collect the data needed
- Purpose limitation: Only use data for appropriate and specified purposes
- Data accuracy: Keep data accurate and up to date
- Data security: Use reasonable security practices to protect data
- Accountability: Be accountable for your data privacy practice!
Importance of Privacy Management
There are many reasons that privacy management is important. It builds ethical responsibility through protecting individual privacy rights. It assists businesses with compliance with data protection laws and regulations and can limit potential liability exposure.
Lastly, privacy management can build your company’s reputation through trust from consumers, lower the chance of cyberattacks and data breaches, help protect private data, and create business continuity.
Key Components of Privacy Management
Privacy management requires a systematic approach through multiple steps with several key components when using personal data responsibly.
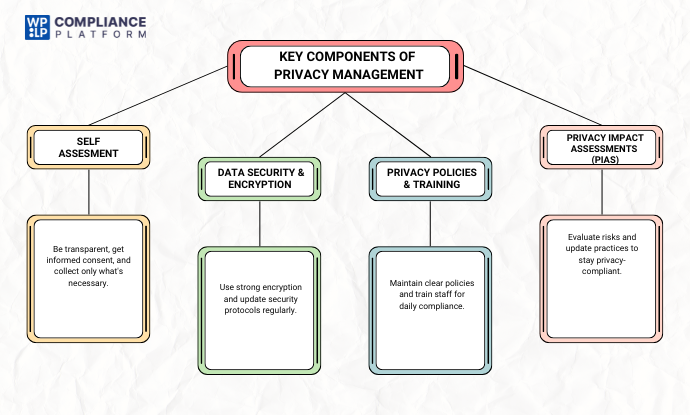
1. Data Collection and Consent Management
Provide individuals with clear and transparent information about the data being collected. Clear trust building means clearly explaining to individuals your organization’s data practices and methodology for data collection, so they are fully informed.
In addition, obtaining consent under lawful processing is both a requirement and a process, and the consent must also be informed and documented. More importantly, take care to collect only the data you need to fulfill your purpose. Take the cautious approach and avoid over-collecting sensitive data to begin with.
2. Data Encryption and Security Measures
Timely security measures provide the vital foundation for privacy management from all angles. For instance, organizations should utilize data encryption to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
The documented security protocols should be reviewed and updated frequently, allowing organizations to keep up with vulnerabilities and threats to any protection measure that is in effect.
Prompt, documented measures around security are crucial to ensuring any private data remains confidential and the integrity of the data remains intact.
3. Privacy Policies and Procedures
Detailed privacy policies and procedures will assist organizations with compliance to laws and standards pertaining to data privacy. Policies and procedures should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect amendments to legislation and changes in organizational practice.
Providing training will help enhance the need for organizational adherence to these policies within daily positions.
4. Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs)
Conducting a PIA helps organizations evaluate how their practices impact personal data and establish processes that mitigate privacy risks accordingly. Updating policies and procedures and conducting annual reviews of PIAs helps organizations remain relevant as privacy continues to be an ongoing challenge.
These components will allow organizations to take a systematic approach to establishing a privacy regime, aiding in trust-building, and demonstrating commitment to protecting personal data.
Why is Privacy Management is Crucial for Organizations?
It also helps ensure the organization can comply with data protection law so it can avoid costly fines and penalties. In a world and economy focused on customer data, organizations can build customer confidence with proper privacy practices while avoiding costly data breaches and reputational harm.
Further, it aids organizations in upholding data protection law and allows them to lessen the burden of costly fines and penalties. When organizations prioritize privacy management, they are able to better protect the data of their customers and their business interests.
Effective privacy management ensures a baseline level of compliance, but is essential to reconnect privacy with strategic viability, for the protection of customer trust, complying with the law, and ensuring sensitive data protection.
Here is a further explanation as to why it matters most:

1. Protecting Customer Trust and Brand Reputation
Most importantly, protecting customer trust ultimately translates into long-term loyalty and a sustained positive organizational perception.
- Establishing trust: customers are increasingly aware of data privacy issues, and consequently, organizations must develop their privacy practices into progressively more transparent and robust frameworks. If an organization can gain trust and demonstrate commitment to data protection, the organization will earn customer loyalty and improve the perception of the overall brand, establishing privacy management as a competitive advantage.
- Reputation Protection: A breach that results in a data privacy scandal can destroy an organization’s reputation. Proactively managing privacy risks helps to reduce the likelihood of a breach or scandal, which protects the brand reputation and ultimately reduces risk by reducing the chance of legal action and customer churn.
2. Legal Compliance and Fines
When organizations put privacy laws into practice, they demonstrate accountability and diligence.
