What is a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) — A Complete Guide for 2025

Summary
DSARs allow individuals to access their personal data, ensuring transparency and compliance. Our article outlines key steps like verifying identity, clarifying requests, and responding on time.
We also highlight best practices such as automation, staff training, and data minimization.
Looking to understand what is DSAR and why you must know about it?
Understanding your data rights is crucial in the present digital era. A DSAR, aka Data Subject Access Request (DSAR), is an individual request to access personal data held by organizations.
DSARs help users know and understand what information is being collected, how it is used, and if it is being shared. Processing these requests efficiently is essential for compliance and transparency.
This article will help you explore DSAR and outline a straightforward five-step process for managing these requests effectively. This will ensure your organization stays compliant while respecting individuals’ data rights.
Remember to read through till the end.
What is a Data Subject Access Request?
To begin with the basics, let’s first understand what a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) is
In Lehman’s terms, a Data Subject Access Request (DSAR) refers to a user’s request to the organization to access their personal data that the organization has about them.
It primarily serves as a medium to provide transparency and allow individuals to understand how their data is being processed, ensuring their rights under data protection laws.
Key Components of a DSAR
While you might have gotten the basic clearance of what DSAR is, there are certain key components you must understand, these include:
- Identity Verification
- Scope of Request
- Response Time
- Data Delivery
- Additional Information
To avoid unauthorized access to personal data, organizations must authenticate the identities of those requesting access. Additionally, businesses must understand the exact data being sought and provide a comprehensive response to users.
Furthermore, when presenting data, it must be done in a clear, concise, and easily accessible manner. This could be electronic or physical papers.
Lastly, organizations should also inform individuals about the objectives for which their data is processed. This should identify the types of data being processed, the parties with whom the data has been exchanged, and the data retention term.
Importance of DSAR in Global Data Privacy Laws
Data Subject Access Requests (DSARs) are crucial under various global privacy laws, designed to protect individuals’ data. These laws require organizations to respond to DSARs promptly and transparently, ensuring compliance and fostering trust with data subjects.
1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Enforced in the European Union, GDPR aims to protect personal data and ensure privacy. It allows individuals to access, correct, and delete their data.
2. California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): CCPA protects California residents, giving them rights similar to those under GDPR. It allows consumers to know what personal data is being collected, request deletion of their data, and opt out of the sale of their data.
3. Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA): PIPEDA, applicable in Canada, governs how private sector organizations handle personal information.
This law also allows individuals to access their data and request corrections from organizations and businesses.
Rights of the Data Subject Under Global Privacy Laws
✔️Right of Access: Users can demand to learn what personal data is collected, how it is processed, and who has access to it.
©️Rectification Rights: Businesses are supposed to rectify or change users’ data on their request.
???? Right to Be Forgotten: Users may request the deletion of their data under specific conditions.
????Right to Restrict Processing: Businesses may need to temporarily halt to the processing of users’ data upon request.
????Data Portability Rights: Users can request their data in a structured, frequently used, and machine-readable format.
⛔Right to Object: Users can object to the processing of their data based on legitimate interests.
????Rights Related to Automated Decision-Making: Users have the right not to be subjected to judgments based entirely on automated processing,
Validity of DSAR: How to Determine if the Request is Legitimate
For DSAR to be compliant, an organization must check the request is valid.
This entails verifying that the data subject has a legal right under data privacy laws for the request, and that they are indeed the owner of the data at issue.
Due consideration should be given to all questionable or unauthorized authorizations to deter fraud, or unauthorized access to data.
So, how do you tell whether the DSAR request is legitimate or not?