- Compliance: Privacy laws and regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA define clear obligations to ensure that organizations handle private data responsibly. Non-compliance can pose significant financial ramifications, not to mention reputational and operational costs. Organizations must comply with the obligations to not only stay in business but also develop and maintain the trust of their customers.
- Being Prepared: The privacy landscape is constantly changing. New regulations and rules are being added and regularly updated. Organizations that pay attention and develop solid privacy practices can stay out of trouble and be viewed as leaders in this space, and organizations will help themselves out by developing competitive advantages.
3. Safeguarding Sensitive Data from Breaches
Preventing data breaches protects customers and the organization from harm and financial damages.
- Reducing harm: Even with strong safeguards in place, organizations are never entirely safe to breaches. A good privacy management program will allow an organization to respond rather quickly and effectively mitigate harm to affected customers and keep the business moving forward.
- Reducing the risk: Data breaches expose vulnerability for both individuals and organizations, which can expose extreme risks including identity fraud, financial loss, and harm to reputation. By integrating robust privacy management approaches, organizations can defensively identify and respond to vulnerabilities, which subsequently helps to reduce the risk of a breach.
Privacy Management Laws and Regulations
Compliance with data protection legislation is an essential component of managing privacy. While data protection legislation varies by jurisdiction, these laws and regulations generally reflect a similar ideology.
Some of the more notable data protection legislation includes the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA)
1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a critical aspect of privacy management, providing a complete legal framework to protect personal data in a responsible manner.
Due to its extensive requirements, it has consequences for organizations processing the personal data of EU citizens. From a privacy management perspective, here is how the GDPR relates to privacy management and how it affects organizations:
Key Elements of the GDPR in Privacy Management
Below are the key elements involved in GDPR privacy management:

1. Scope and Applicability
The GDPR has extra-territorial jurisdiction, meaning that any organization that processes the personal data of residents of the EU (no matter where the data processing occurs or its location) comes under the enforcement of the GDPR.
This worldwide reach strengthens the importance of incorporating privacy management practices into worldwide business practices.
2. Privacy Principles and Data Governance
GDPR specifies six principles that privacy management activities should be built around:
- Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency: Data must be processed in a lawful manner, and organizations must be transparent with how they administer their activities.
- Purpose Limitation: Privacy management systems must prevent data from being used beyond its intended purpose.
- Data Minimization: Organizations are responsible for asking for only the necessary data to reduce the risk that accompanies privacy.
- Accuracy and Accountability: Accuracy of data is necessary to ensure the data is reliable and creates buyer trust.
- Storage Limitation: Privacy management frameworks should have written retention schedules in place to prevent data retention without a basis of need.
- Security Measures: Privacy management systems should have various methods of data protection in place, such as encryption, passwords, and access controls.
3. Rights of Data Subjects
GDPR provides data subjects with rights which include:
- Providing documentation about processing and providing clear communications.
- Determining the method of engagement for access requests and ensuring all access requests are responded to in a timely manner.
- Implementing processes for the rectification, deletion, and portability of individuals’ data.
4. Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
A DPIA is a fundamental component of a broader privacy management under and for GDPR. Organizations must conduct DPIAs on high-risk processing activities to help identify privacy threats and identify the remedies to mitigate those threats.
Fiscal Penalties for Non-Compliance
GDPR imposes strict fines for non-compliance to make privacy management for organizations one of its primary tasks, not to mention the potential fines. There are two categories of fines that can be applied to organizations:
- Lower-Tier Fine: Up to € 10 million or 2% of total worldwide turnover for “less severe infringements” such as not maintaining sufficient records of processing activities.
- Upper-Tier Fine: Up to €20 million or 4% of your annual global turnover for more severe infringements, such as breaches of individuals’ rights or not acquiring appropriate consent.
2. California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) are revolutionary privacy laws in the U.S. that have established requirements for personal data stewardship by organizations and provided consumers with additional privacy rights.
Together, they serve as powerful framework for a privacy program focused on controlling and managing information through transparency and accountability.
Key Aspects of CCPA in Privacy Management
Here are the major components of CCPA privacy management:
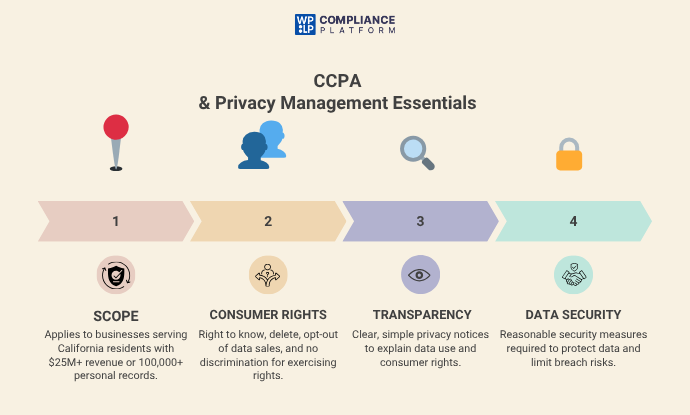
1. Scope and Applicability
The CCPA is applicable to for-profit businesses in California who meet certain criteria, such as gross revenues (including revenue from selling personal information) above $25 million, or processing personal information of 100,000 or more California residents.
This is important, even if you are a business not based in California – if you are targeting or providing services to California residents, you are subject to CCPA..
2. Consumer Privacy Rights Under CCPA
The privacy management systems must be implemented in a manner that gives effect to the consumer rights defined in CCPA:
- Right to Know: The understanding that consumers have the right to know what personal information is being collected, why it is being collected, and how long it will be shared or sold.
- Right to Delete: Consumers may request deletion of their personal information, subject to limited exceptions.
- Right to Opt-Out: Consumers may opt out of any selling of their personal information.
- Right to Non-Discrimination: Organizations may not discriminate against consumers who exercise their rights under CCPA by denying services or charging them a different price.
3. Transparency Requirements
Organizations must use concise and easy-to-read privacy notices that inform consumers’ rights and how their data is processed. Transparency is an essential element of privacy management and builds trust.
4. Data Security and Accountability
While the CCPA does not specify any protections such as encryption, it does hold organizations liable for a data breach if an organization is not using reasonable security. Good privacy management frameworks will include reasonable measures of data security to decrease liabilities and risks.
Non-Compliance Penalties
Fine up to $2,500 for each violation and $7,500 for each intentional violation or violation involving the data of minors.
The requirements under the CCPA now require organizations to implement a privacy by design approach for their organization, including good consent management, data security measures and practices, and overall processes to deal with consumer rights requests.
Other International Privacy Laws in the Context of Privacy Management
In addition to the GDPR, CCAP, and CPRA, there are other global privacy laws that affect privacy management globally. Usually, they involve elements of transparency, consumer rights, and privacy and security data principles, whilst also including regional interests.
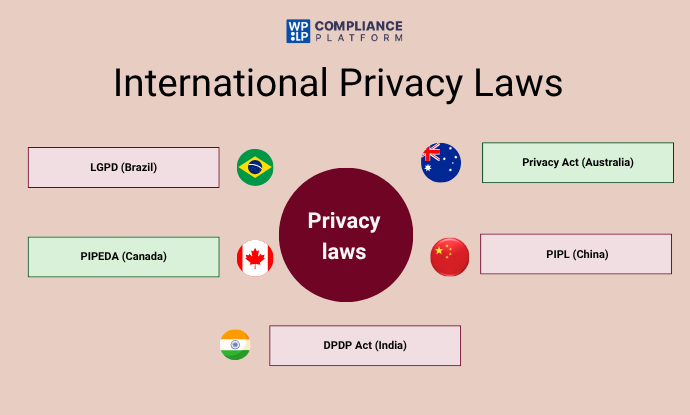
1. LGPD (Brazil)
Brazil’s General Data Protection Law (Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados) is almost identical to the GDPR and offers consumers rights such as access to their data, correct their data, and the erasure of their data. Every organization in Brazil is required to appoint a DPO (Data Protection Officer) and demonstrate a legal basis for processing the consumers data for the purpose of safeguarding their consumer privacy.
2. PIPEDA (Canada)
Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act is the statute that governs data privacy in Canada for commercial privacy contexts. PIPEDA has a few important articles in its underlying principles in relation to obtaining meaningful consent, accuracy, and protection of the data by way of reasonable safeguards.
3. Privacy Act Australia
Australia’s Privacy Act establishes a framework for the protection of personal data through its Australian Privacy Principles (APPs). The APPs cover requirement for APP’s when dealing with personal information, it also mentions protection of personal information, as well as processes related to data collection.
4. China’s PIPL
China’s Personal Information Protection Law establishes strict requirements for the processing of data, its cross-border transfer and a person’s consumption rights, and the penalties for failure to comply can be punitive (think, fines and limits on operations).
5. India’s DPDP Act
India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act promotes data minimisation, purpose limitation, and accountability; and establishes a consent-based regime governing the processing of personal data.
These laws emphasize the importance for organizations to use a flexible, comprehensive framework that can adapt to many regulations.
Steps to Implement Effective Privacy Management
A properly organized privacy management system enables you to shield personal information, comply with regulatory needs and gain trust with consumers.

1. Privacy Assessments and Audits
The first one is to review your current practices for collecting and processing personal data. A privacy audit will allow you to look back on where you could have possible risks and how you are actually meeting the applicable privacy legislations.
With the legislation changing in this respect, think about the fact that you need to conduct regular checks.
2. Creating a Privacy Policy Framework
Enact a policy that clearly describes how personal information is being gathered, utilized, and secured. Your policy should contain boilerplate language, be concise and simple to read for customers, and be updated frequently to ensure it adheres to your changing data practices or other legal requirements.
3. Spend on Data Privacy Tools and Software Solutions
To support your ongoing management of personal data, consider investing in software and tools that can assist you.
They are useful to personal data managers’ protection for employers and managers can spend money on tools that assist in encryption of data and management of consent agreements, and breach detection obligations that aid in sensitive information management and protection compliance programs.
One such robust solution is the WP Legal Pages Compliance Platform that provides you with access to important legal documents and cookie consent management for your website all in one place.
WP Legal Pages Plugin- Generate Key Legal Pages for Your Website

WP Legal Pages Plugin– Create Key Legal Pages for Your Website
The WP Legal Pages, is an all-in-one solution for WordPress users who are looking to create legally compliant pages for their your site and allows you to easily create the legally required pages such as privacy policies, terms and conditions, refund policy, cookie policy etc.
The WP Legal Pages plugin provides fully customizable templates, which will help you to comply with a variety of data protections regulations, particularly if they contain GDPR, CCPA or other privacy laws.
WP Cookie Consent Plugin- Best Tool for Cookies & Consent Management

The WP Cookie Consent, is a super easy to use Tool for managing cookie consent and accurately fulfills all GDPR requirements for your WordPress site. With the WP Cookie Consent you can give visitors clear and full transparency with cookies you are using on your website and allow them to accept, decline or manage their cookie preferences.
Overall, WP Cookie Consent is a great solution for managing cookie consent, it even allows you to customize the color, look and behavior of the cookie consent banner to suit your design and legal needs.
4. Incorporate Privacy Management into Business Processes
Make privacy a fundamental part of your business processes. Be sure to get everyone involved, from HR to marketing in your data protection activities. Make sure that employees are trained in best practice and understand their responsibilities in protecting the personal data of customers.
Common Privacy Management Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding common mistakes is crucial to compliance, protecting user data, and preserving customer trust.

- Lack of Transparency – Having no clear or easily understood way to present how personal data is collected, used, and shared destroys trust and will present you with compliance issues. Always have a clear, easy-to-read privacy policy.
- Ignoring Data Minimisation – When a business collects more data than necessary to meet a purpose, you are exposing itself to more risk and potentially violating its laws and regulations. Always collect only that which is necessary for the intended purpose.
- Not Getting Consent Correctly – Not seeking express consent in some fashion could introduce penalties of concern to your situation. Always ensure that users provide informed or best consent, understanding that they can read and clearly understand the privacy practices.
- Failing to Secure the Data – Without sufficient protection of your data, sensitive information is at risk of breaches. Always ensure you have strong security protocols both for the storing and sending (with encryption, etc) of sensitive user data.
- Ignoring Privacy Audits – Privacy audits should never be a ‘one-and-done’ audit. You should conduct regular audits so that there is an opportunity to track if you have missed potential risks or your compliance status with changing laws and regulations. Regular audits allow you to take a thorough examination of your privacy practices.
- Failing to Educate your Staff – Staff must understand your data privacy policies and that your policies and procedures are compliant with the law. Educating staff on privacy policies and roles , policies, and procedures will reduce the potential for poor practice and keep you in line with applicable legislative regulations.
- Not Updating Privacy Policies – Always ensure that your privacy policies are updated, reflecting current practices, as well as changes in data laws and regulations.
FAQ
Privacy management is safeguarding personal data, adhering to applicable data protection regulations, and ensuring people’s privacy is protected in relation to the collection, use, and storage of their information.
A privacy management platform is software with capabilities like consent management, risk assessments, and data mapping that assists businesses in automating privacy procedures while guaranteeing adherence to data protection laws.l;;
Conclusion
Privacy management has become an imperative aspect of any business strategy. Here, it refers to preventing unauthorized access to customer records, adhering to data privacy standards, and fostering a culture that considers and allows for data privacy protection measures.
Effective measures ensure adherence to all legal frameworks, such as the CPRA, CCPA, and GDPR, while drastically increasing the confidence of customers and the business’s reputation overall.
Implementing measures and strategies aimed at data privacy allows the business to overcome data security challenges while enjoying excellent customer confidence and a competitive edge.
Thus, to overcome privacy risks, we recommend the WP Legal Pages compliance platform, which will keep you compliant with privacy laws and regulations worldwide.
If you liked this article, you can also consider reading:
- Top CCPA Fines for Non-Compliance: Key Cases and How to Avoid Penalties
- Florida Digital Bill of Rights (FDBR) — A Complete Guide
- What is the EU’s Digital Services Act (DSA)?
Are you ready to safeguard privacy management on your website? Grab WP Legal Pages Compliance Platform now!