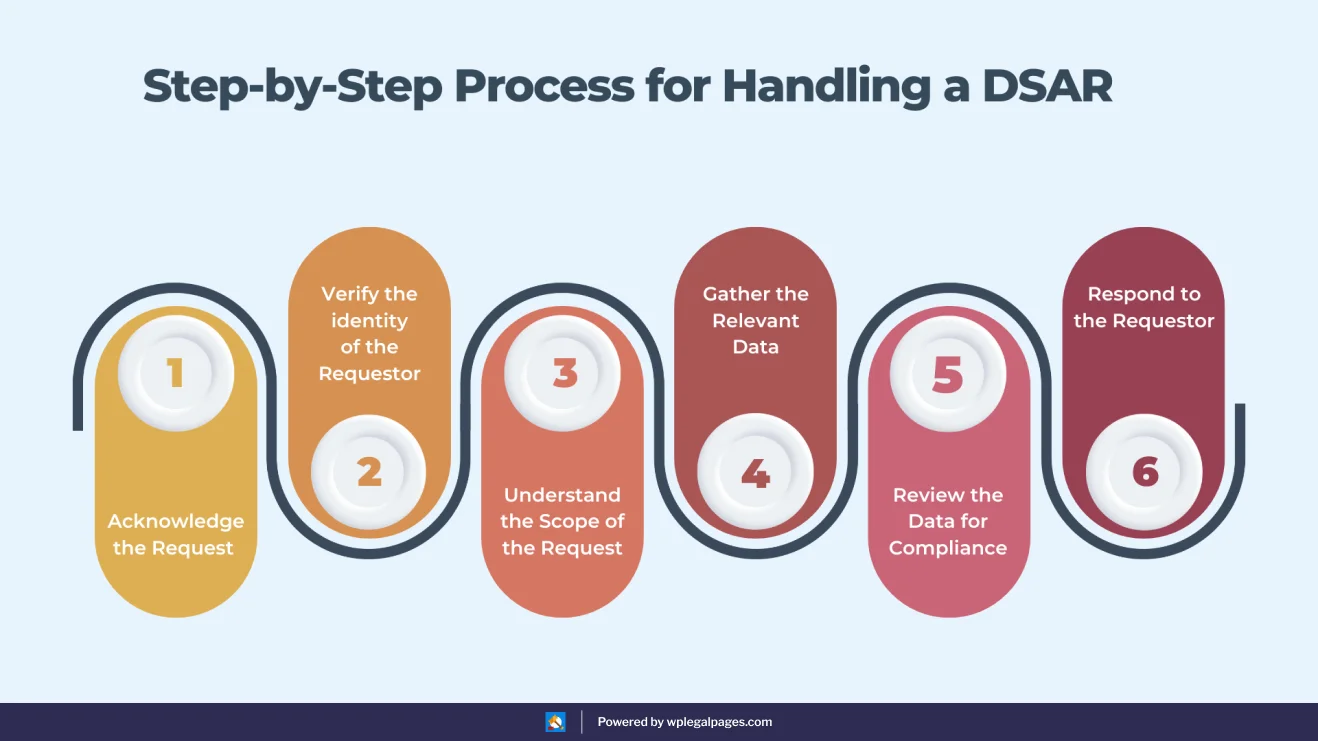
Step 1: Acknowledge the Request
When you receive a DSAR, immediately acknowledge receipt to the requestor to create transparency and trust.
Give an approximate time frame of your response—usually around 1 month, as is common with GDPR and the like. This response lets the users know their request is in progress and provides a timeframe.
Step 2: Verify the Identity of the Requestor
Secondly, the identity of the one making the DSAR should be checked to avoid misuse. Procedures include e-mail verification, governmental identification, or other proof of identification.
“This kind of verification is really important because it helps protect a user’s personal data and helps maintain compliance with privacy laws by making sure that it’s actually the person themselves who can access their data,” explained Facebook.
Step 3: Know the Extent of the Request
Specify the details of the data you want, and we can provide an accurate answer. By having the conversation with the requester, the scope of their request may be narrowed or made more specific.
Setting the scope helps to concentrate the organization on collecting the data that matters and not what isn’t needed.
Step 4: Put the Right Information Together
Gather information from internal databases and files as requested. If needed, collect data from all involved third-party providers.
This process must be comprehensive to drink up all ‘relevant’ data and not to miss the critical records, that may fit within the request.
Step 5: Check whether you Have Given Consent or not.
Review the collected information to ensure compliance with privacy laws, and identify any exceptions, such as national security or law privilege.
Your information is sensitive, which might cause the rights of others. You can block / cut any information in the sensitive remains. It also saves the company from potential lawsuits and respects everyone’s involvement.
6: Reply to the Requestor
It is nonsensical to provide the requested information in a format that is not even commonly accepted or available. Inform the data subject of his or her rights to rectification or erasure, and any other information about the processing.
Inform the requestor of their right to appeal or pursue further action if unsatisfied, ensuring a comprehensive and transparent response.
FAQ
A DSAR is a request by an individual to access personal data held by an organization. It allows individuals to understand how their data is collected, processed, and shared.
DSARs ensure transparency, giving individuals control over their data. They’re vital for compliance with privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA, which mandate timely and accurate responses to these requests.
Under regulations like the GDPR, organizations must typically respond to a DSAR within one month of receiving the request, although this timeframe may vary depending on local laws and regulations.
Best practices include creating a DSAR policy, using automated tracking tools, training staff on privacy regulations, and minimizing unnecessary data storage for efficient, compliant processing
Conclusion
Data Subject Access Requests (DSARs) are crucial for safeguarding individuals’ privacy and fostering transparency in the management of personal data.
Understanding DSARs and implementing a structured, compliant approach to process them can help organizations build trust, comply with global privacy regulations, and minimize potential risks.
Embracing the best data practices empowers organizations to responsibly uphold individuals’ data rights responsibly, fostering a positive relationship between companies and their users in today’s data-driven world.
Further, if you liked this article, you can also consider reading:
